Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
Creative Bioarray provides comprehensive in vivo pharmacodynamics studies utilizing a well-established animal model known as the carrageenan-induced paw edema model. This model is particularly effective for swiftly evaluating the anti-inflammatory properties of your drug candidates. By employing this established methodology, researchers can efficiently evaluate the efficacy of potential drug candidates in reducing inflammation, thereby accelerating the drug development process and ensuring the rapid progression of drug candidates to further stages of clinical evaluation.
Inflammation serves as the body’s initial protective response against injuries caused by various factors, both internal and external. These factors may encompass physical damage, chemical substances, microbial attacks, and even cancer. To evaluate the anti-inflammatory properties of drugs in acute inflammation, researchers frequently employ a reliable method of inducing paw edema. This is achieved through the intraplantar injection of carrageenan, a polysaccharide derived from seaweed. This method promptly triggers swelling, pain sensitivity, and redness in the paw, which are induced by proinflammatory agents like histamine, bradykinin, tachykinin, reactive oxygen species, and reactive nitrogen species. In this specific model, inflammation reaches its peak within a 4-hour timeframe.
Our Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Available Animal
Rat
- Modeling Method
The right hind paw receives intraplantar injection of carrageenan to induce paw edema model.
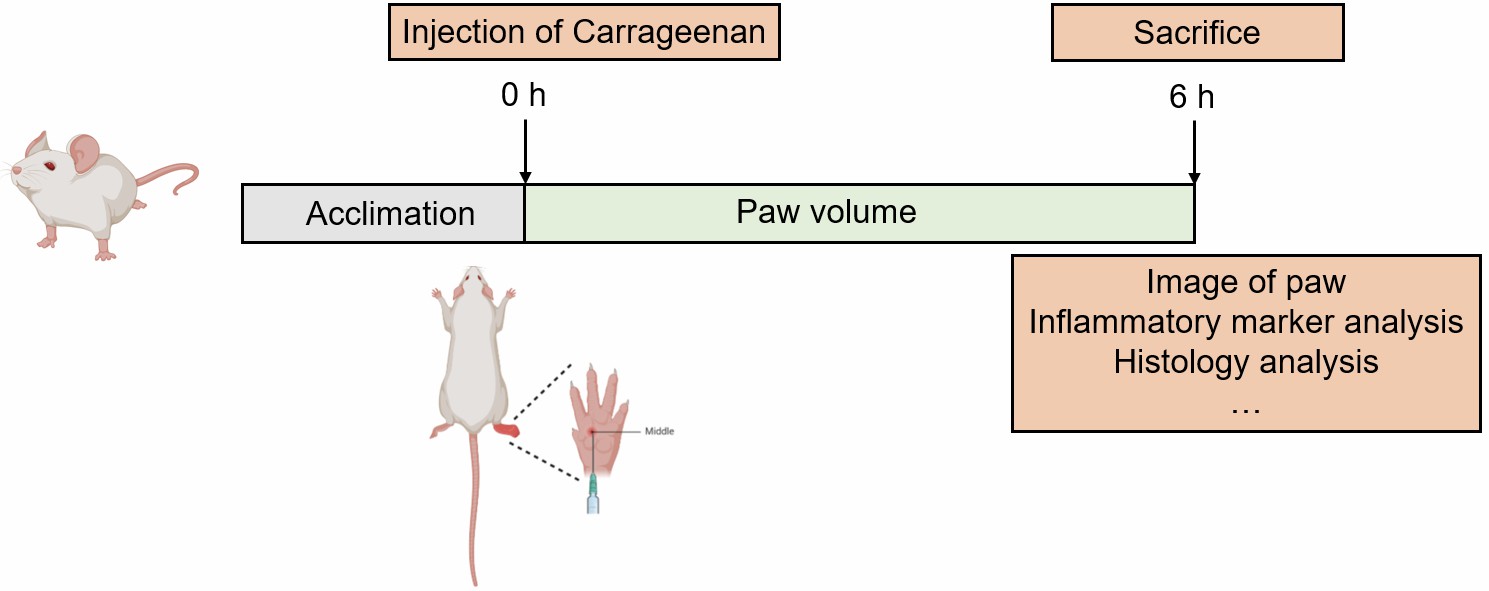 Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of the modeling method of carrageenan-induced paw edema model
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of the modeling method of carrageenan-induced paw edema model
- Endpoints
- Image of paw
- Paw volume
- Inflammatory marker analysis
- Histology analysis
- qPCR or Western blot
- Other customized endpoints
Example Data
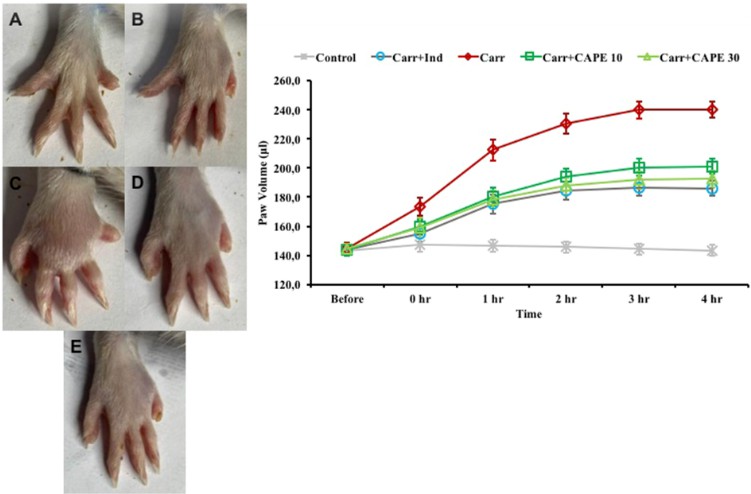 Fig. 2 Effects of Carr, Ind, and CAPE on paw volume of rats. A: Control, B: Carr + Ind, C: Carr, D: Carr + CAPE 10, E: Carr + CAPE 30. (Semis et al. 2021)
Fig. 2 Effects of Carr, Ind, and CAPE on paw volume of rats. A: Control, B: Carr + Ind, C: Carr, D: Carr + CAPE 10, E: Carr + CAPE 30. (Semis et al. 2021)
Quotation and Ordering
With our advanced preclinical technology platforms and skilled teams, Creative Bioarray offers a comprehensive range of services for in vivo efficacy studies. We guarantee exceptional quality results and efficient turnaround time. If you are interested in our services, please do not hesitate to contact us at any time or submit an inquiry to us directly.
Reference
- Semis, H.S., et al. Investigation of the anti-inflammatory effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester in a model of λ-Carrageenan–induced paw edema in rats. Human & experimental toxicology, 2021, 40(12_suppl): S721-S738.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Oral Mucositis Model
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
- Graft-versus-host Disease (GvHD) Models
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Schizophrenia Model
- Depression Models
- Pain Models
-
Metabolic Disease Models
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Animal Model of Hyperuricemia
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model
- High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Methionine and Choline Deficient (MCD) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Gubra-Amylin NASH (GAN) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Model
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer (DFU) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthotopic Kidney Transplantation Model
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Model
- Peritoneal Fibrosis Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
- Otology Disease Models