Complete Freund's Adjuvant (CFA)-Induced Inflammatory Pain Model
As a trusted research partner in the field of preclinical drug development, Creative Bioarray prides itself in offering an extensive array of innovative inflammatory pain models. These models serve as a robust platform for establishing the proof-of-concept, facilitating the potential assessment, and advancing the development of effective treatment strategies for a diverse range of pain-related medical conditions. By leveraging our expertise in inflammatory pain research, we aim to contribute significantly to the advancement of pain management and improve the quality of life for patients suffering from various pain disorders.
CFA is composed of mineral oil containing a suspension of whole or pulverized heat-killed mycobacteria. Its adjuvant activity is attributed to the sustained release of antigens from the oily depot and the stimulation of a local innate immune response, resulting in a delayed hypersensitivity reaction at the injection site, characterized by intense inflammation and hyperalgesia. The CFA-induced inflammatory pain model has been well characterized in Creative Bioarray and is routinely used for screening novel compounds targeted for inflammatory pain.
Our Complete Freund's Adjuvant (CFA)-Induced Inflammatory Pain Model
- Available Animal
- Rat
- Mouse
- Modeling Method
Animals undergo an intraplantar injection of CFA into the hind paw to induce inflammatory pain.
- Endpoints
- Behavioral tests: Von Frey test, Hot plate test, etc.
- Body weight
- Clinical observation
- qPCR or Western blot
- Histology analysis
- Other customized endpoints
Example Data
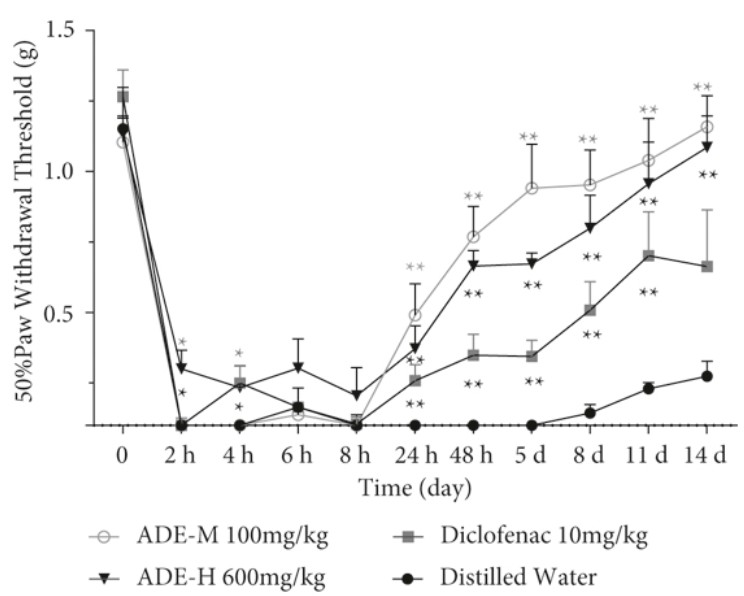 Fig. 1 CFA-induced mechanical allodynia. (Zhu et al. 2022)
Fig. 1 CFA-induced mechanical allodynia. (Zhu et al. 2022)
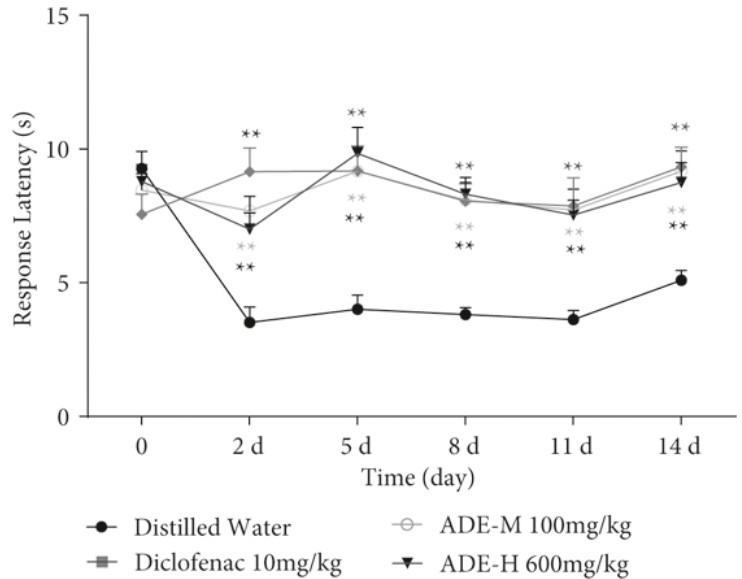 Fig. 2 CFA-induced thermal hyperalgesia. (Zhu et al. 2022)
Fig. 2 CFA-induced thermal hyperalgesia. (Zhu et al. 2022)
In addition, we also provide other inflammatory pain models that maybe you are interested in:
- Formalin-Induced Inflammatory Pain Model
- Capsaicin-Induced Inflammatory Pain Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Inflammatory Pain Model
Quotation and Ordering
As a preeminent preclinical CRO partner, Creative Bioarray offers our clients swiftly scheduled, cost-effective, and impeccably precise services, adhering to the utmost standards of quality. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us at any time or submit an inquiry to us directly.
References
- Zhu C, Wang M, Guo J, et al. Angelica dahurica Extracts Attenuate CFA-Induced Inflammatory Pain via TRPV1 in Mice. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022; 2022:4684830.
- Navarro-Alvarez N, Gonçalves BMM, Andrews AR, Sachs DH, Huang CA. A CFA-Induced Model of Inflammatory Skin Disease in Miniature Swine. Int J Inflam. 2018; 2018:6916920.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Oral Mucositis Model
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
- Graft-versus-host Disease (GvHD) Models
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Schizophrenia Model
- Depression Models
- Pain Models
-
Metabolic Disease Models
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Animal Model of Hyperuricemia
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model
- High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Methionine and Choline Deficient (MCD) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Gubra-Amylin NASH (GAN) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Model
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer (DFU) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthotopic Kidney Transplantation Model
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Model
- Peritoneal Fibrosis Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
- Otology Disease Models