Potassium Oxonate-Induced Hyperuricaemia Model
Hyperuricemia is a main cause of diabetes, metabolic syndrome and chronic kidney disease and it is characterized by abnormally high levels of plasma uric acid (UA) in human. Xanthine oxidase (XOD) plays an important role during the formation of UA and can transform xanthine and hypoxanthine into it. Both excessive consumption of purine foods and a lack of genetic enzymes can cause hyperuricemia.
Potassium oxonate (PO) is a kind of triazabenzene compound and can inhibit the activity of uricase, leading to a rise in the level of UA. PO-induced hyperuricemia is an animal model that mimic the increase of UA in hyperuricemia patients. This model is usually used by drug developers and biomedical scientists to study the pathogenesis of hyperuricemia.
Creative Bioarray, with a prestigious team in the industry, focuses on providing customized experiment services to help customers assess the efficacy of compounds and study the associated pathological mechanisms of Type 1 diabetes through PO-induced hyperuricemia model.
Species available
- Rat
- Mouse
Our capabilities
- Rodents are administrated by intraperitoneal injection, gavage etc.
- We detect the degree of kidney injury by H&E staining.
- We test the activities of MDA, SOD and GSH-PX by Elisa.
Assays available
- Biochemical analysis
- Pathological evaluation
With extensive experience in the field of hyperuricaemia, we are confident to help you overcome any upcoming challenges. Our experts are fully capable of customizing our protocols and assays to meet your specific needs. With our help, we wish to facilitate your research with high efficiency.
Study examples
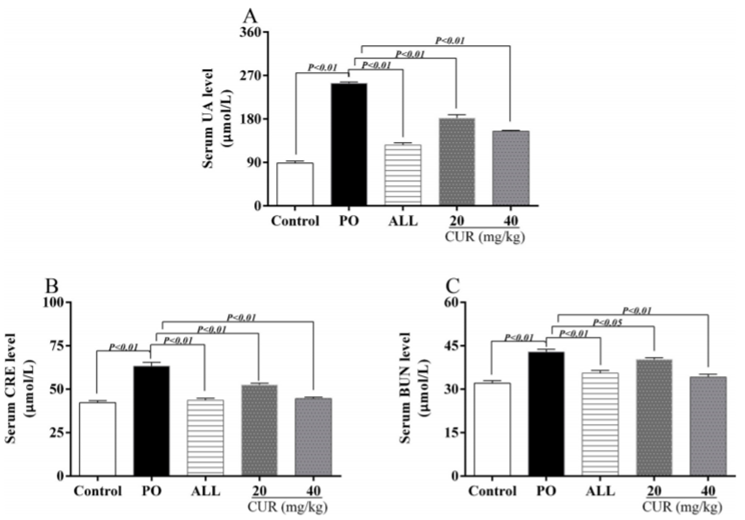 Figure. 1. Effects of CUR on hyperuricemia and kidney injury in hyperuricemic mice. (A) The level of serum UA. (B) The level of serum CRE. (C) The level of serum BUN.
Figure. 1. Effects of CUR on hyperuricemia and kidney injury in hyperuricemic mice. (A) The level of serum UA. (B) The level of serum CRE. (C) The level of serum BUN.
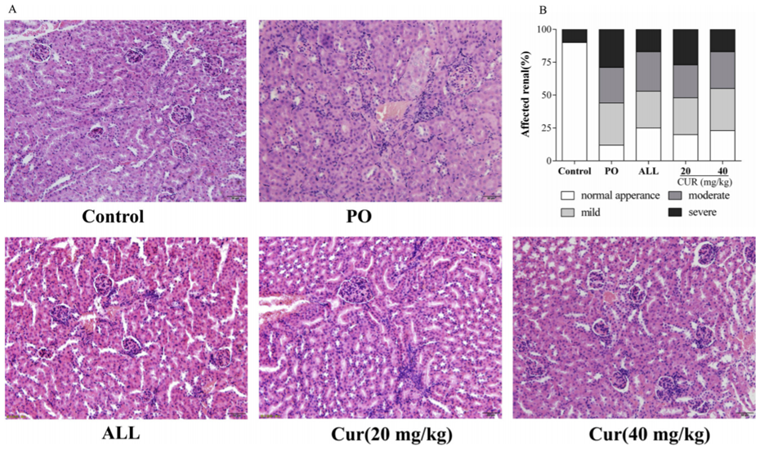 Figure. 2. Effect of CUR on kidney pathological changes for PO-induced hyperuricemic mice. (A) The representative pictures of kidney histopathology (200×). (B) Affected renal (%) (n = 3).
Figure. 2. Effect of CUR on kidney pathological changes for PO-induced hyperuricemic mice. (A) The representative pictures of kidney histopathology (200×). (B) Affected renal (%) (n = 3).
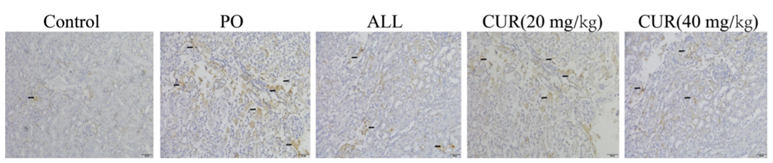 Figure. 3. Effects of CUR on the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Figure. 3. Effects of CUR on the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Quotation and ordering
If you have any special needs or questions regarding our services, please feel free to contact us. We look forward to cooperating with you in the future.
Reference
Chen Y, et al. Curcumin attenuates potassium oxonate-induced hyperuricemia and kidney inflammation in mice[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 2019, 118: 109195.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Oral Mucositis Model
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
- Graft-versus-host Disease (GvHD) Models
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Schizophrenia Model
- Depression Models
- Pain Models
-
Metabolic Disease Models
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Animal Model of Hyperuricemia
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model
- High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Methionine and Choline Deficient (MCD) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Gubra-Amylin NASH (GAN) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Model
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer (DFU) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthotopic Kidney Transplantation Model
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Model
- Peritoneal Fibrosis Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
- Otology Disease Models