Exosome Quantification
In the past decade, exosomes have received much attention due to their potential applications in molecular biology, and biomedical fields. The accurate and reliable quantification of exosomes is crucial to better understand exosomes and their relationship with various diseases.
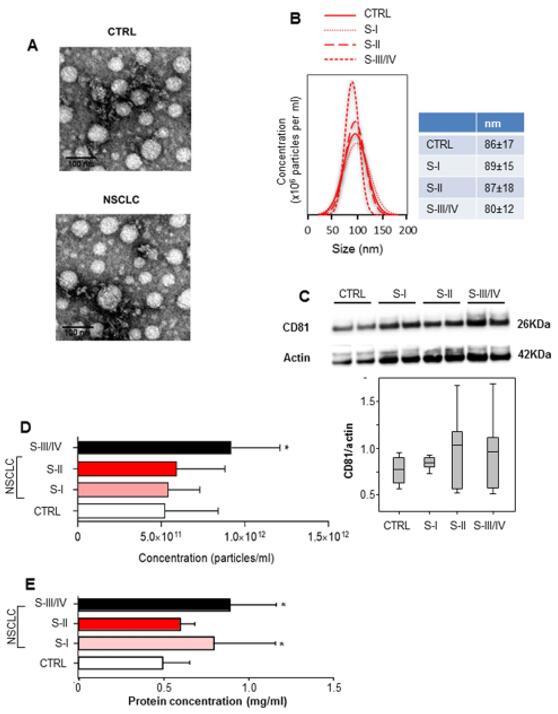 Figure 1 Characterization and quantifcation of exosome levels in serum samples from healthy controls and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients.
Figure 1 Characterization and quantifcation of exosome levels in serum samples from healthy controls and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients.
Exosome quantification mainly depends on their characteristic physical properties, such as size, mass, and density, or on membrane proteins presented on their surface. Creative Bioarray offers a range of options to meet most exosome quantitation demands. We provide reliable, and optimized tools at the most competitive price for quantitative analysis of exosomes in diverse biological samples such as plasma, urine, etc.
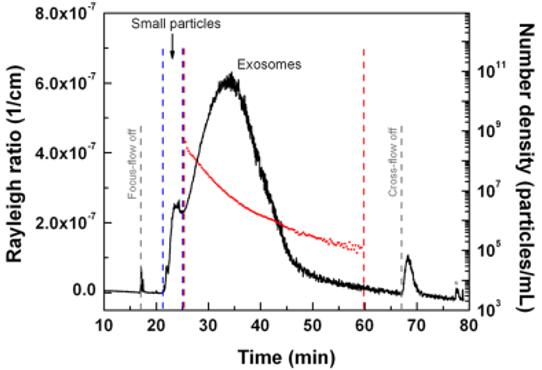 Figure 2 An AF4-MALS fractogram of exosome sample and calculated number of particles (number density of particles per mL) for larger exosome population as a function of elution time.
Figure 2 An AF4-MALS fractogram of exosome sample and calculated number of particles (number density of particles per mL) for larger exosome population as a function of elution time.
Here in Creative Bioarray, we provide a series of exosome quantification services listed as below, choose the exosome quantitation method that is best for your studies:
- ELISA-based Immunoaffinity capture (IAC) assay
- Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA)
- Asymmetrical-flow field flow fractionation (AF4) coupled with multidetection assay
- Dynamic light scattering (DLS) assay
- Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) assay
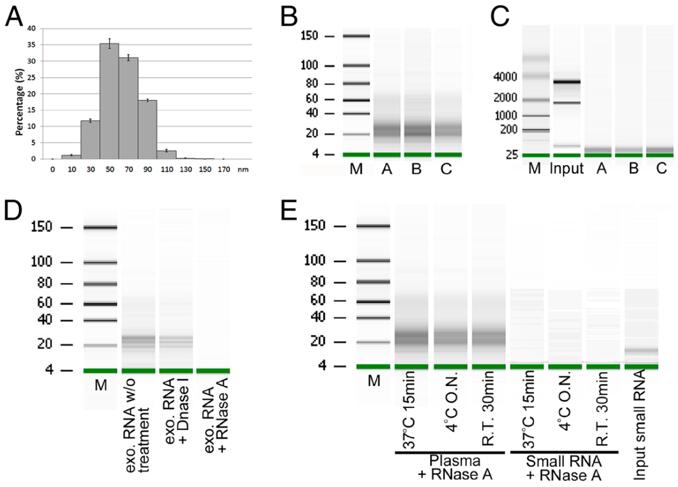 Figure 3 Exosome isolation and exosomal small RNA quantification.
Figure 3 Exosome isolation and exosomal small RNA quantification.
In Creative Bioarray, we also provide exosomal RNA quantification service. If you have any special needs in our Exosome Quantification Service, please contact us. Let us know what you need and we will accommodate you. We look forward to working with you in the future.
References
- Grimolizzi, F.; et al. Exosomal miR-126 as a circulating biomarker in non-small-cell lung cancer regulating cancer progression. Sci Rep. 2017, 7(1): 15277.
- Sitar, S.; et al. Size characterization and quantification of exosomes by asymmetrical-flow field-flow fractionation. Anal Chem. 2015, 87(18): 9225-9233.
- Huang, X.; et al. Characterization of human plasma-derived exosomal RNAs by deep sequencing. BMC Genomics. 2013, 14(1): 319.
Explore Other Options
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.
Services
-
Cell Services
- Cell Line Authentication
- Cell Surface Marker Validation Service
-
Cell Line Testing and Assays
- Drug-Resistant Cell Models
- Cell Viability Assays
- Cell Proliferation Assays
- Cell Migration Assays
- Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay Service
- SRB Assay
- Cell Apoptosis Assays
- Cell Cycle Assays
- Cell Angiogenesis Assays
- DNA/RNA Extraction
- Cellular Phosphorylation Assays
- Stability Testing
- Sterility Testing
- Endotoxin Detection and Removal
- Phagocytosis Assays
- Cell-Based Screening and Profiling Services
- 3D-Based Services
- Custom Cell Services
- Cell-based LNP Evaluation
-
Stem Cell Research
- iPSC Generation
- iPSC Characterization
-
iPSC Differentiation
- Neural Stem Cells Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Astrocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- T Cell, NK Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Hepatocyte Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Beta Cell Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Brain Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Cardiac Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Kidney Organoid Differentiation Service from iPSC
- GABAnergic Neuron Differentiation Service from iPSC
- Undifferentiated iPSC Detection
- iPSC Gene Editing
- iPSC Expanding Service
- MSC Services
- Stem Cell Assay Development and Screening
- Cell Immortalization
-
Molecular Biology Solutions
- Chromosome & Genomic Analysis
-
Cytogenetics & Molecular Cytogenetics Analysis
- Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization (FISH)
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH) & RNAscope
- ImmunoFISH (FISH+IHC)
- I-FISH
- Splice Variant Analysis (FISH)
- RNA FISH in Plant
- mtRNA Analysis (FISH)
- Digital ISH Image Quantification and Statistical Analysis
- Telomere Length Analysis (Q-FISH)
- Telomere Length Analysis (qPCR assay)
- Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR)
- QuantiGene Plex Assay
- Probe Development & Quality Control
- ISH/FISH Analysis for Therapeutic R&D
- Cell Line Characterization
- Pathogen & Microbial Analysis
- Histology Services
- Exosome Research Services
- Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics (DMPK)
-
Safety Evaluation Services
- High-Throughput Toxicity Screening
- High-Content Cytotoxicity Screening
- In Vitro Cardiotoxicity
- In Vitro Genotoxicity
- Hepatotoxicity
- In Vitro Neurotoxicity
- In Vitro Nephrotoxicity
- In Vitro Dermal Toxicology
- Ocular Toxicity
- In Vitro Cytotoxicity
- Endocrine Disruption Screening Assay
- In Vivo Toxicity Study