Human Colonic Epithelial Cells
Cat.No.: CSC-C1488
Species: Human
Source: Colon; Intestine
Cell Type: Epithelial Cell
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
HCoEpiC are isolated from human colonic tissue. HCoEpiC are cryopreserved at passage one and delivered frozen. Each vial contains >5 x 105 cells in 1 ml volume. HCoEpiC are characterized by immunofluorescent method with antibodies to CK18 and CK19. HCoEpiC are negative for HIV-1, HBV, HCV, mycoplasma, bacteria, yeast and fungi. HCoEpiC are guaranteed to further culture for 10 population doublings in the conditions provided by Creative Bioarray.
Human Colonic Epithelial Cells are a kind of primary cell from normal human colon. The colon is a part of the digestive system. The surface of the inner wall of the colon is covered by epithelial cells. Epithelial cells are responsible for nutrient absorption, mucus secretion and maintenance of intestinal barrier function. During culture, these cells can form monolayers resembling the arrangement of intestinal epithelium in vivo. Furthermore, colonic epithelial cells express cell adhesion molecules, including integrins α3, α5, α6, β1 and β4, as well as HLA class II molecules.
Colonic epithelial cells can be applied in a variety of research fields. Firstly, they are necessary for the study of the immune system of intestine. Since epithelial cells are an important part of the immune system, they can mimic the immune responses in vivo and help scientists to understand the interaction between immune cells and epithelial cells. Secondly, the cells can be applied to the study of intestinal diseases. Intestinal diseases, such as colitis and colon cancer, are closely related to the dysfunction of intestinal epithelial cells. Colonic epithelial cells can be applied to the study of the pathogenesis of diseases and the potential treatment. Last but not least, colonic epithelial cells have a great value in the research of drug absorption and metabolism. Intestinal epithelial cells are the major place for drug absorption, so colonic epithelial cells can be applied to the study of the mechanism of drug absorption and metabolism in the intestine.
Co-Culture of Epithelial Cells with Clostridium scindens
A dynamic interaction between the human gastrointestinal epithelium and intestinal microbiota is key to understanding and treating intestinal diseases. Human colonic epithelial cells from a healthy donor were cultured with Clostridium scindens (C. scindens), Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), or both. A special platform with controlled oxygen levels created separate anaerobic and aerobic environments. Epithelial cells and C. scindens remained viable in co-culture for 48 hours.
C. scindens was tested with epithelial cells to see if they can coexist without an immune system. Epithelial cell viability and barrier function were evaluated: no significant cell death was observed (control: 9.8% vs. C. scindens: 10.8%, p = 0.64, Figure 1A). No significant change in cell death indicators (control: 9.5% vs. C. scindens: 6.1%, p = 0.24, Figure 1B). TEER values decreased over time but were not significantly different (control: 168 ± 18 vs. 150 ± 37 Ω·cm² with C. scindens, p = 0.45). ZO-1 tight junctions were similar with and without C. scindens (Figure 1C). Cell measurements showed no significant differences (area, circularity, perimeter). These results indicate C. scindens proliferation did not harm cells, except at extremely high numbers (~5×10⁶ cells), which increased cell death.
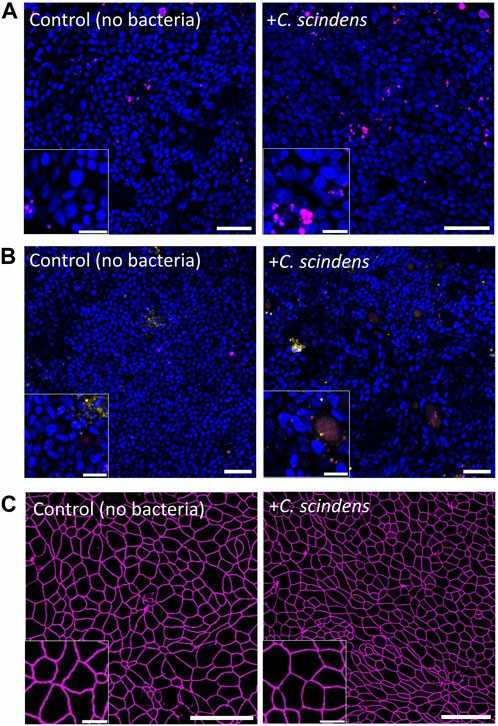 Fig. 1. Co-culture of primary human colonic epithelial cells with C. scindens (Wang H, Kim R, et al., 2024).
Fig. 1. Co-culture of primary human colonic epithelial cells with C. scindens (Wang H, Kim R, et al., 2024).
Circ_0085323 Depletion Ameliorated TNF-a–Induced Inflammation and Apoptosis of NCM460 Cells
Previous studies have demonstrated that circRNA is involved in the occurrence of ulcerative colitis (UC). However, the mechanism of circ_0085323 in the occurrence of UC has not been reported. In the present study, AN's team explored whether the circ_0085323/miR-495-3p/TRAF3 axis was involved in the occurrence of UC in vitro.
First, the effects of si-hsa_circ_0085323 on circ_0085323 expression in Normal human colonic epithelial cells (NCM460) were examined. The results showed that si-hsa_circ_0085323 could significantly downregulate the expression of circ_0085323 in NCM460 cells (Fig. 2A). Then, the effects of si-hsa_circ_0085323 on the proliferation, viability, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8 secretion, LDH activity, and apoptosis of TNF-α-stimulated NCM460 cells were detected. The results showed that TNF-α induced the decrease of cell proliferation and viability, but the effects were reversed after the silencing of circ_0085323 (Fig. 2, B and C). TNF-α promoted the secretion of IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8 and the activity of LDH, and the effects were reversed after the silencing of circ_0085323 (Fig. 2, D and E). TNF-α induced the increase of apoptosis in NCM460 cells, and the effects were reversed after the silencing of circ_0085323 (Fig. 2F). TNF-α induced the increase of the expression of cleaved caspase-3, cleaved caspase-9, and cleaved PARP, and the effects were reversed after the silencing of circ_0085323 (Fig. 2G). These results showed that the silencing of circ_0085323 could reverse the TNF-α-induced injury of NCM460 cells.
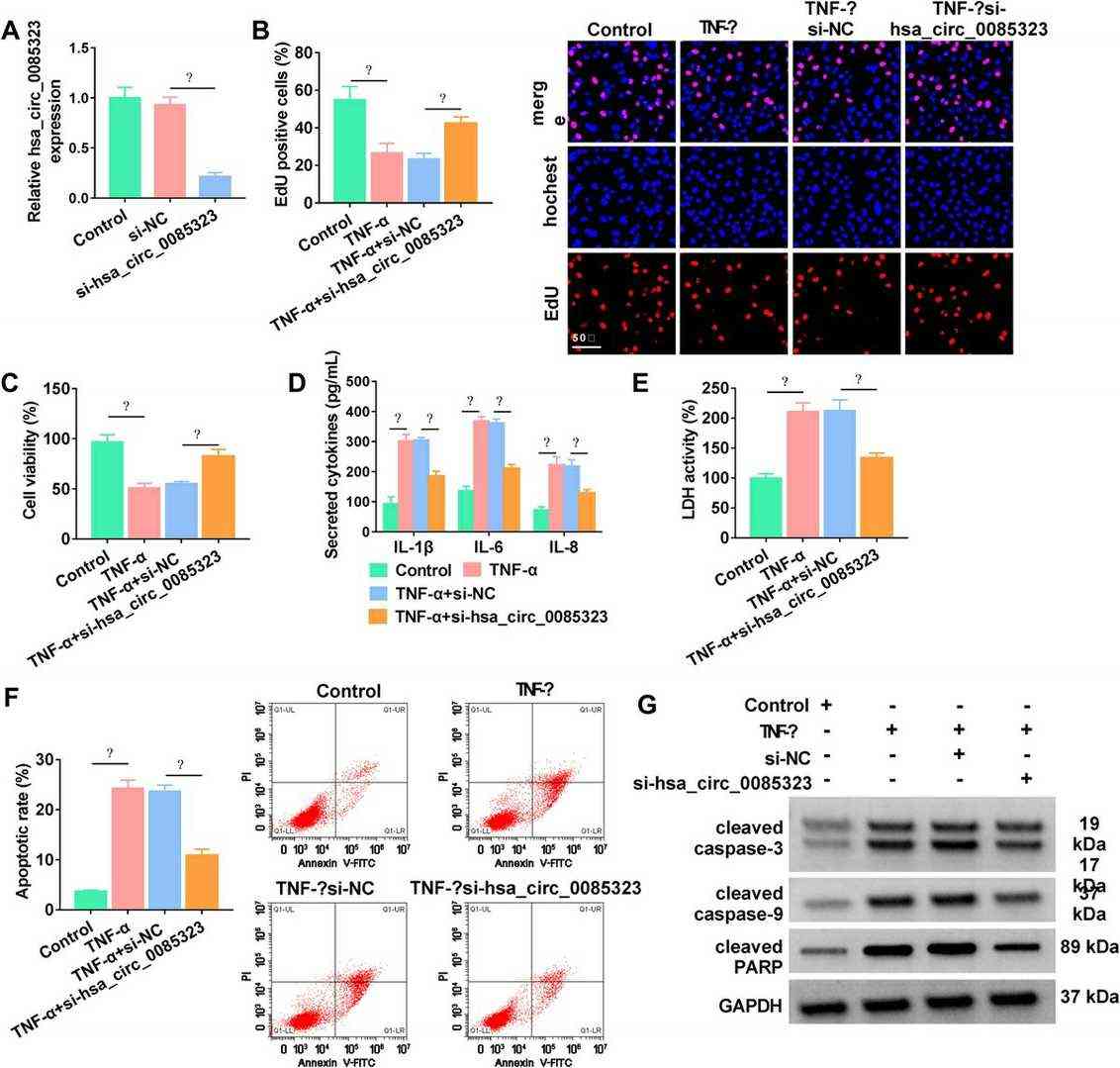 Fig. 2. Circ_0085323 knockdown attenuated TNF-α–caused NCM460 cell injury (An Q, Yang SS, et al., 2023).
Fig. 2. Circ_0085323 knockdown attenuated TNF-α–caused NCM460 cell injury (An Q, Yang SS, et al., 2023).
Each vial contains at least 0.5 x 10^6 cells cells.
Human Colonic Epithelial Cells are primary cells, which are isolated from tissues. And we can also provide the Immortalized Human Colonic Epithelial Cells for you.
Ask a Question
Write your own review