Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
Creative Bioarray offers a diverse range of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) models that serve as invaluable tools for investigating the therapeutic efficacy and mechanism of action of novel therapies. These models are highly reliable and are tailored to meet the unique needs of our clients, allowing for precise and accurate results. In addition, our team of experts can also design and conduct customized studies to meet the specific requirements of your research project. With our HIE models and personalized research solutions, you can take your research to the next level.
Perinatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) is a serious medical condition that presents a severe and potentially fatal form of brain injury in newborns during childbirth. The condition arises when there is an insufficient supply of oxygen and blood flow to the infant's brain during the perinatal period, resulting in the death of brain cells within a brief timeframe. Unfortunately, the brain damage caused by hypoxia during childbirth is permanent and cannot be reversed through surgical procedures or medications. Therefore, HIE is considered a permanent injury that can have devastating and long-lasting effects on a child's health and development. Treatment options primarily involve therapeutic interventions and medication to assist in managing the effects of any brain damage that has occurred.
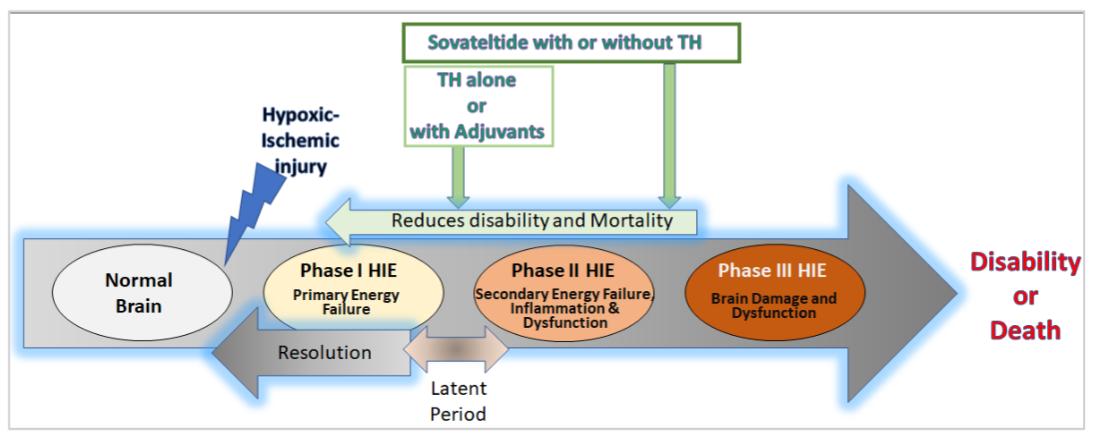 Fig. 1 Diagrammatic representation of the phases of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE)
Fig. 1 Diagrammatic representation of the phases of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE)
Our Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Modeling Method: Modified Rice-Vannucci Model
On the 7th day after birth, rats are fully anesthetized, and a small incision is made in the center of their necks. Subsequently, the right common carotid artery (RCCA) is occluded and transected, and the incision is sutured closed. The rats are then exposed to 8% hypoxia at 37℃ for a duration of 2.5 hours. - Available Animal
Rat - Endpoints
- Clinical score: Zea Longa
- Behavioral tests: Morris water maze test, Rotarod test, Cylinder test, etc.
- Histology analysis: H&E staining, TTC staining, TUNEL staining
- Brain weight
- Body weight
- Other customized endpoints: available upon request
……
Example Data
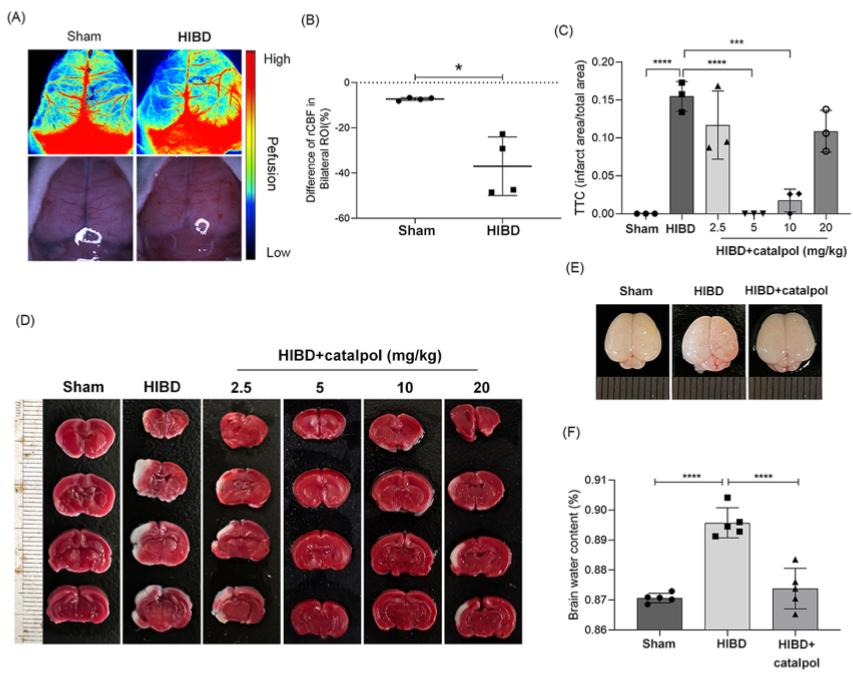 Fig. 2 Catalpol alleviated brain injury in a neonatal rat model of HIBD. (A) Laser speckle contrast imaging was used to dynamically monitor the cerebral cortical surface blood flow after HIBD, and the ROIs were used for the cerebral blood flow (CBF) assessment. (B) Quantification of CBF in bilateral ROIs. (C) Calculation of the infarct area by TTC staining. (D) The results of TTC stained coronal brain sections 24 h after HI brain injury modeling. (E) The brains were isolated from each group 24 h after HI brain injury modeling. (F) The brain ratio of wet to dry was calculated in each group.
Fig. 2 Catalpol alleviated brain injury in a neonatal rat model of HIBD. (A) Laser speckle contrast imaging was used to dynamically monitor the cerebral cortical surface blood flow after HIBD, and the ROIs were used for the cerebral blood flow (CBF) assessment. (B) Quantification of CBF in bilateral ROIs. (C) Calculation of the infarct area by TTC staining. (D) The results of TTC stained coronal brain sections 24 h after HI brain injury modeling. (E) The brains were isolated from each group 24 h after HI brain injury modeling. (F) The brain ratio of wet to dry was calculated in each group.
Quotation and Ordering
With years of experience in pharmacology and efficacy studies, Creative Bioarray is dedicated to providing personalized and comprehensive solutions that are tailored to meet the unique needs of each client. With a focus on quality and affordability, we are committed to providing the best services at the most reasonable prices. We look forward to sharing our professional expertise with our clients to facilitate their studies.
References
- Ranjan, A.K., Gulati, A. Advances in therapies to treat neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2023, 12(20): 6653.
- Lin, J., et al. Catalpol alleviates hypoxia ischemia-induced brain damage by inhibiting ferroptosis through the PI3K/NRF2/system Xc-/GPX4 axis in neonatal rats. European Journal of Pharmacology, 2024: 176406.