Hepatotoxicity
Drug-induced liver injury (DILI), or hepatotoxicity, is a significant safety liability in both early discovery and clinical development. More than 1,000 drugs, herbal products, and dietary supplements have been implicated in hepatotoxicity, and DILI represents one of the leading causes of acute liver failure in clinical settings. Concerns around liver safety have also resulted in numerous FDA black box warnings and remain a major factor contributing to delays, dose adjustments, or termination of drug development programs.
DILI can arise from intrinsic toxicity, idiosyncratic reactions, or indirect injury driven by reactive metabolites, immune activation, mitochondrial dysfunction, or bile acid transporter disruption. These processes can trigger hepatocyte apoptosis, necrosis, or cholestasis, ultimately compromising liver function.
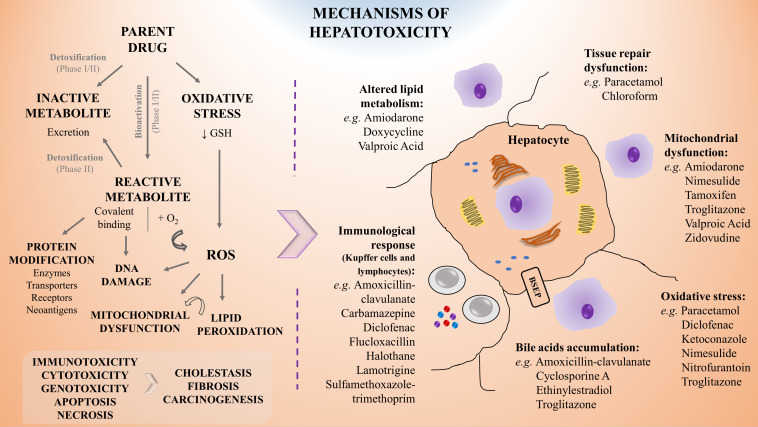 Fig. 1. The mechanisms of hepatotoxicity including examples of associated drugs (Serras AS, Rodrigues JS, et al. 2021).
Fig. 1. The mechanisms of hepatotoxicity including examples of associated drugs (Serras AS, Rodrigues JS, et al. 2021).
Given its complex mechanisms and high clinical relevance, early and accurate hepatotoxicity assessment is essential. By leveraging human-relevant models and mechanistic assays, Creative Bioarray provides sensitive, translational insights into liver safety risks, enabling better decision-making earlier in the development pipeline and effectively mitigating risk.
Comparison of Liver Toxicity Models
| 2D Hepatocytes | 3D Co-culture Models | Animal Models | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Features | Monolayer primary cells or cell lines | Multi-cellular liver microtissues | Rodents or NHPs with intact systemic physiology |
| Advantages | Low cost, high-throughput, easy handling | Improved metabolic activity, long-term stability, better mimic in vivo responses | Whole-body context, captures ADME & immune responses, regulatory acceptance |
| Limitations | Short-lived function, limited metabolism, low physiological relevance | Higher cost, lower throughput, more complex assays | Species differences, poor prediction of idiosyncratic DILI, costly, ethical constraints |
| Applications | Early screening, metabolism & mechanism studies | Chronic toxicity, mechanistic DILI, fibrosis & inflammation | Regulatory tox, PK/PD, systemic toxicity |
Our High-quality Solutions for Hepatotoxicity Testing
Comprehensive Models for Human-Relevant Toxicity Evaluation
We provide a cutting-edge, multi-tiered approach to liver toxicity assessment, integrating 2D in vitro assays, advanced 3D hepatic models, and in vivo systemic toxicity studies in a stepwise and translational manner. This human-relevant platform delivers predictive and mechanistic insights to support informed decision-making throughout the drug development pipeline.
Cytochrome P450 (CYP) and Mechanism-Based In Vitro Assays
Cytochrome P450–mediated metabolism represents a central component of hepatotoxicity evaluation. We offer a comprehensive panel of mechanism-focused in vitro assays to assess metabolism-related liver liabilities, including:
- Cytochrome P450 inhibition and induction profiling
- Phospholipidosis assessment (high-content imaging–based)
- Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) activation
- Pregnane X receptor (PXR) activation
- Drug-induced CYP induction potential
These in vitro metabolism platforms enable early evaluation of drug biotransformation and represent a crucial first step for identifying reactive metabolites and predicting potential drug–drug interaction (DDI) risks.
Our 2D hepatocyte platforms utilize HepG2 cells and primary human hepatocytes to support rapid, cost-effective screening strategies. These models are well suited for:
- Early-stage, high-throughput cytotoxicity assessment
- Viability-based and high-content, multi-parameter analysis
- Evaluation of apoptosis, mitochondrial dysfunction, and enzyme induction
2D systems provide an efficient first-pass filter to identify compounds with overt hepatocellular liabilities.
We offer advanced 3D hepatocyte culture systems derived from multiple species, designed to more closely mimic the structural and functional complexity of the liver in vivo. Compared with conventional 2D cultures, these models:
- Recapitulate in vivo-like architecture and cell–cell interactions
- Support long-term and repeated-dose exposure studies
- Exhibit significantly enhanced metabolic competence and functional stability
Our proprietary 3D liver microtissue platform has demonstrated >90% accuracy in distinguishing hepatotoxic compounds from non-toxic controls in a validation panel of 50 known DILI and non-DILI drugs, highlighting its strong translational relevance.
In Vivo Toxicity
In vivo studies are conducted to evaluate systemic toxicity, while comprehensively covering liver-related endpoints within an integrated safety framework. Using rodent models, we assess:
- Systemic toxicity and pharmacokinetics
- Hepatic metabolism and exposure
- Liver histopathology and biomarker responses
These studies provide critical context for translating in vitro findings into whole-organism safety assessments.
Key Endpoints
Our liver toxicity assessment platform delivers a comprehensive evaluation of cellular, metabolic, and functional endpoints, enabling early detection of potential hepatotoxicity and mechanistic insights for drug development:
Cellular Health and Viability
Cytotoxicity and apoptosis assessment using high-content imaging and biochemical assays.
Mitochondrial Function and Oxidative Stress
Detection of mitochondrial impairment and ROS generation.
CYP-Mediated Metabolism and DDI
Profiling of major cytochrome P450 isoforms and reactive metabolites.
Hepatic Transporter Analysis
Functional assessment of OATP, BSEP, MRP2, and other key transporters.
Inflammatory Response and Cytokine Profiling
Measurement of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and other immune markers.
Lipid Accumulation and Cholestasis Assessment
Steatosis and cholestasis evaluation using imaging and bile acid profiling.
Gene and Protein Expression Changes
Transcriptomic and proteomic analyses for mechanistic insights.
Quotation and Ordering
Integrate superior liver safety data into your drug development pipeline. Partner with our experts to design a customized hepatotoxicity testing strategy that enables early risk mitigation, predictive insights, and faster, regulator-aligned decision-making.
Reference
- Serras AS, Rodrigues JS, et al. A Critical Perspective on 3D Liver Models for Drug Metabolism and Toxicology Studies. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. 9:626805.
Explore Other Options