Microsomal Stability Assay
- Service Details
- Features
- FAQ
- Explore Other Options
In the initial stages of drug development, it is imperative for scientists to thoroughly investigate drug metabolism and stability, as these factors are crucial to ensuring both the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical compounds. In this context, in vitro metabolic assays offer a significant advantage by allowing the examination of drug-enzyme interactions in isolation from the complex variables present in physiological systems. Among these assays, hepatic microsomes are particularly favored because they encompass a comprehensive array of phase I and phase II metabolic enzymes, such as cytochrome P450 and UGT. Consequently, these in vitro systems closely mimic the hepatic metabolic processes that occur in vivo, thereby providing critical insights into the biotransformation of drugs within the human body.
The microsomal stability assay provided by Creative Bioarray efficiently evaluates the metabolic stability of candidates, supplying researchers with essential metabolic data that supports drug optimization and innovative development.
Characteristics of microsomal stability assay:
- Broad Metabolic Pathway Coverage: Contains various phase I and II metabolic enzymes, capable of comprehensively evaluating the drug's metabolic pathways.
- Species-Specific Evaluation: Utilizes microsomes from different species to reduce individual variability and effectively study interspecies metabolic differences.
- Simple and Cost-Effective Operation: Easy to prepare and use, suitable for high throughput and cost-efficient processes.
- Evaluation of Metabolic Clearance Rate: Measures the clearance rate of compounds during incubation, predicting their metabolic stability.
- Supports Drug Optimization: Provides critical metabolic data for early research, facilitating compound optimization and enhancement of bioavailability.
Our Microsomal Stability Assay Service
Workflow
1
Preparation
Select test compounds, hepatic microsome solutions, NADPH, and other reagents.
2
Mixing and Incubation
Mix the compound with hepatic microsomes and incubate at 37°C, adding NADPH to initiate the metabolic reaction
3
Termination and Sampling
Add terminating solution at set time points (0, 15, 30, 60 minutes) to stop the reaction, then prepare the samples for subsequent analysis.
4
Analysis
Analyze samples using HPLC-MS/MS to determine the remaining amount of the compound.
5
Data Processing
Calculate parameters such as half-life and clearance rate to assess compound stability.
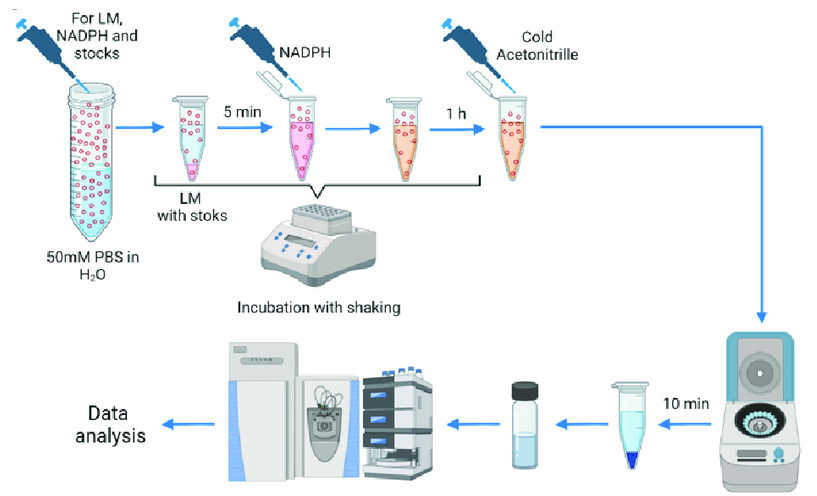 Stages
of the microsomal stability experiment according to the standard protocol (Tupertsev B, Osipenko S, et al.,
2023).
Stages
of the microsomal stability experiment according to the standard protocol (Tupertsev B, Osipenko S, et al.,
2023).
| Microsomal Stability Assay | Details |
| Species | Human, rat, mouse, (other available) |
| Test Compound Concentration | 1 µM (different concentrations available on request) |
| Microsomes Concentration | 0.5 mg/mL (different concentrations available on request) |
| Time Points | 0, 5, 15, 30, 45 and 60 minutes |
| Replicates | 2 |
| Cofactor | 1 mM NADPH (other cofactors available on request) |
| Compound Requirements | 50 µL of 10 mM DMSO solution or 1 mg of solid material |
| Negative Control |
Vehicle (0.1% DMSO) Heat inactivated microsomes |
| Positive Controls |
Verapamil (rapid clearance) Diazepam (low clearance) |
| Analysis Method | HPLC-MS/MS |
| Data Delivery | Apparent intrinsic clearance (CLint, app), half-life (t1/2), parent remaining (%) including standard error of mean (SEM) |
More metabolic stability assays:
Creative Bioarray's microsomal stability assay can be further extended to metabolite profiling and give out more information about the metabolism of your compound.
Conduct metabolic studies using complete human hepatocyte models to provide cellular-level metabolic information, aiding in the prediction of a drug's clearance rate in vivo.
Perform metabolic stability analysis using liver S9 fractions, combining phase I and II metabolic evaluations for a more comprehensive understanding of the compound's metabolic pathways.
Features

Reliable Data
Equipped with advanced LC-MS/MS technology to ensure data accuracy and reliability.

Experienced Team
Our scientists have extensive experience in drug metabolism research, providing expert technical support and advice.
Comprehensive Analysis
We offer a wide range of species to ensure relevance and comparability across different models.
FAQ
1. What is metabolic stability analysis?
Metabolic stability analysis evaluates the degradation rate of compounds in biological samples (e.g., liver microsomes, hepatocytes, S9 fractions). This analysis provides insights into the in vivo metabolic stability, half-life, and clearance rate of compounds, which are crucial for predicting their pharmacokinetic properties during drug development.
2. What are the advantages of using liver microsomes for drug metabolism research?
Liver microsomes from hepatocyte endoplasmic reticulum contain many CYP450 enzymes that drive drug metabolism. Advantages include:
- Rich in Metabolic Enzymes: Contains abundant CYP450 enzyme systems to simulate the main drug metabolism process.
- Simple Operation: Easy to prepare with controllable incubation conditions, suitable for high-throughput screening.
- Low Cost: More cost-effective to prepare and use than complete hepatocytes.
- Predicting In Vivo Clearance Rate: Measuring liver microsomal metabolism helps scientists estimate actual drug clearance rates to support pharmacokinetic analysis.
3. What are the differences between hepatocyte stability and microsomal stability?
- Enzyme System Differences: Hepatocytes possess enzymes aldehyde oxidase (AO) and xanthine oxidase (XO) that help metabolism but these enzymes exist in lower amounts or lack entirely in microsomal preparations.
- Structural Differences: Hepatocytes have intact structures including cell membranes, whereas microsomes are non-structured enzymatic sources, leading to differences in permeability and uptake/excretion processes.
- Transporter Effects: Hepatocytes express various drug transporters (e.g., OATP, BCRP) that affect uptake and excretion, impacting metabolic rates, whereas microsomes do not contain these transporters.
4. Why can microsomal CLint data predict in vivo clearance rate?
Microsomal intrinsic clearance (CLint) indicates the rate at which a compound is metabolized by enzymes in liver microsomes. It forms the basis for predicting in vivo clearance as the liver is the main metabolic organ. CLint reflects a drug's potential hepatic clearance capacity and can be extrapolated to whole-body clearance through proper modeling and scaling, crucial for drug dosing and optimization.
5. How is microsomal stability data interpreted?
Key parameters include:
- Half-life (t1/2): Time for drug concentration to decline by half. A longer half-life indicates slower metabolism and better stability.
- Intrinsic Clearance (CLint): Volume of drug metabolized per unit time. Lower CLint indicates slower metabolism and lower in vivo clearance.
- Metabolite Formation: Identifying metabolites helps understand primary metabolic pathways and aids in drug structure optimization.
Explore Other Options