
RAMOS
Cat.No.: CSC-C1015
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Ascites
Morphology: Lymphoblast
Culture Properties: Suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
CSF1PO: 10,11
D13S317: 13,14
D16S539: 10,13
D5S818: 7,12
D7S820: 11
THO1: 7,9.3
TPOX: 8,9
vWA: 15,16
Immunology: CD3 -, CD10 +, CD13 -, CD19 +, CD20 +, CD34 -, CD37 +, CD38 +, cyCD79a +, CD80 +, CD138 -, HLA-DR +, sm/cyIgG -, sm/cy
The Ramos cell line was isolated from the peripheral blood of Burkitt lymphoma patient. Burkitt lymphoma attacks B lymphocytes which function as essential components of the immune system by producing antibodies to battle infections. B lymphocytes make up the primary cellular component of lymphoid tissues such as lymph nodes, spleen and bone marrow. The Ramos cell line originates from peripheral blood B lymphocytes which usually recognize and respond to foreign antigens.
Ramos cells are capable of secreting IgM (λ light chain), an important function of B lymphocytes. The cells express various receptors including the interleukin 4 (IL-4) receptor and the CD23 receptor which binds IgE at low affinity, and each cell surface features approximately 1,500 interleukin 4 binding sites. Additionally, Ramos cells are tumorigenic in nude mice. The Ramos cell line is particularly valuable in studies related to B cell development, function, and malignancy. For example, researchers utilize these cells to explore B cell receptor (BCR) signaling pathways and gene expression while identifying the mechanisms that lead to normal B cells becoming malignant.
Low PCNA Monoubiquitination in Ramos Cells after Treatment with Genotoxic Agents Correlates with a High Amount of USP1 Deubiquitinase
Somatic hypermutation (SHM) of immunoglobulin (Ig) genes is essential for generating high-affinity antibodies in B cells. This process involves AID and DNA repair factors, creating mutations in G/C and A/T bases. However, the mechanism of A/T mutagenesis remains unclear due to the lack of a cellular model that fully replicates this process. In this study, Lerner et al.used the Ramos cell line, which exhibits G/C-biased SHM, to investigate the role of PCNA ubiquitination in A/T mutagenesis.
They investigated whether PCNA ubiquitination is deregulated in Ramos cells by treating them with UVC light or H2O2 and monitoring PCNA monoubiquitination by western blotting. As shown in Figure 1A, PCNA monoubiquitination was barely detectable in Ramos cells compared to non-Burkitt cells. This suggests that PCNA monoubiquitination is weak or inefficient in Ramos cells. Since PCNA monoubiquitination is reversible and regulated by the balance between ubiquitin ligases and the deubiquitinase USP1, we analyzed USP1 expression in Ramos and other Burkitt lymphoma cell lines by western blotting (Fig. 1B–D). Ramos and BL cell lines expressed high levels of USP1 compared to tonsillar B cells, while non-BL cells showed normal levels. Elevated USP1 levels were also found in mantle cell lymphoma-derived B cells. These results suggest that high USP1 expression in Ramos cells leads to low PCNA monoubiquitination, which could explain the reduced A/T mutations.
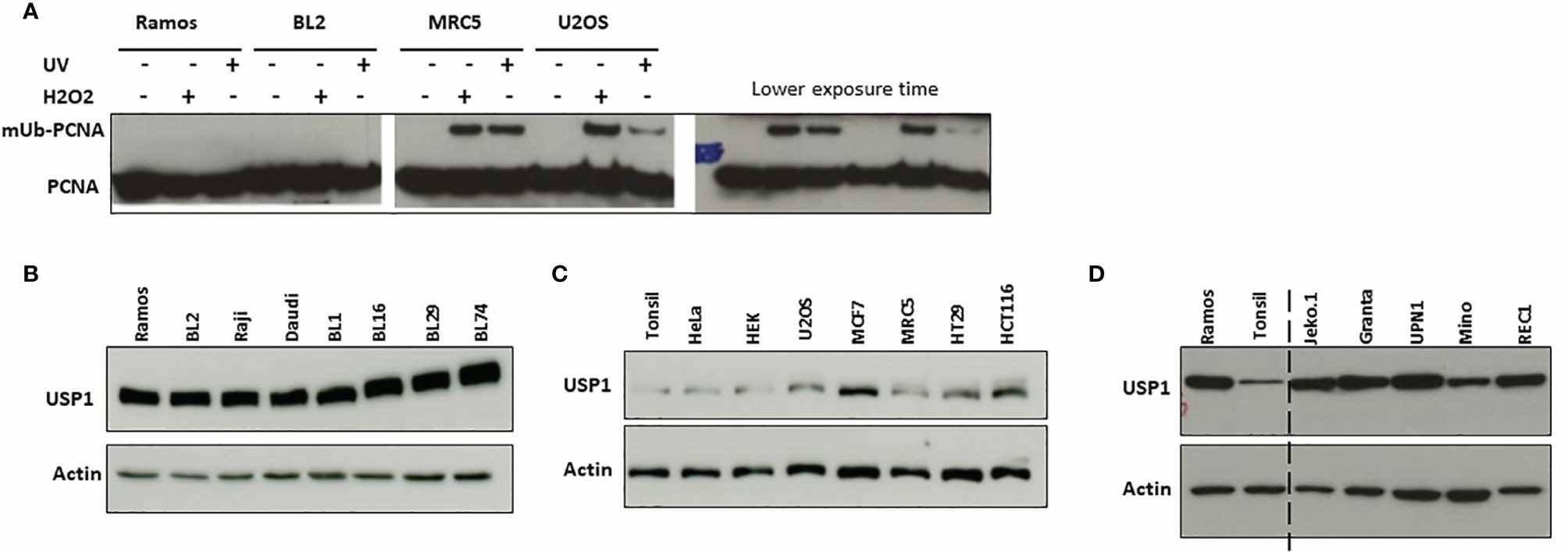 Fig. 1. Induction of monoubiquitination of PCNA and USP1 expression in Ramos and BL2 cells (Lerner LK, Bonte D, et al., 2022).
Fig. 1. Induction of monoubiquitination of PCNA and USP1 expression in Ramos and BL2 cells (Lerner LK, Bonte D, et al., 2022).
IL-4 and IL-21 Disrupted the B Cell Tolerance Checkpoint and Promoted the Survival of Hyperactivated Ramos Cells
Interleukins 4 (IL-4) and 21 (IL-21) are involved in autoimmune diseases, but their roles in B cell survival are not fully understood. B cell hyperactivity is a characteristic of autoimmune diseases, where autoreactive B cells contribute to disease progression. In this study, Hui's team activated Ramos B cells with anti-IgM to induce apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. We then examined the effects of IL-4 and IL-21 on anti-IgM-induced apoptosis.
The optimal dose of anti-IgM was determined by WST-8 assay after 48 hours, with 2 μg/ml selected for further experiments due to significant reduction in Ramos cell proliferation (Fig. 2A). Long-term anti-IgM treatment (24–48 hours) decreased survival protein activation (AKT and p65) and increased caspase 3 activity, while reducing cell cycle proteins (Fig. 2B and C). No cell cycle arrest proteins (p21 and p27) were detected, indicating that anti-IgM induces cell death by suppressing survival and cell cycle proteins. Next, Ramos cells were pretreated with IL-4 or IL-21 before anti-IgM challenge for 48 hours. Anti-IgM activated dose-dependent apoptosis in AV/PI assay which IL-4 and IL-21 reversed (Fig. 3A). Both low and high concentrations of IL-4 returned cell viability to normal levels according to Fig. 3B and C. At a concentration of 50 ng/ml, IL-21 demonstrated dose-dependency by offering stronger protection against anti-IgM-induced apoptosis compared to other concentrations (Fig. 3D and E).
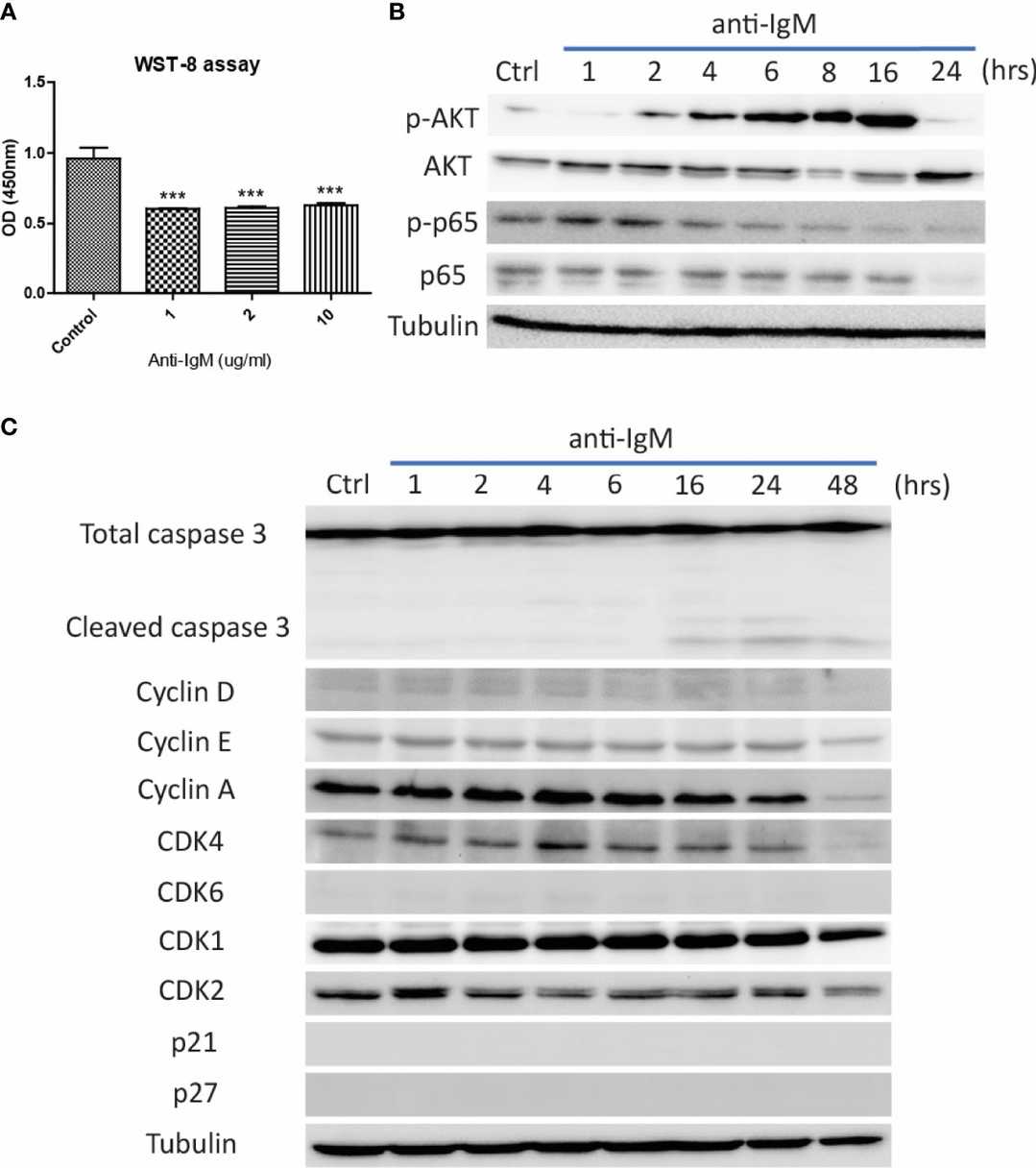 Fig. 2. Detrimental effects of anti-IgM on Ramos B cells (Hui AW, Wu WC, et al., 2022).
Fig. 2. Detrimental effects of anti-IgM on Ramos B cells (Hui AW, Wu WC, et al., 2022).
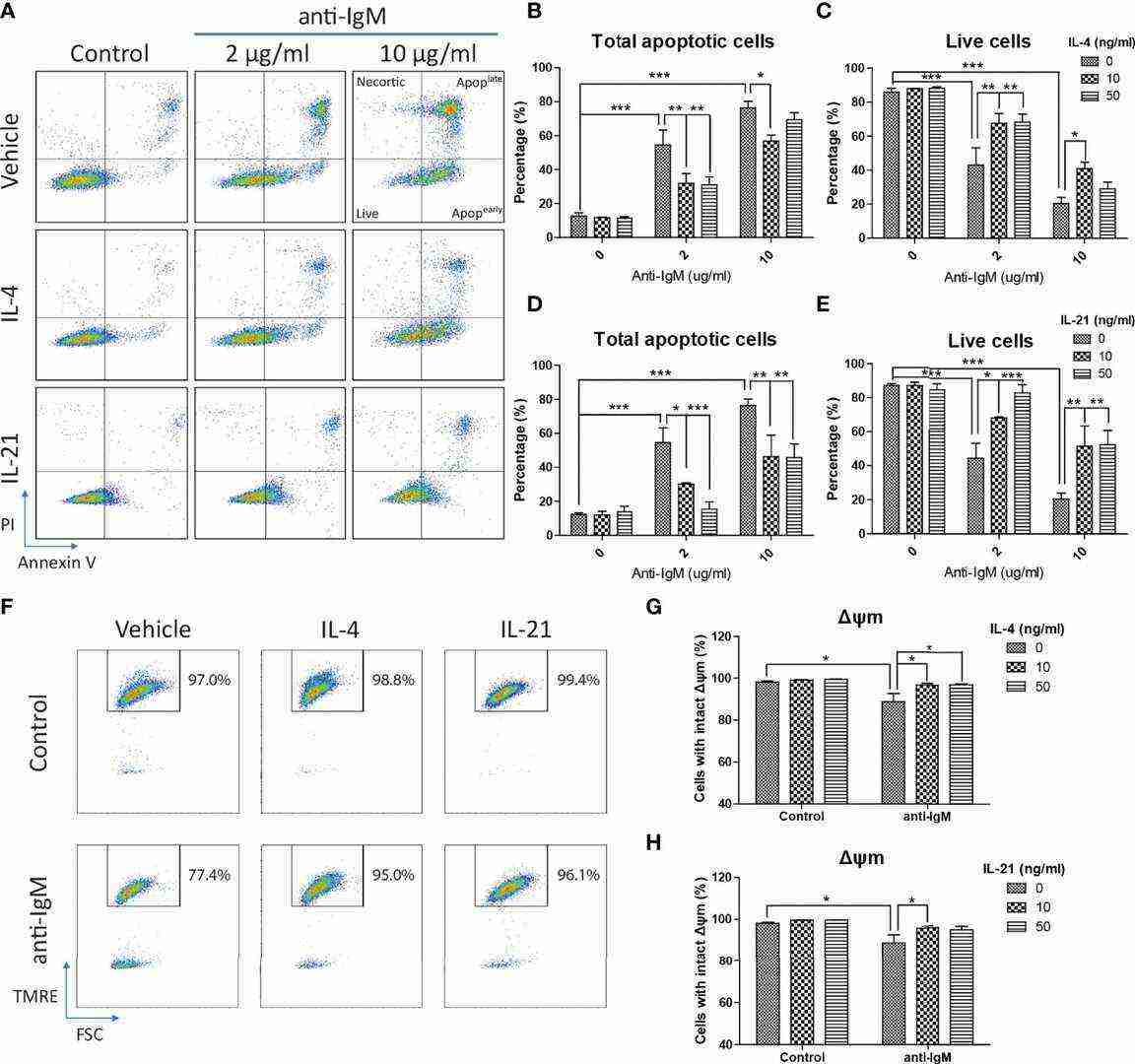 Fig. 3. IL-4 and IL-21 rescued anti-IgM induced apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction (Hui AW, Wu WC, et al., 2022).
Fig. 3. IL-4 and IL-21 rescued anti-IgM induced apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction (Hui AW, Wu WC, et al., 2022).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells





