Sulforhodamine B (SRB) Assay
- Features
- Workflow
- Applications
- Case Studies
- Explore Other Options
The sulforhodamine B (SRB) assay was developed by Skehan and colleagues to measure drug-induced cytotoxicity and cell proliferation for large-scale drug-screening applications. Sulforhodamine B, an anionic aminoxanthene dye, can form an electrostatic complex with the basic amino acid residues of proteins under moderately acid conditions, which provides a sensitive linear response with cell number and cellular protein measured at cellular densities ranging from 1 to 200% of confluence. The SRB assay possesses a nondestructive and indefinitely stable colorimetric end point and the color development is rapid and stable and is readily measured at absorbance between 560 and 580nm. With many practical advances including a favorable signal-to-noise ratio and a resolution of 1000-2000 cells/well, the SRB assay serves as an appropriate and sensitive assay to measure drug-induced cytotoxicity even at large-scale application.
Creative Bioarray Advantages
- High sensitivity
- Accurate and reproducible
- Low signal-to-noise ratio
- High resolution (1000-2000 cells/well)
- Linear results ranging from 1 to 200% of confluence
- colorimetric, nondestructive, and indefinitely stable end point
- Rapid and low-cost
- Suitable for high-throughput screening
Workflow
- Seeding of Microtiter Plates for Growth Kinetics
- Choice of Drug Dose Range and Seeding of Culture Plates for Cytotoxicity Assays
- SRB Procedure
- Data Processing and Interpretation of Results
Applications
- Cell growth/proliferation
- Cytotoxicity measurement/screening
- Chemosensitivity
Results Sample
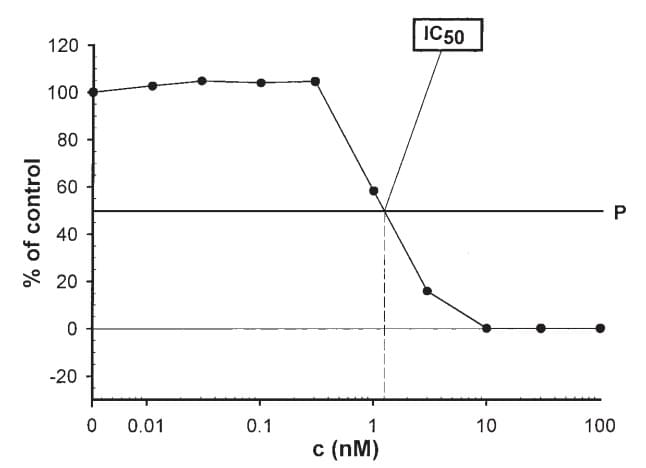
Figure 1. Graphic determination of IC50
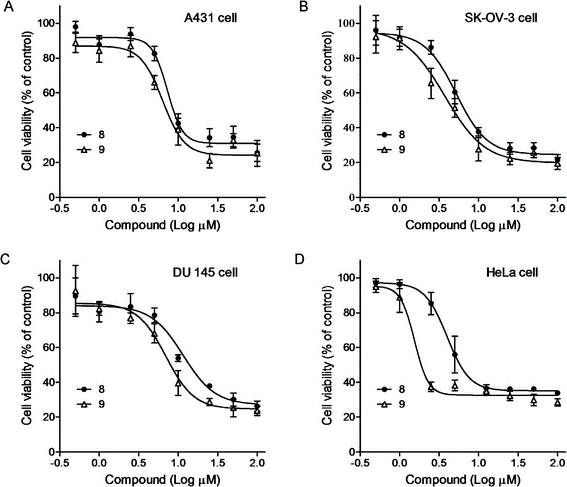
Figure 2. Effects of compounds on cell proliferation
Quote and Ordering
Please fill out the chart below or contact us to discuss your project with our experts and get a quote.
Payment methods supported: Invoice / Purchase Order, Wire Transfer, and Credit Card.
References
- Skehan, P., Storeng, R., Scudiero, D., Monks, A., McMahon, J., Vistica, D., Warren, J. T., Bokesch, H., Kenney, S., and Boyd, M. R. (1990) New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer-drug screening. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 82, 1107-1112.
- Perez, R. P., Godwin, A. K., Handel, L. M., and Hamilton, T. C. (1993) A comparison of clonogenic, microtetrazolium and sulforhodamine B assays for determination of cisplatin cytotoxicity in human ovarian carcinoma cell lines. Eur. J. Cancer 29A, 395-399.
- Griffon, G., Merlin, J. L., and Marchal, C. (1995) Comparison of sulforhodamine B, tetrazolium and clonogenic assays for in vitro radiosensitivity testing in human ovarian cell lines. Anticancer Drugs 6, 115-123.
- Papazisis, K. T., Geromichalos, G. D., Dimitriadis, K. A., and Kortsaris, A. H. (1997) Optimization of the sulforhodamine B colorimetric assay. J. Immunol. Methods 208, 151-158.
Explore Other Options
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.
Services
-
Cell Services
- Cell Line Authentication
- Cell Surface Marker Validation Service
-
Cell Line Testing and Assays
- Drug-Resistant Cell Models
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assays
- Cell Migration Assays
- Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay Service
- SRB Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- Cell Cycle Assays
- Cell Angiogenesis Assays
- DNA/RNA Extraction
- Cellular Phosphorylation Assays
- Stability Testing
- Sterility Testing
- Endotoxin Detection and Removal
- Phagocytosis Assays
- Cell-Based Screening and Profiling Services
- 3D-Based Services
- Custom Cell Services
- Cell-based LNP Evaluation
-
Stem Cell Research
- iPSC Generation
- iPSC Characterization
-
iPSC Differentiation
- Neural Stem Cells Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Astrocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- T Cell, NK Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Hepatocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Beta Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Brain Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Kidney Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- GABAnergic Neuron Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Undifferentiated iPSC Detection
- iPSC Gene Editing
- iPSC Expanding Service
- MSC Services
- Stem Cell Assay Development and Screening
- Cell Immortalization
-
Molecular Biology Solutions
- Chromosome & Genomic Analysis
-
Cytogenetics & Molecular Cytogenetics Analysis
- Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization (FISH)
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH) & RNAscope
- ImmunoFISH (FISH+IHC)
- I-FISH
- Splice Variant Analysis (FISH)
- RNA FISH in Plant
- mtRNA Analysis (FISH)
- Digital ISH Image Quantification and Statistical Analysis
- Telomere Length Analysis (Q-FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (qPCR assay)
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR)
- QuantiGene Plex Assay
- Probe Development & Quality Control
- ISH/FISH Analysis for Therapeutic R&D
- Cell Line Characterization
- Pathogen & Microbial Analysis
- Histology Services
- Exosome Research Services
- Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics (DMPK)
-
Safety Evaluation Services
- High-Throughput Toxicity Screening
- High-Content Cytotoxicity Screening
- In Vitro Cardiotoxicity
- In Vitro Genotoxicity
- Hepatotoxicity
- In Vitro Neurotoxicity
- In Vitro Nephrotoxicity
- In Vitro Dermal Toxicology
- Ocular Toxicity
- In Vitro Cytotoxicity
- Endocrine Disruption Screening Assay
- In Vivo Toxicity Study