Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
Creative Bioarray offers in vivo pharmacology studies using a well-established animal model for adenine-induced chronic kidney disease (CKD). This model has been validated and is valuable for evaluating the potential renal protection of test compounds quickly. Our team of scientists will collaborate with you to meet your specific needs, assisting with the initial study design, as well as the final reporting and analysis of your data.
CKD is a progressive condition that unfortunately has no cure and is associated with high levels of morbidity and mortality. The main causes of CKD include diabetes, hypertension, obesity, and chronic inflammation. In CKD, there is a buildup of fibrosis, which is a repair process triggered by various stimuli and factors, leading to excessive accumulation of connective tissue components. Currently, there is no universally accepted systematic approach for screening and treating CKD, highlighting the importance of understanding the underlying pathological mechanisms. Animal models of CKD have played a crucial role in advancing our knowledge of kidney disease development and have provided valuable platforms for testing interventions and assessing the effectiveness of compounds or medications.
Our Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Available Animal
Rat
- Modeling Method
After acclimation, the rats are randomized into a model group and a control group. The model group receives a daily oral gavage of adenine for 21 days, while the control group receives a daily oral gavage of saline for the same duration.
- Endpoints
- Blood biochemistry analysis: phosphate, urea, creatinine
- Histology analysis
- Blood pressure
- qPCR or Western blot
- Other customized endpoints
Example Data
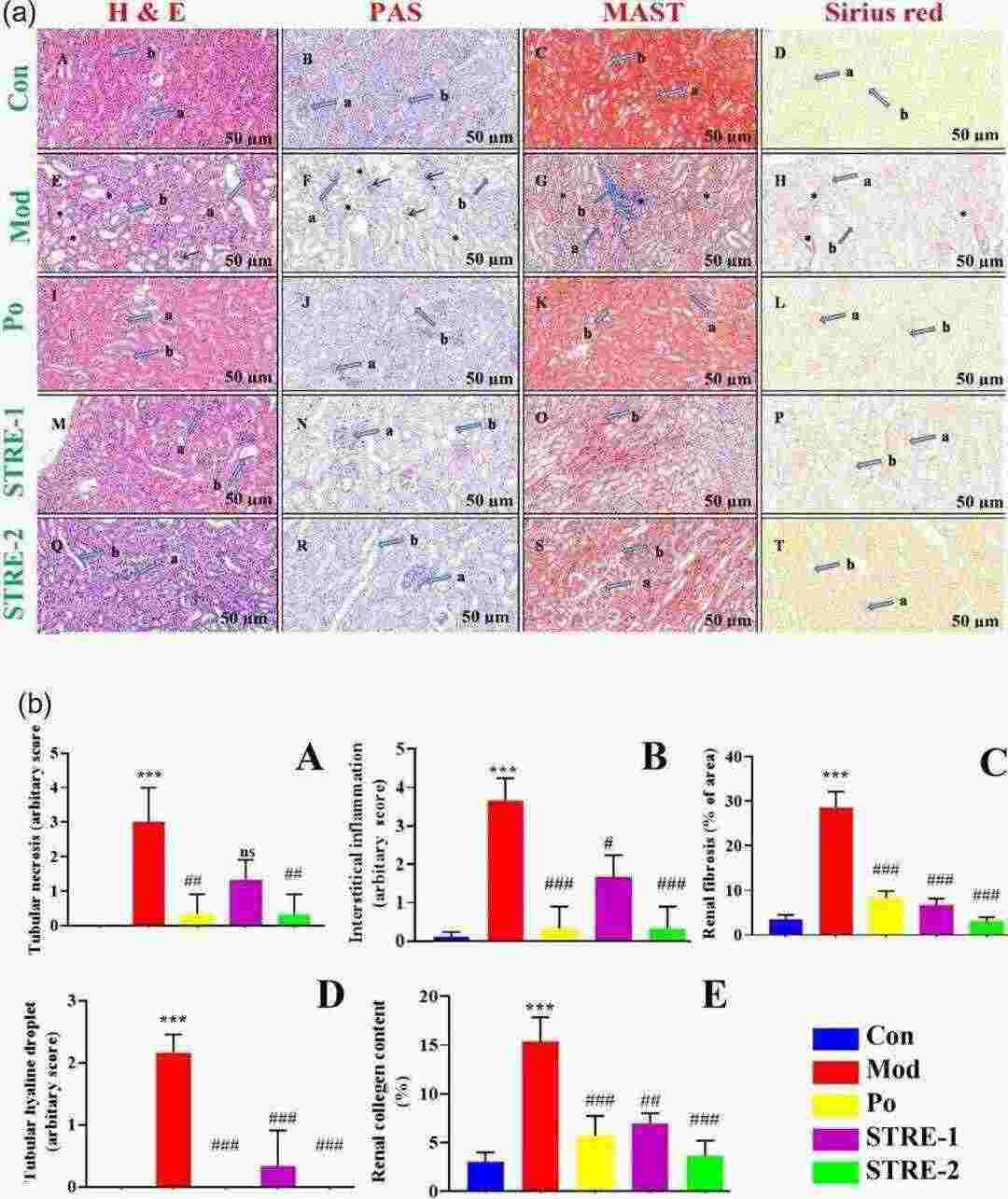 Fig. 1 ab. Effect of Stevia residue extract on renal histology in adenine-induced CKD mice revealed by hematoxylin and eosin (H & E), Periodic acid–Schiff (PAS), Masson's trichrome (MAST), and Sirius Red staining. (Mehmood et al. 2020)
Fig. 1 ab. Effect of Stevia residue extract on renal histology in adenine-induced CKD mice revealed by hematoxylin and eosin (H & E), Periodic acid–Schiff (PAS), Masson's trichrome (MAST), and Sirius Red staining. (Mehmood et al. 2020)
Quotation and Ordering
Creative Bioarray is a leading Contract Research Organization (CRO) that specializes in preclinical studies. Our extensive expertise has enabled us to develop a diverse array of animal models specifically designed to evaluate novel drugs and therapeutic strategies for urology diseases. Our unwavering commitment to quality guarantees that you receive dependable services meticulously customized to your unique research needs.
References
- Yang, Q., et al. Adenine-induced animal model of chronic kidney disease: current applications and future perspectives. Renal Failure, 2024, 46(1): 2336128.
- Mehmood, A., et al. Renoprotective effect of stevia residue extract on adenine-induced chronic kidney disease in mice. Journal of functional foods, 2020, 72: 103983.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Oral Mucositis Model
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
- Graft-versus-host Disease (GvHD) Models
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Schizophrenia Model
- Depression Models
- Pain Models
-
Metabolic Disease Models
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Animal Model of Hyperuricemia
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model
- High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Methionine and Choline Deficient (MCD) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Gubra-Amylin NASH (GAN) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Model
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer (DFU) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthotopic Kidney Transplantation Model
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Model
- Peritoneal Fibrosis Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
- Otology Disease Models