Spatial Transcriptomics Solutions
- Service Details
- Features
- Applications
- FAQ
- Explore Other Options
Unlock Spatial Insights: Advanced Spatial Transcriptomics Services for Cutting-Edge Research
Spatial transcriptomics technology provides detailed transcriptomic data of samples with precise localization within tissue sections. By integrating these molecular insights with spatial positioning, it offers researchers a powerful way to understand the activity state of cells in their natural environment and their interactions with surrounding tissues. This approach is particularly suited for analyzing the distribution of cell types, intercellular interactions, and the spatial regulation of gene expression in complex tissues.
Our spatial transcriptomics services leverage advanced spatial barcoding–based and probe-based transcriptomic technologies to generate high-throughput gene expression data while preserving spatial context within tissue sections. By integrating next-generation sequencing with precise spatial indexing, we enable researchers to map gene expression patterns directly onto histological architecture across diverse sample types, including fresh frozen and FFPE tissues.
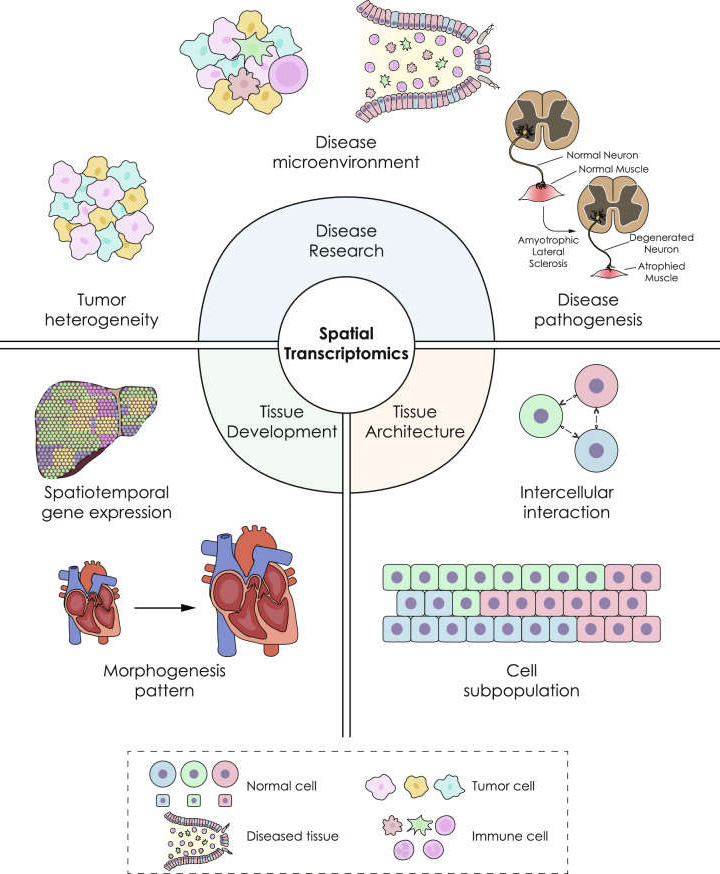 Application scenarios of spatial transcriptomics (Du J, Yang YC, et al. 2023).
Application scenarios of spatial transcriptomics (Du J, Yang YC, et al. 2023).
Our Spatial Transcriptomics Technology
Workflow
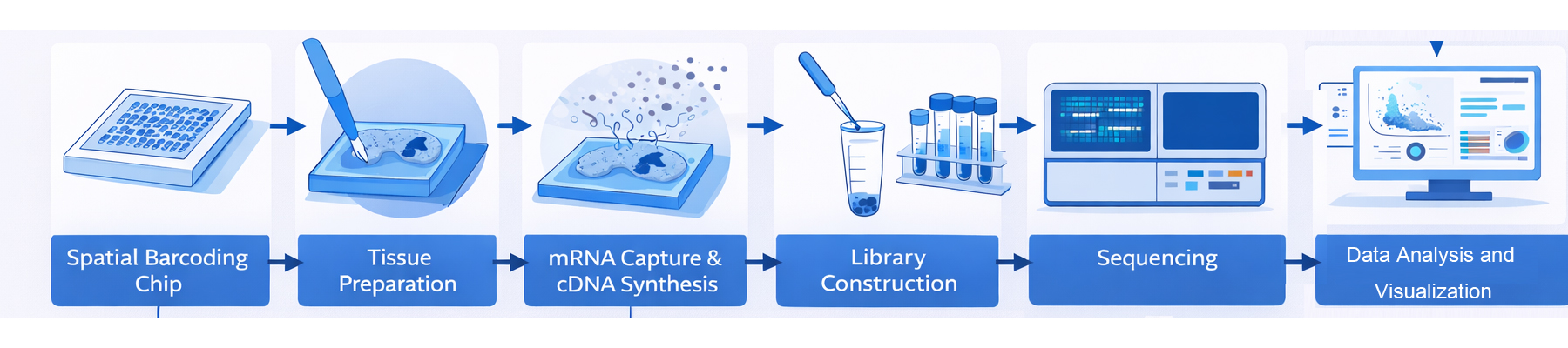
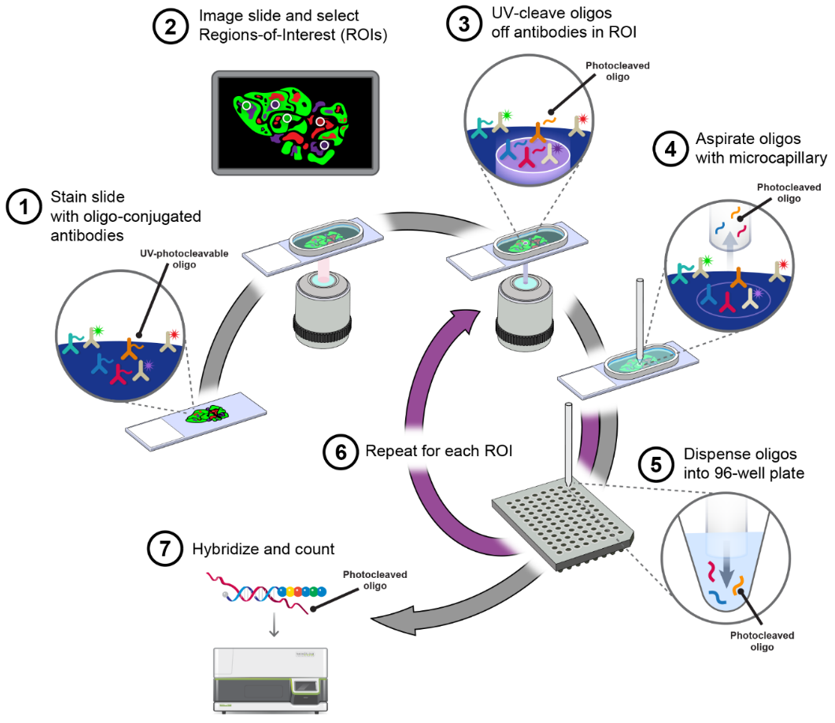
Our spatial transcriptomics service is based on a high-density spatial barcoding probe chip that enables in situ capture of mRNA directly from intact tissue sections. By assigning each transcript a unique spatial Coordinate ID (CID), this technology accurately reconstructs gene expression patterns within their native spatial context. With high throughput, ultra-high resolution, and a large field of view, it supports panoramic spatial transcriptomic analysis across tissue, cellular, subcellular, and molecular scales within a single sample.
Features
High-Resolution Detection
Leveraging advanced spatial barcoding-based transcriptomics technologies, this service delivers high-precision spatial resolution.
Comprehensive Gene Coverage
With high-throughput sequencing technology, it can detect the expression of thousands of genes within a single tissue section.
Multi-Sample Compatibility
Compatible with both fresh tissues and formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissues.
Powerful Data Analysis Tools
Offering user-friendly data analysis and visualization tools.
Scalability and Flexibility
Supports various experimental designs and data analysis needs.
Compatibility with Histological Staining
Compatible with traditional hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining or immunofluorescence (IF) staining.
What Can You Do with Our Spatial Transcriptomics Solutions?
- Oncology: Tumor microenvironment, tumor heterogeneity, cancer progression and metastasis mechanisms.
- Comprehensive Gene Coverage: With high-throughput sequencing technology, it can detect the expression of thousands of genes within a single tissue section.
- Neuroscience: Brain mapping, nervous system development, neurodegenerative diseases.
- Immunology: Immune cell infiltration, immune microenvironment, allergies and autoimmune diseases, infectious diseases.
- Pathology: Pathological slides analysis, disease biomarker discovery.
FAQ
1. What is spatial transcriptomics, and why is it important?
Spatial transcriptomics is a technology that describes expression profiling of cells with spatial context. Which allows scientists to see differences in expression across organs, tissues and diseases by looking at transcripts at multiple spatial sites within a tissue. By combining conventional single-cell sequencing technologies with in situ technologies and other omics approaches, spatial transcriptomics enables the study of cellular heterogeneity with spatial resolution. It provides a more specific research agenda for disease research and contributes to disease biology and targeted therapeutic development.
2. What should be done with frozen embedded samples for spatial transcriptomics?
There are two common methods: pre-freezing and embedding or simultaneous freezing and embedding. Pre-freezing process is a quick, cold immersion in isopentane with a pre-cooled forceps, till the tissue is completely frozen, and then embedding in OCT compound. The simultaneous approach consists of depositing new tissue in a petri dish, adding room temperature OCT embedding medium, so that an OCT coat surrounds the tissue, and placing it in an OCT embedding mould and freezing on dry ice or in isopentane.
3. Can samples be directly frozen in liquid nitrogen?
Direct freezing in liquid nitrogen is not recommended, as the boiling process might cause cavitation around the tissue, leading to asynchronous cooling in different regions, potentially altering the internal structure or even causing tissue fragmentation.
4. How does the Spatial technology achieve spatial localization of gene expression?
The Visium Spatial slides are equipped with a high-density array of oligonucleotide probes, each carrying a unique spatial barcode. After permeabilization, mRNA is released and binds to the probes, with the resulting transcript information acquired during sequencing carrying spatial barcode data. Software analysis then precisely matches gene expression data with the spatial location on the tissue section.
5. What is the role of pre-treatment steps for FFPE tissues?
Dewaxing removes paraffin to re-expose the tissue, while antigen retrieval restores antigen epitopes masked during the fixation process, thereby enhancing mRNA accessibility. This facilitates the efficient binding of spatial barcode probes and accurate gene expression capture.
6. How can spatial transcriptomics data be maximally utilized for analysis?
For a biological perspective, integrate spatial transcriptomics data with other data types like single-cell RNA sequencing, whole-genome sequencing, tissue histology, and immunofluorescence staining to give you the full biological picture. Dedicated software and bioinformatics tools can also be used to visualize and interpret spatial transcriptomics data.
Reference
- Du J, Yang YC, et al. Advances in spatial transcriptomics and related data analysis strategies. J Transl Med. 2023. 21(1):330.
Related Services
Explore Other Options