Cell Proliferation Assay Services
- Service Details
- Features
- Applications
- FAQ
- Explore Other Options
Cell proliferation refers to the process of cell division and reproduction, which is the foundation for biological growth, development, reproduction, and heredity. It holds significant importance in fields such as cell biology, oncology, and pharmacology. Accurately measuring cell proliferation helps researchers understand cell growth characteristics, the effects of drugs on cell proliferation, and changes in the cell cycle.
With more than a decade of expertise in working with tumor cell lines, Creative Bioarray offers comprehensive cell proliferation assay services. We provide a range of assay methods tailored to specific cell types, protocols, and customer preferences for accurate proliferation measurement.
Our Cell Proliferation Assay Services
Workflow
Step 1: Requirement Analysis
Discuss experimental design based on customer needs, including cell type, detection methods, and time points.
Step 2: Experimental Design
Craft the optimal detection plan according to customer requirements.
Step 3: Sample Preparation and Handling
Prepare and handle samples following standard operating procedures.

Step 4: Experiment Execution
Perform experimental operations using appropriate cell proliferation detection methods.
Step 5: Data Analysis and Reporting
Fit proliferation curves, calculate IC50/EC50, conduct statistical significance analyses.
Methods
- DNA Synthesis Detection
- Cell Metabolism Detection
- ATP Concentration Detection
- Cell Tracing Detection
- Cell Membrane Integrity Detection
- Proliferation Marker Detection
- 3D Cell Proliferation Assays
DNA Synthesis Detection
BrdU incorporation assay:
- Principle: Bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU), a thymidine analog, is incorporated into newly synthesized DNA strands during the S phase. Immunofluorescence and flow cytometry enable detection of BrdU-labeled cells which measure proliferation activity.
- Procedure: Cell culture → BrdU pulse labeling → Fixation/permeabilization → Anti-BrdU antibody incubation → Fluorescence detection/flow analysis.
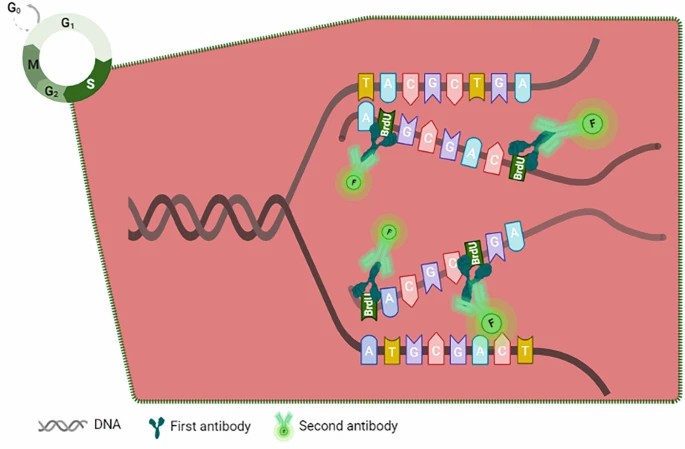 Fig. 1. The BrdU incorporation process (Yu JH, Wang ZX, et al., 2022).
Fig. 1. The BrdU incorporation process (Yu JH, Wang ZX, et al., 2022).
Cell Metabolism Detection
XTT and MTT assay:
- Principle: XTT (tetrazolium salt) and MTT (thiazolyl blue) are reduced by mitochondrial dehydrogenases in live cells to soluble or insoluble formazan products, with intensity correlating to cell number.
- Procedure: Cell culture → XTT/MTT reagent addition → Incubation → For MTT, dissolve formazan → Spectrophotometer or plate reader detection (XTT: 450 nm, MTT: 570 nm).
Resazurin assay:
- Principle: Resazurin, a blue precursor, is metabolized by live cells into highly fluorescent resorufin, correlating with metabolic activity.
- Procedure: Cell culture → Resazurin reagent addition → Incubation → Fluorescence detection (Excitation: 530 nm, Emission: 590 nm).
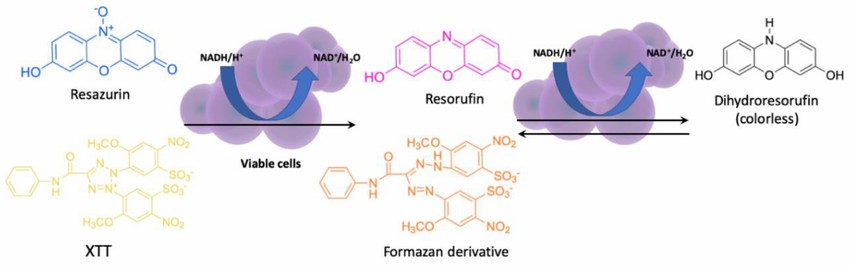 Fig. 2. The principle of XTT and resazurin assay (Jaśkiewicz M, Janczura A, et al., 2019).
Fig. 2. The principle of XTT and resazurin assay (Jaśkiewicz M, Janczura A, et al., 2019).
Alamar blue assay:
- Principle: Alamar Blue functions as a cell viability fluorescent indicator by undergoing reduction through mitochondrial dehydrogenases to form a red fluorescent compound which demonstrates a direct relationship with both cell numbers and metabolic rates.
- Procedure: Cell culture → Alamar Blue addition → Incubation → Fluorometer or fluorescent plate reader detection (Excitation: 530 nm, Emission: 590 nm).
ATP Concentration Detection:
ATP luminescence assay:
- Principle: ATP functions as an essential component of cellular energy metabolism while its levels show a direct relationship with both cellular activity and cell numbers. ATP activates luciferase which oxidizes luciferin to produce luminescence whose intensity reveals ATP levels and thus estimates live cell numbers.
- Procedure: Cell lysis → Luciferase reagent addition → Incubation → Luminescence detection (chemiluminescence instrument).
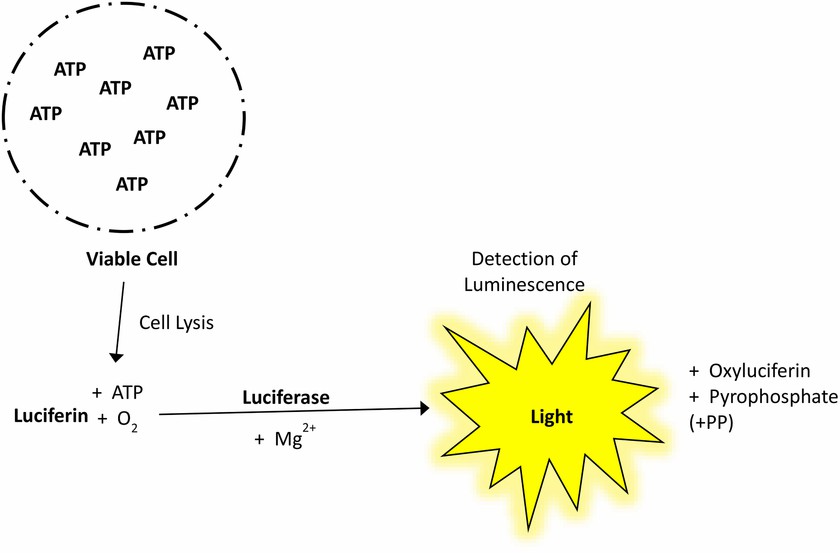 Fig. 3. Schematic illustration of the principles of ATP assay (Kamiloglu S, Sari G, et al., 2020).
Fig. 3. Schematic illustration of the principles of ATP assay (Kamiloglu S, Sari G, et al., 2020).
Cell Tracing Detection:
CFSE assay:
- Principle: Carboxyfluorescein diacetate succinimidyl ester (CFSE) enters cells and hydrolyzes into fluorescent molecules, distributing equally during division and decreasing in intensity to reflect generational proliferation.
- Procedure: Cell labeling with CFSE → Culturing → Flow cytometry detection of fluorescence decay.
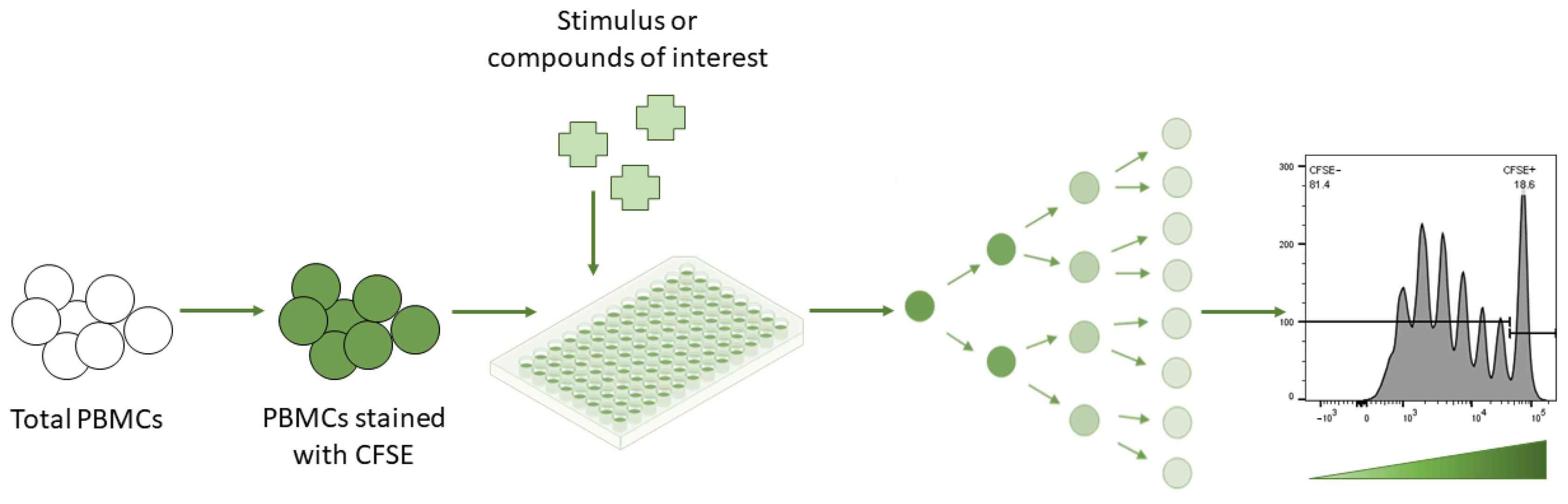 Fig. 4. Lymphocyte proliferation assay—CFSE assay (Ganesan N, Ronsmans S, et al., 2023)
Fig. 4. Lymphocyte proliferation assay—CFSE assay (Ganesan N, Ronsmans S, et al., 2023)
Cell Membrane Integrity Detection:
LDH release assay:
- Principle: Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), a cytosolic enzyme, remains within cells when membranes are intact. Membrane damage releases LDH into culture supernatant. LDH activity in supernatant reflects membrane damage extent.
- Procedure: Cell culture → Supernatant collection → LDH substrate addition → Measure lactate dehydrogenase activity → Calculate membrane damage extent.
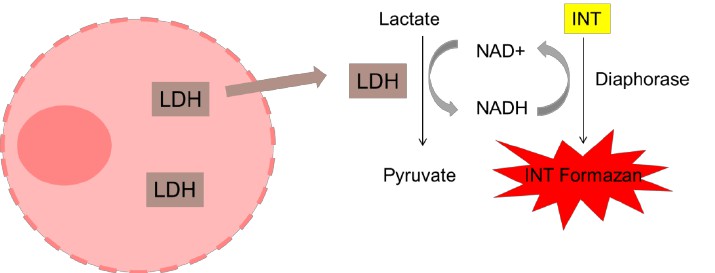 Fig. 5. Schematic representation of the principle of the LDH release assay (Forest V, Figarol A, et al., 2015).
Fig. 5. Schematic representation of the principle of the LDH release assay (Forest V, Figarol A, et al., 2015).
Trypan blue staining assay:
- Principle: Viable cell membranes block Trypan Blue, while nonviable or damaged cells allow dye entry, staining cells blue.
- Procedure: Mix cell suspension with Trypan Blue dye → Viable cells remain unstained, nonviable cells stain → Microscope observation and count.
Proliferation Marker Detection:
- Principle: Proliferation markers like Ki-67, PCNA, and Cyclin D1 are key proteins in cell cycle regulation, with expression levels closely tied to proliferation status. Examining these markers' expression elucidates cell cycle regulation and evaluates drug effects.
- Procedures:
Immunofluorescence: Cell culture → Fixation/permeabilization → Primary antibody (Ki-67/PCNA/Cyclin D1) incubation → Fluorescent secondary antibody incubation → Fluorescence microscopy imaging.
Western Blot: Cell lysis → Protein extraction → SDS-PAGE electrophoresis → Transfer → Primary/secondary antibody incubation → Chemiluminescence detection.
Flow Cytometry: Cell culture → Fixation/permeabilization → Intracellular antigen labeling antibody incubation → Flow analysis.
3D Cell Proliferation Assays:
Creative Bioarray also offers 3D cell proliferation assays using the Soft Agar assay with optimized growth and assay conditions based on our 3D culture experience. A 2D vs 3D comparison can also be included.
Creative Bioarray Cell Proliferation Assay Advantages

Flexible
Suitable assay methods chosen based on customer's cell type and requirements.

Accurate
Data strongly correlates to cell number.

Sensitive
Capable of detecting low cell numbers.

Fast
Enables high-throughput with quick results.
What can You do with Our Cell Proliferation Assay Services?
- Cancer Research: Evaluate drug efficacy in inhibiting tumor cell growth and aid in developing cancer therapies.
- Drug Development: Screen drug candidates for their impact on cell growth, ensuring safety and effectiveness.
- Toxicology Testing: Assess the effects of chemicals on cell proliferation to determine toxicity.
- Regenerative Medicine: Analyze stem cell growth for tissue engineering and therapy optimization.
- Basic Research: Study cellular mechanisms, such as cell cycle and signal transduction.
FAQ
1. How sensitive is cell proliferation detection?
The sensitivity varies with different detection methods. For example, fluorescence-based methods typically have higher sensitivity and can detect lower cell counts. We select the appropriate detection method based on the client's sample specifics before the experiment to ensure accurate results.
2. How are the results of cell proliferation detection presented?
We provide clients with a detailed experimental report, which includes the experimental methods, results (such as cell proliferation rate and cell count), data analysis, and conclusions. The results are typically presented in both charts and text format for easy understanding and use by clients.
3. Can I use specific cell lines?
Of course, we support the detection of various cell lines. You just need to provide detailed information when submitting your request.
Quotations and ordering
Our customer service representatives are available 24hr a day! We thank you for choosing Creative Bioarray service.
References
- Yu J, Wang Z, et al.BrdU Incorporation Assay to Analyze the Entry into S Phase. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. 2579:209-226.
- Forest V, Figarol A, et al. Adsorption of lactate dehydrogenase enzyme on carbon nanotubes: how to get accurate results for the cytotoxicity of these nanomaterials. Langmuir. 2015. 31(12):3635-43.
- Jaśkiewicz M, Janczura A, et al. Methods Used for the Eradication of Staphylococcal Biofilms. Antibiotics (Basel). 2019. 8(4):174.
- Kamiloglu S, Sari G, et al. Guidelines for cell viability assays. Food Frontiers. 2020.
- Ganesan N, Ronsmans S, et al. Methods to Assess Proliferation of Stimulated Human Lymphocytes In Vitro: A Narrative Review. Cells. 2023. 12(3):386.
Explore Other Options