Spinal Nerve Ligation (SNL) Model
Creative Bioarray is a pioneering company that specializes in providing cutting-edge preclinical models for pain research. We have established the spinal nerve ligation (SNL) model, a widely recognized neuropathic pain model that simulates chronic pain conditions in rodents. We complement this model with a comprehensive suite of outcome measures, including behavioral tests and biomarker analyses. These tools enable researchers to thoroughly investigate potential drug candidates.
SNL, a well-established model of neuropathic pain, is induced by tightly ligating spinal nerves. In this peripheral neuropathy model, the L5 and L6 spinal nerves are isolated and can be tightly ligated using surgical silk. This leads to axonal degeneration, affecting all types of axons approximately equally. Subsequently, pronounced mechanical allodynia ensues, accompanied by spontaneous pain behaviors and cold allodynia, persisting for months without recovery. This model provides a controlled environment for researchers to explore the underlying mechanisms of pain and to evaluate the efficacy of potential therapeutic interventions aimed at alleviating this debilitating condition.
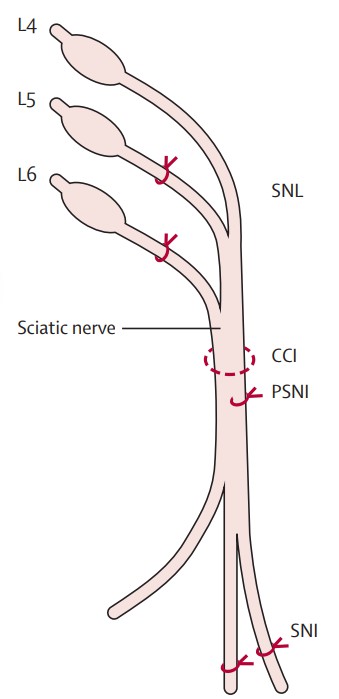 Fig. 1 Traumatic nerve injury models used in rodents. (Calvo et al. 2012)
Fig. 1 Traumatic nerve injury models used in rodents. (Calvo et al. 2012)
Our Spinal Nerve Ligation (SNL) Model
- Available Animal
- Rat
- Mouse
- Modeling Method
After anesthetization, a precise dorsal midline incision is executed to reveal the vertebrae. The L5 and L6 spinal nerves are then carefully dissected free from the encasing tissue and firmly ligated using a silk suture while L4 is left untouched. This method can induce long-lasting mechanical and cold allodynia while minimizing motor impairments.
- Endpoints
- Behavioral tests: Von Frey test, Cold plate test, Hot plate test etc.
- Body weight
- Histology analysis
- qPCR or Western blot
- Other customized endpoints
Example Data
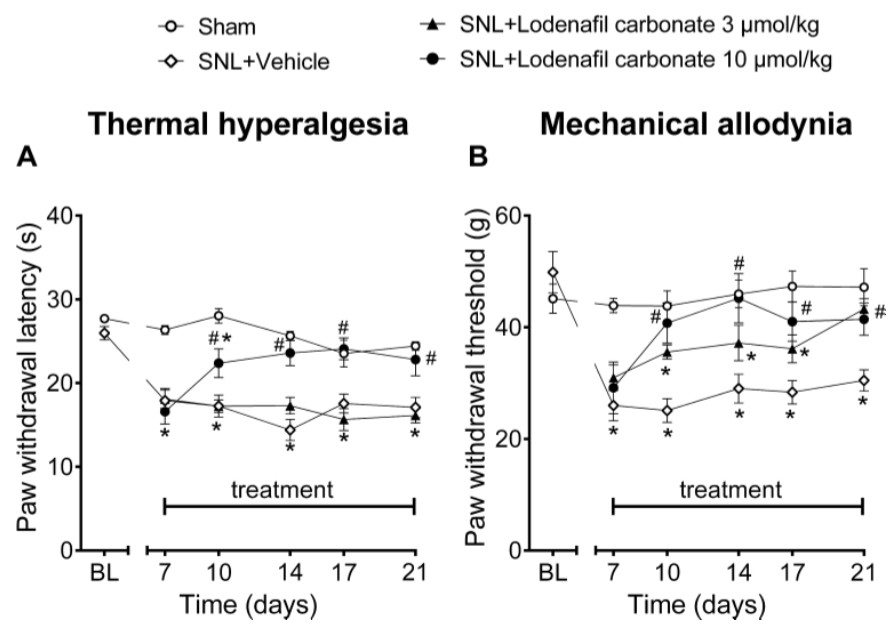 Fig. 2 Thermal latencies (A) and mechanical thresholds (B) in the ipsilateral hind paw before and after oral treatment of vehicle or lodenafil carbonate (3, 10 μmol/kg) in SNL rats. (Vieira et al. 2021)
Fig. 2 Thermal latencies (A) and mechanical thresholds (B) in the ipsilateral hind paw before and after oral treatment of vehicle or lodenafil carbonate (3, 10 μmol/kg) in SNL rats. (Vieira et al. 2021)
In addition, we also provide other neuropathic pain models that maybe you are interested in:
- Diabetes-Induced Neuropathic Pain Model
- Chemotherapy-Induced Neuropathic Pain Model
- Chronic Constriction Injury (CCI) Model
- Spared Nerve Injury (SNI) Model
- Partial Sciatic Nerve Ligation (PSL/PSNL) Model
Quotation and Ordering
Creative Bioarray offers an extensive array of preclinical services at the most competitive prices. We're eager to leverage our advanced facilities and extensive expertise to enhance the effectiveness of your innovative research and facilitate the progression of your pharmaceuticals towards clinical trials. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us at any time or submit an inquiry to us directly.
References
- Vieira, M.C., et al. Antinociceptive Effect of Lodenafil Carbonate in Rodent Models of Inflammatory Pain and Spinal Nerve Ligation-Induced Neuropathic Pain. Journal of pain research, 2021: 857-866.
- Calvo, M., et al. The role of the immune system in the generation of neuropathic pain. Lancet Neurol. 2012;11(7):629-642.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Oral Mucositis Model
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
- Graft-versus-host Disease (GvHD) Models
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Schizophrenia Model
- Depression Models
- Pain Models
-
Metabolic Disease Models
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Animal Model of Hyperuricemia
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model
- High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Methionine and Choline Deficient (MCD) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Gubra-Amylin NASH (GAN) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Model
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer (DFU) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthotopic Kidney Transplantation Model
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Model
- Peritoneal Fibrosis Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
- Otology Disease Models