Autologous Blood-Induced Intracerebral Hemorrhage (ICH) Model
Creative Bioarray has established a stable intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) model induced by autologous blood. We provide services including in vivo and in vitro testing for clients worldwide to facilitate your brilliant studies. According to your specific needs, our scientists will work with you to assist you from initial study design to final reporting and analysis of your data to provide you with reliable, reproducible results at the most favorable prices.
ICH is an extremely serious form of stroke that is impossible to treat It mostly occurs in the basal ganglia, a white matter-rich area that is especially vulnerable to mechanical stress in response to hemorrhage, resulting in hemiplegia, partial sensory impairment, ectopic blindness, and other complications. The intracerebral injection of the autologous blood model is a simple and effective technique for the production of brain parenchymal hematoma.
Our Autologous Blood-Induced Intracerebral Hemorrhage (ICH) Model
- Available Animal
Rat
- Modeling Method
Animals are immobilized in a prone position on a stereotaxic apparatus. After amputating the tail tip, blood is extracted from the resulting wound. Next, a precise hole is drilled through the right parietal bone. Carefully, a micro-syringe is inserted to a depth of 5.5 mm, targeting the right striatum. Finally, the autologous blood is gradually infused to induce the cerebral hemorrhage model. Animals in the sham group are subjected to the same procedures as the ICH mice, but no blood is injected.
- Endpoints
- Clinical score: Longa score, Bederson score
- Survival rate
- Histology analysis: H&E staining, TUNEL staining, IHC
- Cytokine analysis
- Brain water content
- qPCR or Western blot
- Other customized endpoints
Example Data
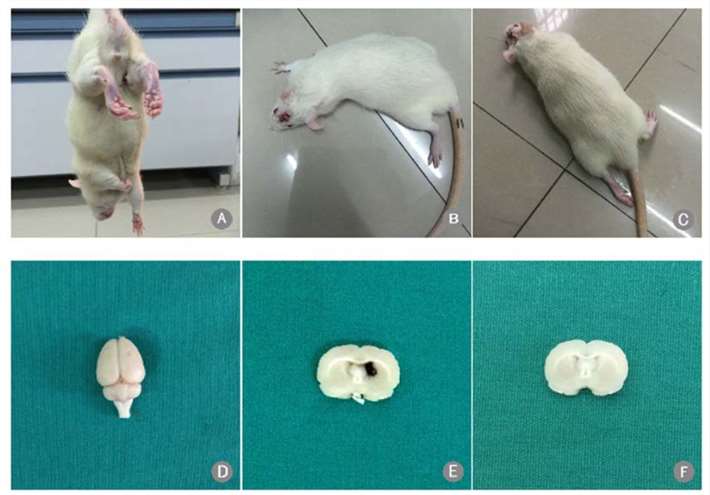 Fig. 1 Scoring of intracerebral hemorrhage model and hematoma formation. (A–C) Rats with Zea Longa scores of 1, 2, and 3, respectively; (D) gross brain specimen after autologous blood infusion; (E) hematoma following ICH; and (F) no hematoma in the sham-operated rats. (Li et al. 2020)
Fig. 1 Scoring of intracerebral hemorrhage model and hematoma formation. (A–C) Rats with Zea Longa scores of 1, 2, and 3, respectively; (D) gross brain specimen after autologous blood infusion; (E) hematoma following ICH; and (F) no hematoma in the sham-operated rats. (Li et al. 2020)
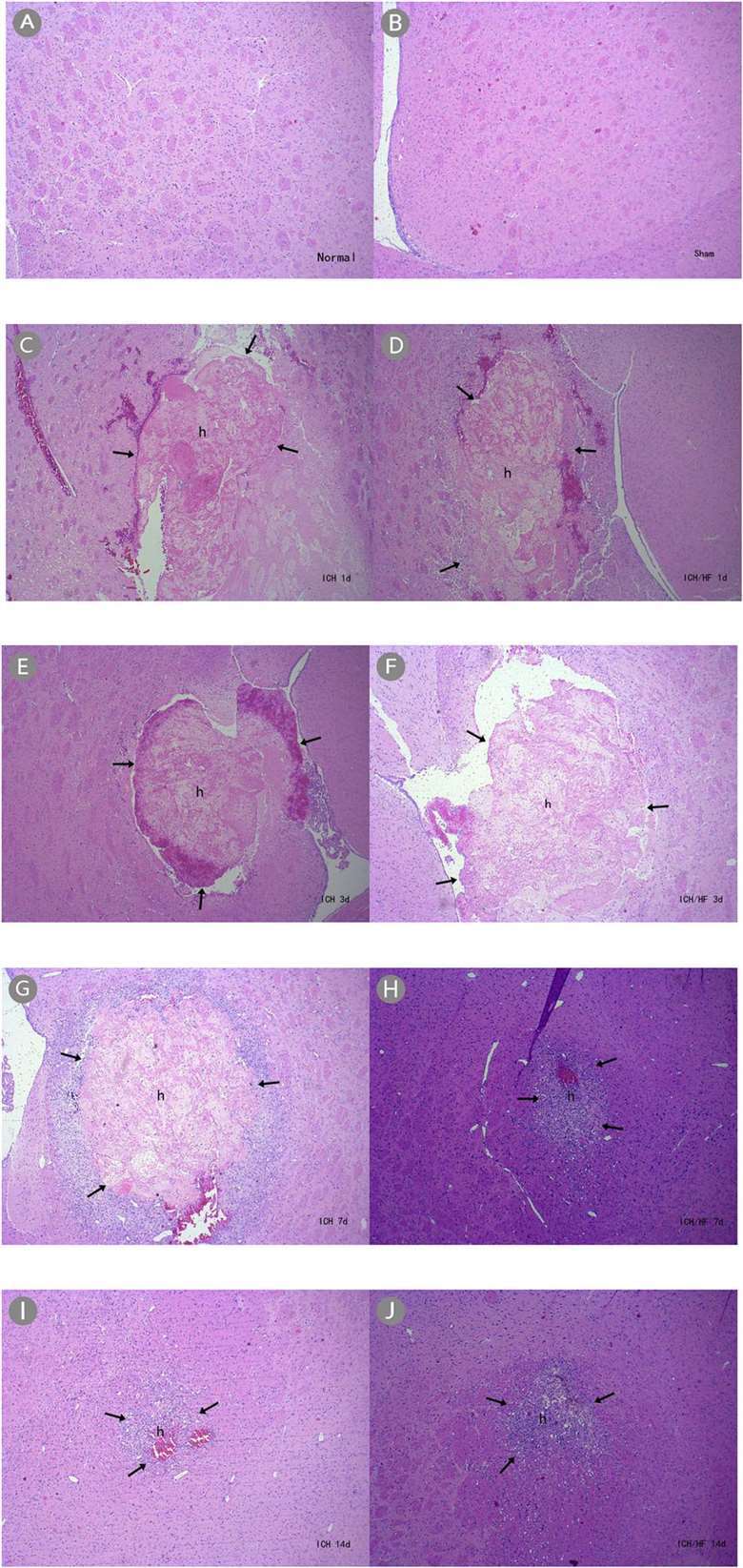 Fig. 2 H&E staining showing hematoma formation (×40). (A) Normal and (B) sham-operated groups had normal brain tissue in the basal ganglia; (C–J) ICH and ICH/HF groups had hematomas at each time point. (Li et al. 2020)
Fig. 2 H&E staining showing hematoma formation (×40). (A) Normal and (B) sham-operated groups had normal brain tissue in the basal ganglia; (C–J) ICH and ICH/HF groups had hematomas at each time point. (Li et al. 2020)
In addition, we also provide another ICH model that maybe you are interested in:
Quotation and Ordering
Creative Bioarray is delighted to offer our state-of-the-art technology and vast expertise in rodent disease models to support our clients' research and project development. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us at any time or submit an inquiry to us directly.
References
- Li, L., et al. Hydrochloride fasudil attenuates brain injury in ICH rats. Translational Neuroscience, 2020, 11(1): 75-86.
- Paiva, W.S., et al. Animal models for the study of intracranial hematomas (Review). Exp Ther Med, 2022; 25(1):20.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Oral Mucositis Model
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
- Graft-versus-host Disease (GvHD) Models
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Schizophrenia Model
- Depression Models
- Pain Models
-
Metabolic Disease Models
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Animal Model of Hyperuricemia
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model
- High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Methionine and Choline Deficient (MCD) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Gubra-Amylin NASH (GAN) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Model
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer (DFU) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthotopic Kidney Transplantation Model
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Model
- Peritoneal Fibrosis Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
- Otology Disease Models