Dibutyltin Dichloride (DBTC)-Induced Pancreatitis Model
At Creative Bioarray, we have accumulated extensive knowledge and expertise in conducting pancreatitis studies. Our team of experts has established a highly effective pancreatitis model induced by dibutyltin dichloride (DBTC), which enables us to evaluate the efficacy of test compounds in treating pancreatitis. With our advanced model and state-of-the-art facilities, we are committed to providing our clients with accurate and reliable results for their research projects related to pancreatitis.
DBTC is a kind of fat-soluble substance, by the liver, and gallbladder drainage to the pancreatic duct, causing cell necrosis and epithelial hyperplasia of the pancreatic duct, and obstruction of the pancreatic duct. DBTC causes CP in rats via a single intravenous injection. DBTC induces acute pancreatic inflammation within 24 hours, which progresses to chronic inflammation in a week, and then to progressive fibrotic lesions over the following 2 months, with chronic and acute inflammation (mediated by T cells and macrophages). This model has become widely used in research on the pathogenesis of pancreatitis and drug efficacy analysis due to its low modeling cost and simple methodology.
Our Dibutyltin Dichloride (DBTC) Induced Pancreatitis Model
- Animal Available
Rat - Modeling Method
At Creative Bioarray, we induce the pancreatitis model by tail vein injection of DBTC. - Group Setting
- Control group
- Model group
- Three dose groups of test compounds
- Endpoints
- Images of pancreas
- Body weight
- Food intake
- Histology analysis: H&E staining, Sirius red staining
- Cytokine analysis: TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, etc.
- Serum analysis: Amylase, Lipase, etc.
- qPCR and Western Blot
- Other customized endpoints: available upon request
Example Data
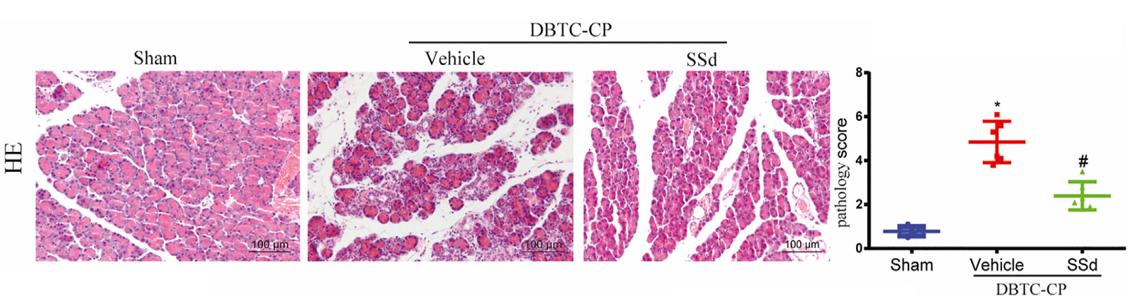 Fig. 1 The pathological score of H and E staining (original magnification, ×200)
Fig. 1 The pathological score of H and E staining (original magnification, ×200)
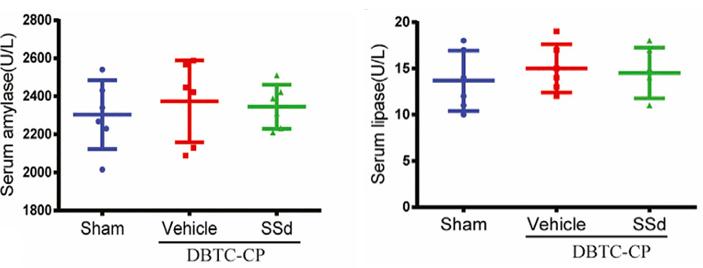 Fig. 2 Serum amylase levels and lipase levels
Fig. 2 Serum amylase levels and lipase levels
Additionally, we also offering other pancreatitis models maybe you interested:
Quotation and Ordering
Creative Bioarray, a trusted provider of disease models, is dedicated to providing guidance for your research. Our team of specialists can work with you to custom a detailed study design to meet your specific needs. If you are interested in our services, please do not hesitate to contact us at any time or submit an inquiry to us directly.
Reference
- Li, C., et al. Saikosaponin D attenuates pancreatic injury through suppressing the apoptosis of acinar cell via modulation of the MAPK signaling pathway. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2021, 12: 735079.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Oral Mucositis Model
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
- Graft-versus-host Disease (GvHD) Models
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Schizophrenia Model
- Depression Models
- Pain Models
-
Metabolic Disease Models
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Animal Model of Hyperuricemia
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model
- High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Methionine and Choline Deficient (MCD) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Gubra-Amylin NASH (GAN) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Model
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer (DFU) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthotopic Kidney Transplantation Model
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Model
- Peritoneal Fibrosis Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
- Otology Disease Models