Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
Creative Bioarray boasts extensive expertise in conducting preclinical studies on acute kidney injury (AKI) through the use of rodent models. Our team has meticulously crafted a refined model for renal ischemia-reperfusion injury (RIRI), which stands out as a pivotal tool for the meticulous screening, rigorous testing, and comprehensive evaluation of your prospective drug candidates.
The RIRI model simulates the pathological sequence of ischemia/reperfusion injury (IRI), which initially involves a restriction in blood supply to the kidney, subsequently followed by the restoration of blood flow and re-oxygenation. This process, when occurring in the kidney, can lead to AKI, a clinical syndrome characterized by rapid kidney dysfunction and associated with high mortality rates. The cardinal factors that contribute to kidney damage during RIRI include oxidative stress, excessive accumulation of calcium in the cytosol, mitochondrial uncoupling, liberation of iron ions, and the activation of an inflammatory immune response. The RIRI model serves as a valuable tool for studying the mechanisms underlying AKI and evaluating potential therapeutic strategies for its prevention and treatment.
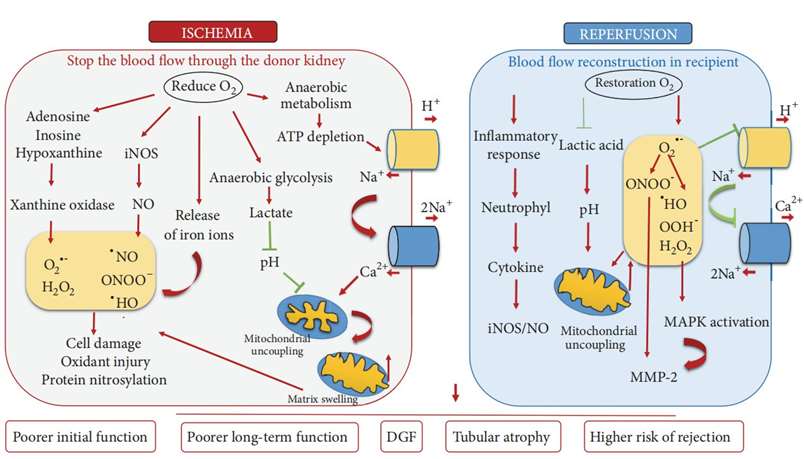 Fig. 1 Mechanisms of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. (Krzywonos-Zawadzka et al. 2019)
Fig. 1 Mechanisms of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. (Krzywonos-Zawadzka et al. 2019)
Our Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Model
- Available Animal
- Rat
- Mouse
- Modeling Method
Animals are fasted for 8-12 hours before surgery. Following anesthesia, a midline incision is made starting from the xiphoid process. The abdominal cavity is then accessed, and the kidney is mobilized and released from its attachments. The renal artery is prepared for complete occlusion using surgical bulldog clips for 45-60 minutes to implement the ischemia-reperfusion protocol.
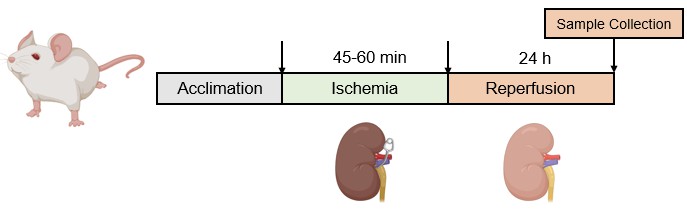 Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of the method for establishing the RIRI model
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of the method for establishing the RIRI model
- Endpoints
- Serum analysis: BUN, creatinine, etc.
- Histology analysis
- Cytokine analysis
- qPCR or Western blot
- Other customized endpoints
Example Data
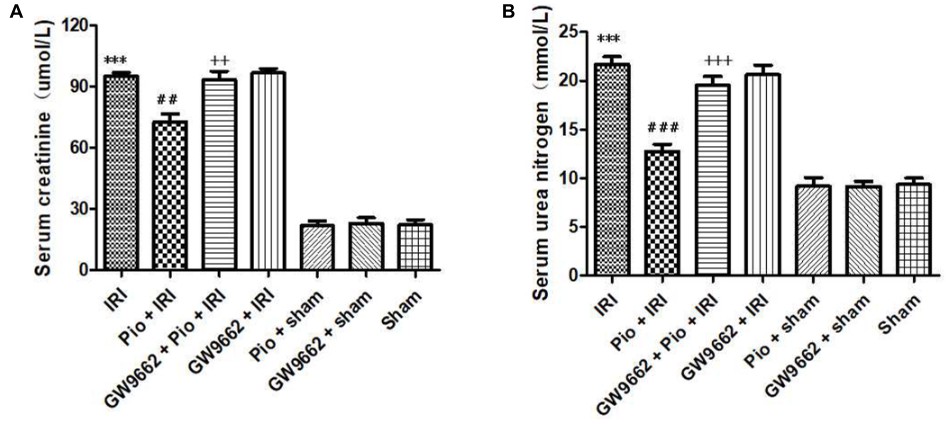 Fig. 3 Pioglitazone treatment improves renal IRI. (A) Serum creatinine levels in different groups at 24 h after renal IRI. (B) Serum urea nitrogen levels in different groups at 24 h after renal IRI. (Zou et al. 2021)
Fig. 3 Pioglitazone treatment improves renal IRI. (A) Serum creatinine levels in different groups at 24 h after renal IRI. (B) Serum urea nitrogen levels in different groups at 24 h after renal IRI. (Zou et al. 2021)
Quotation and Ordering
Creative Bioarray provides urological study services, focusing on conducting preclinical efficacy, proof-of-concept, and mechanism of action studies in different rodent models. Our scientists have the necessary skills and experience to evaluate the efficacy of your preclinical drug candidates. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us at any time or submit an inquiry to us directly.
References
- Zou, G., et al. Pioglitazone ameliorates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury via inhibition of NF-κB activation and inflammation in rats. Frontiers in Physiology, 2021, 12: 707344.
- Krzywonos-Zawadzka, A., et al. Pharmacological protection of kidney grafts from cold perfusion-induced injury. BioMed Research International, 2019, 2019.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Oral Mucositis Model
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
- Graft-versus-host Disease (GvHD) Models
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Schizophrenia Model
- Depression Models
- Pain Models
-
Metabolic Disease Models
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Animal Model of Hyperuricemia
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model
- High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Methionine and Choline Deficient (MCD) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Gubra-Amylin NASH (GAN) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Model
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer (DFU) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthotopic Kidney Transplantation Model
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Model
- Peritoneal Fibrosis Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
- Otology Disease Models