Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
Cisplatin (cis-diamminedichloroplatinum II; CP) is used widely as an antitumor drug in the treatment of cancer. But this compound is accompanied with renal toxicity, which is a major clinical concern. To help understand mechanisms involved in the development of kidney injury, cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity model has been developed by researchers. Cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity model is essential in the investigation of underlying mechanisms of acute kidney injury. This model is well appreciated and widely used due to its simplicity. Creative Bioarray uses the cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity model for studying the mechanism of cute kidney injury and developing related therapeutic drugs.
Application and advantages
Cisplatin is the most commonly used chemotherapy drug. Due to its nephrotoxicity, cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity model is considered an ideal model for studying the early pathophysiological features of acute nephrotoxicity. With this model, you can apply your research to the following aspects:
- Study the mechanism by which statins protect against nephrotoxicity.
- Develop new compounds to protect against nephrotoxicity of cisplatin.
- Understand the cellular and molecular mechanisms of nephrotoxicity.
Available Assays provided by Creative Bioarray including
- Clinical observations
- Kidney weight
- Biochemical parameter analysis
- Serum levels examination
- Histology & immunohistochemistry
Data & Figures
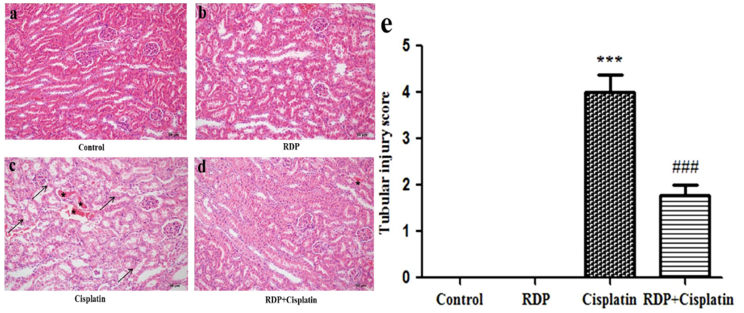 Fig. 1. RDP treatment attenuated the renal histological changes induced by cisplatin in mice: (a) control group; (b) RDP alone group; (c) cisplatin-injected group; (d) RDP plus cisplatin group. Arrows show damaged tubular cells, stars show intratubular cast formation. H&E staining. Magnification 200X. Tubular score (e). Each data points represent mean±S.E.M.
Fig. 1. RDP treatment attenuated the renal histological changes induced by cisplatin in mice: (a) control group; (b) RDP alone group; (c) cisplatin-injected group; (d) RDP plus cisplatin group. Arrows show damaged tubular cells, stars show intratubular cast formation. H&E staining. Magnification 200X. Tubular score (e). Each data points represent mean±S.E.M.
Other urological disease models are also available:
Quotation and ordering
For more details, please do not hesitate to contact us.
Reference
Tilyek A et al. The protective effects of Ribes diacanthum Pall on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2016, 178:297-306.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Oral Mucositis Model
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
- Graft-versus-host Disease (GvHD) Models
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Schizophrenia Model
- Depression Models
- Pain Models
-
Metabolic Disease Models
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Animal Model of Hyperuricemia
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model
- High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Methionine and Choline Deficient (MCD) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Gubra-Amylin NASH (GAN) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Model
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer (DFU) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthotopic Kidney Transplantation Model
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Model
- Peritoneal Fibrosis Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
- Otology Disease Models