Cecum Ligation and Puncture (CLP)-Induced Sepsis Model
Creative Bioarray, a prominent contract research organization (CRO), offers a stable cecum ligation and puncture (CLP)-induced sepsis model for clients to investigate the mechanisms of sepsis or evaluate the efficacy of their drug candidates. Our high-quality service ensures that our clients can obtain dependable and precise results to accelerate their research.
Sepsis, a potentially fatal condition triggered by infections due to an imbalance between inflammation and immunosuppression, remains a significant public health issue, affecting approximately 18 million individuals globally each year, with mortality rates ranging from 28 to 50%. Notably, there are currently no targeted pharmacotherapies available for the treatment of sepsis. Therefore, a profound understanding of the pathogenic mechanisms underlying this disease is urgently needed to facilitate the development of novel and more effective therapeutic strategies. To explore the pathophysiology of sepsis, various animal models have been established. Among them, the sepsis model induced by CLP is the most commonly used, as it closely mimics the progression and characteristics of human sepsis.
Our Cecum Ligation and Puncture (CLP)-Induced Sepsis Model
- Available Animal
Rat
Mouse - Modeling Method
Step 1: After anesthetization, animals are secured on an operating table, and undergo hair removal and disinfection.
Step 2: A longitudinal incision is made in the appropriate area, followed by sequential incisions in the cortical and muscle layers to expose the caecum.
Step 3: Meticulously, the caecum is extracted using tweezers and secured with a surgical line. Then use a syringe needle to create a puncture in the ligated region, followed by gentle squeezing of the caecum to expel a small quantity of fecal matter.
Step 4: The ligated and punctured caecum is repositioned within the abdominal cavity, and the muscle and skin layers are sequentially sutured using a surgical line.
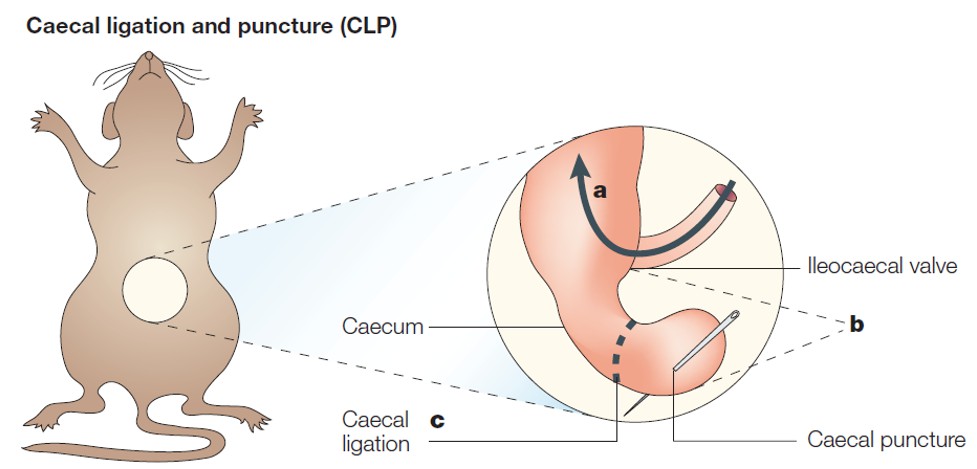 Fig. 1 CLP-induced sepsis model
Fig. 1 CLP-induced sepsis model
- Endpoints
- Survival rate
- Cytokine analysis: IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6, etc.
- Histology analysis: H&E staining
- Serum analysis: creatinine kinase, BUN, ALT, AST, etc.
- qPCR or Western Blot
- Other customized endpoints: available upon request.
Example Data
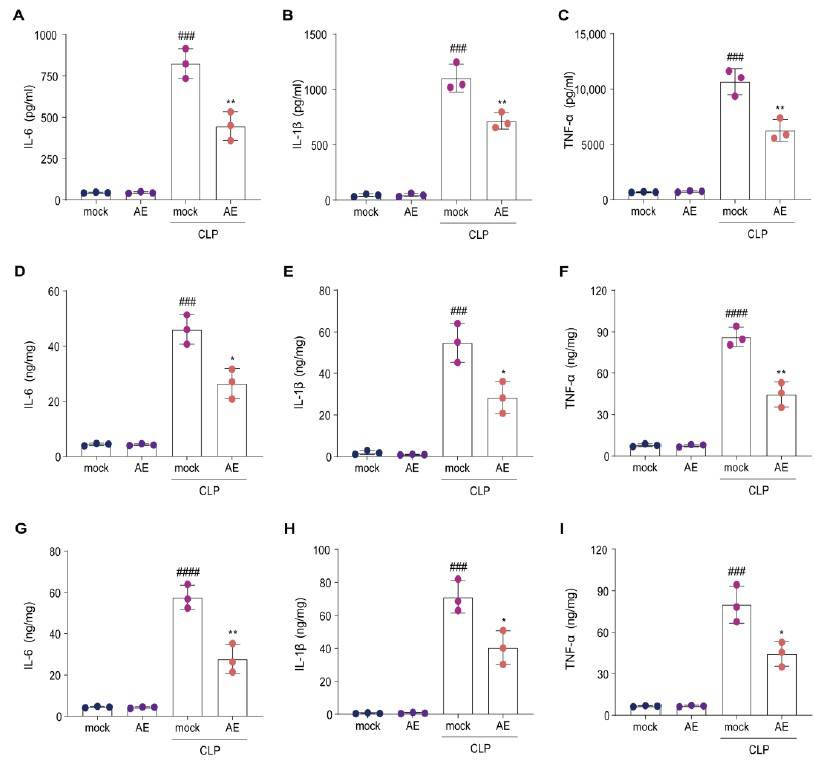 Fig. 2 Alterations in inflammatory cytokines in mice afflicted with sepsis induced by CLP subsequent to treatment with AE. The levels of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-β in (A–C) the serum, (D–F) lung, (G–I) liver
Fig. 2 Alterations in inflammatory cytokines in mice afflicted with sepsis induced by CLP subsequent to treatment with AE. The levels of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-β in (A–C) the serum, (D–F) lung, (G–I) liver
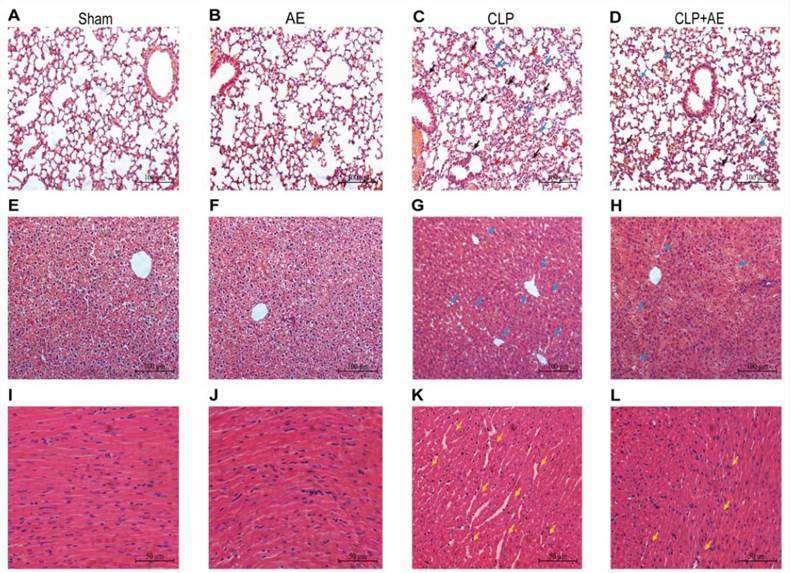 Fig. 3. AE's protective effects against lung, liver, and heart tissue lesions in mice with CLP-induced sepsis. Representative microscopic images of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of (A–D) lung, (E–H) liver, and (I–L) heart tissue from mice with CLP-induced sepsis
Fig. 3. AE's protective effects against lung, liver, and heart tissue lesions in mice with CLP-induced sepsis. Representative microscopic images of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of (A–D) lung, (E–H) liver, and (I–L) heart tissue from mice with CLP-induced sepsis
In addition, we also provide other sepsis models that maybe you are interested in:
- Colon Ascendens Stent Peritonitis (CASP)-Induced Sepsis Model
- Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Sepsis Model
Quotation and Ordering
Creative Bioarray has a group of professional experts who not only specialize in animal surgery to establish an optimal animal model but are also experienced in data interpretation. With our extensive experience and state-of-the-art techniques, we are confident in delivering top-notch services tailored to your specific research requirements. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us at any time or submit an inquiry to us directly.
References
- Buras, J., et al. Animal Models of sepsis: setting the stage. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2005, 4: 854-865.
- Su, J., et al. Aloe-Emodin Ameliorates Cecal Ligation and Puncture-Induced Sepsis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(15): 11972.