Kidney Stone Model
Creative Bioarray has successfully developed a wide range of experimental models for kidney diseases. One such model we offer is designed to simulate human kidney stones. We take great pride in providing thoroughly validated and dependable models for testing compounds. This ensures that any data obtained from these models is not only biologically pertinent, but also holds clinical significance. Our unwavering dedication to excellence guarantees the dependability and relevance of the data for your research requirements.
Kidney stones, which affect around 8% of the population, are primarily composed of calcium oxalate (80%), with the rest being uric acid, struvite, and other rarer types. Despite advancements in treatments such as ureteroscopy, shock wave lithotripsy, and percutaneous nephrolithotomy, recurrence rates remain high, and pharmacological options such as citrate and thiazide diuretics have limitations. To address this, various in vitro and in vivo urolithiasis models have been developed to study the pathogenesis of calcium oxalate stones and to test new therapies. Our kidney stone model is designed to facilitate a deeper understanding of stone formation and to accelerate the development of more effective treatments. We welcome your inquiry to discover how our model can support your research and contribute to advancements in urology.
Our Kidney Stone Model
- Available Animal
Rat
- Modeling Method
Following the acclimation period, rats in the model group receive ethylene glycol via their drinking water and are administered ammonium chloride solution intragastrically daily for a duration of six weeks.
- Endpoints
- Clinical observation of kidney
- Serum analysis: urea, uric acid, creatinine, calcium, and phosphorus
- Micro CT of kidney
- Histology analysis
- qPCR or Western Blot
- Other customized endpoints
Example Data
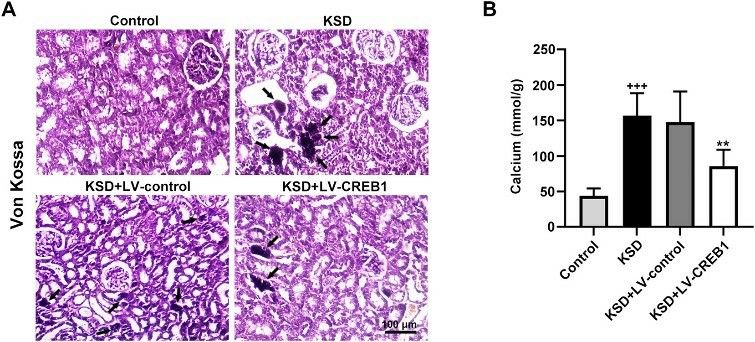 Fig. 1 Upregulation of CREB1 reduced crystals deposition in the kidney of KSD rats. (A) Von Kossa staining for detecting crystals deposition in renal tissue of the rats. (B) The level of calcium in renal tissue of the rats. (Yu et al. 2021)
Fig. 1 Upregulation of CREB1 reduced crystals deposition in the kidney of KSD rats. (A) Von Kossa staining for detecting crystals deposition in renal tissue of the rats. (B) The level of calcium in renal tissue of the rats. (Yu et al. 2021)
Quotation and Ordering
At Creative Bioarray, our team of seasoned scientists is ready to collaborate with you to choose the most appropriate in vivo model for your research needs. We also provide assistance with study design, implementation, and data analysis to ensure the success of your project. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us at any time or submit an inquiry to us directly.
References
- Khan, A. In vitro and in vivo models for the study of urolithiasis. Urologia Journal. 2018;85(4):145-149.
- Yu, L., et al. CREB1 protects against the renal injury in a rat model of kidney stone disease and calcium oxalate monohydrate crystals-induced injury in NRK-52E cells. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 2021, 413: 115394.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Oral Mucositis Model
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
- Graft-versus-host Disease (GvHD) Models
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Schizophrenia Model
- Depression Models
- Pain Models
-
Metabolic Disease Models
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Animal Model of Hyperuricemia
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model
- High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Methionine and Choline Deficient (MCD) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Gubra-Amylin NASH (GAN) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Model
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer (DFU) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthotopic Kidney Transplantation Model
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Model
- Peritoneal Fibrosis Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
- Otology Disease Models