P388
Cat.No.: CSC-C6291J
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
Morphology: lymphoblast-like
Culture Properties: Suspension cells
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Store in liquid nitrogen.
The P388 cell line originates from lymphoma cells in DBA/2 mice which develop into lymphocytic leukemia through exposure to 3-methylcholanthrene (3-MC). Researchers established the cell line by injecting the cells into the mouse peritoneal cavity where they transformed into an ascites form. Therefore, P388 cells come from peripheral blood or ascites tissues and belong to the lymphoma category.
The P388 cell line demonstrates multiple biological functions. Firstly, P388 cells can trigger T-cell proliferation while displaying Ia antigens during mixed lymphocyte reactions. Secondly, P388 cells demonstrate remarkable value for researching immune regulation mechanisms and tumor biology dynamics. For example, researchers use P388 cells to study immune cell interactions and cytokine production as well as anti-tumor drug action mechanisms.
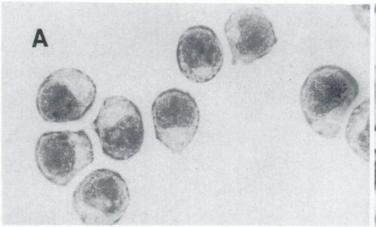 Fig. 1. Light microscopic of P388 cells (Ling Y, Priebe W, et al., 1993).
Fig. 1. Light microscopic of P388 cells (Ling Y, Priebe W, et al., 1993).
Effect of 2-DG and Tm on Cell Proliferation
The Warburg effect describes cancer cells' dependence on glycolysis for energy production under normal oxygen levels. Targeting cancer cells' dependence on glycolysis presents an effective approach for cancer treatment strategies. The chemotherapy agent idarubicin (IDA), an anthracycline derivative, remains a standard treatment for leukemia but encounters therapeutic resistance challenges. Research demonstrates that 2-Deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG) could help overcome cancer resistance by attacking the modified metabolic pathways of cancer cells.
Matsuo et al. examined the cytotoxic effects of 2-DG on IDA-resistant P388 leukemia cells using cell viability assays and evaluates the combined effects of 2-DG and IDA on cell death. They compared the cytotoxicity of the glycolysis inhibitor 2-DG on P388 and P388/IDA cell lines. The IC50 of 2-DG on P388 was higher than the tested concentrations (>500 µM), while on P388/IDA cells was 392.6±41.1 µM (Fig. 1A). 2-DG both suppressed glycolysis and induced ER stress. To examine the impact of ER stress on the cells, the effect of Tm was assessed. The IC50 of Tm on P388 and P388/IDA cells was 9.2±1.6 and 16.8±2.4 ng/ml (P<0.05), respectively (Fig. 1B). The effect of Tm on P388 cells was about 1.8-fold higher than that in P388/IDA cells.
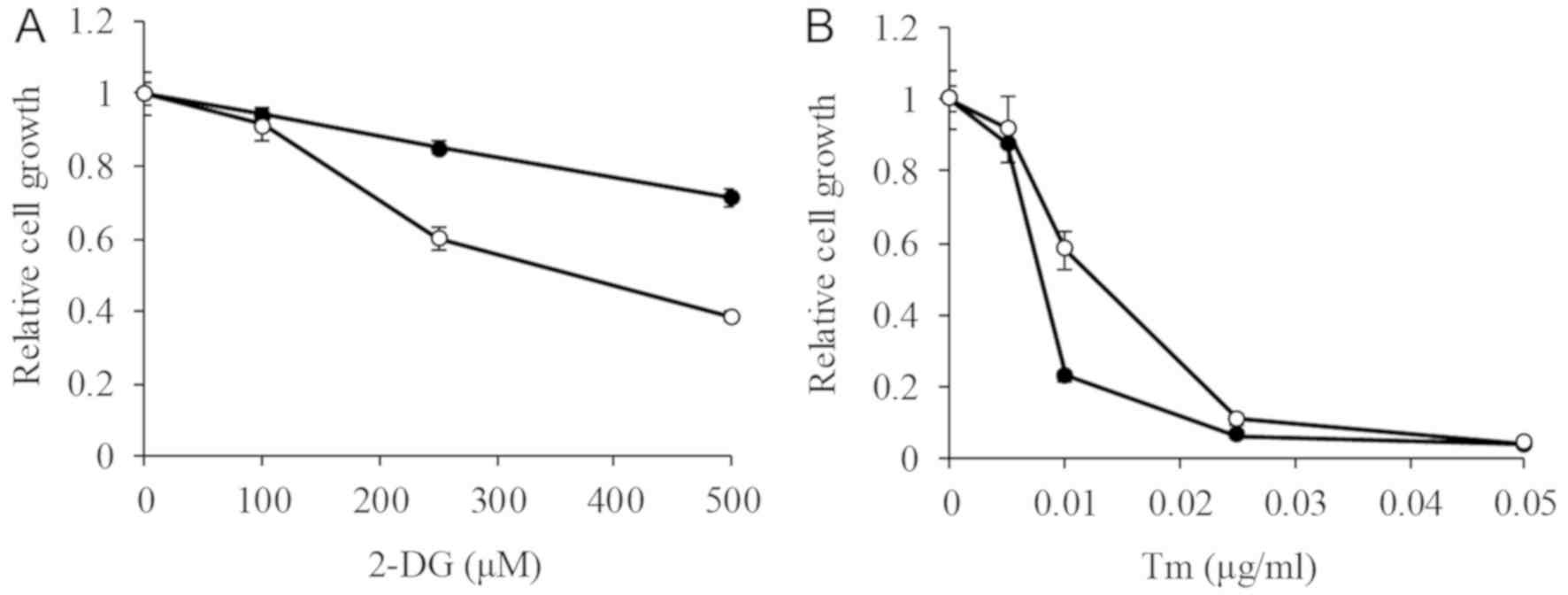 Fig. 1. - 2-DG and Tm cytotoxicity in P388 and P388/IDA cells (Matsuo T, Konya Y, et al., 2020).
Fig. 1. - 2-DG and Tm cytotoxicity in P388 and P388/IDA cells (Matsuo T, Konya Y, et al., 2020).
trans-N-benzyl Hydroxyl Cinnamamide Based Compounds from Cinnamic Acids and Cytotoxicity Study
Hydroxycinnamic acids and their derivatives are recognized for their antioxidant, antiviral, and anticancer properties. Ester and amide derivatives often show higher bioactivity than free acids. In this study, three hydroxycinnamamide compounds (5a, 5b, and 5c) were synthesized from p-coumaric, caffeic, and ferulic acids using benzylamine through acetylation, chlorination, amidation, and deacetylation steps. The cytotoxicity was tested against P388 murine leukemia cells using the MTT method.
Figure 2 shows the cytotoxic activity of compounds 5a–c. The results indicate that substituents in the phenyl ring of hydroxycinnamic moieties affect activity. Previously, caffeamide compounds exhibited higher cytotoxicity than coumaramide analogues due to more phenolic groups. However, in this study, 5a and 5c showed higher cytotoxic activity than 5b, possibly because 5a and 5c, with lower deprotonation states, can penetrate cells more effectively. Comparing the IC50 values of 5a and 5b to N-(o-tolyl) analogues suggests that both hydroxycinnamic and amine moieties are crucial for cytotoxicity against P388 murine leukemia cells. Notably, N-(o-tolyl)caffeamide exhibited strong cytotoxic activity with an IC50 of 0.91 µg/mL, contrasting with 5b. Additionally, 5a and 5c differ only by a methoxy group on C-8 in 5c, which forms an intramolecular hydrogen bond, reducing its ability to release radical hydrogen and lowering its cytotoxic activity compared to 5a (Fig. 2).
 Fig. 2. The cytotoxicity of synthesized compounds against leukemia murine P388 cell (Zenta F, Seokamto N H, et al., 2022).
Fig. 2. The cytotoxicity of synthesized compounds against leukemia murine P388 cell (Zenta F, Seokamto N H, et al., 2022).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells