CARD-FISH for Environmental Microorganisms
- Service Details
- Features
- FAQ
- Explore Other Options
CARD-FISH (catalyzed reporter deposition-fluorescence in situ hybridization) is an advanced molecular tool developed from traditional FISH techniques. Traditional FISH often faces limitations of low signal intensity when dealing with microorganisms with low metabolic activity or target nucleic acid levels. CARD-FISH employs tyramide signal amplification (TSA), achieving enzyme-mediated signal amplification, and significantly enhancing detection sensitivity. This substantial increase in sensitivity makes CARD-FISH highly applicable for environmental microorganism detection, especially in complex environments. Despite its technical complexity, CARD-FISH offers unparalleled advantages in identifying and tracking environmental microorganisms. The technique can detect not only rRNA but also target mRNA, plasmid, or chromosomal genes, providing broad application potential.
Creative Bioarray provides CARD-FISH services for a variety of microbial samples based on professional knowledge background and solid experience reserve.
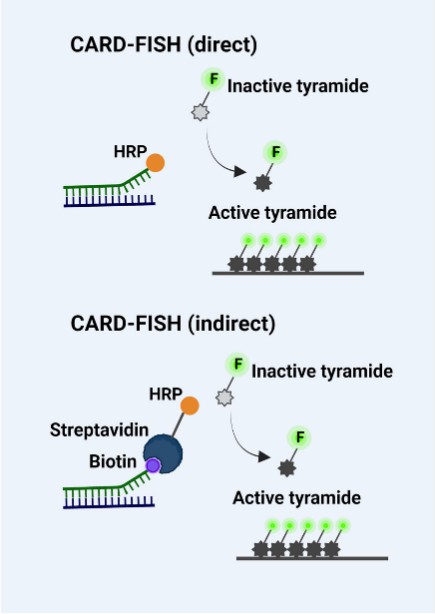 Fig. 1. Principle steps of CARD-FISH (Barbosa A, Miranda S, et al., 2023).
Fig. 1. Principle steps of CARD-FISH (Barbosa A, Miranda S, et al., 2023).
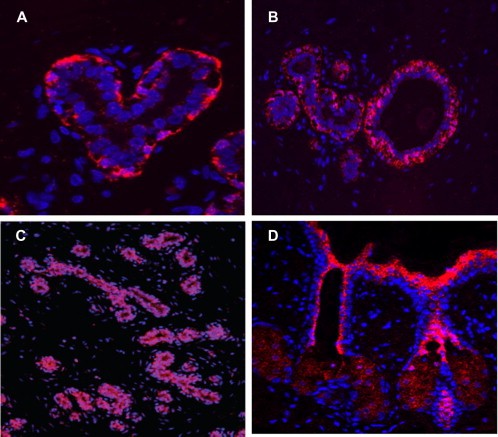 Fig. 2. Demonstration of microRNA using Tyramide Signal Amplification (Cy3 labelled). Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue) (Cassidy A, Jones J. et al., 2014).
Fig. 2. Demonstration of microRNA using Tyramide Signal Amplification (Cy3 labelled). Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue) (Cassidy A, Jones J. et al., 2014).
Advantages of CARD-FISH Technology
- High sensitivity: CARD-FISH significantly enhances fluorescence signals through enzyme-mediated amplification, making it 26-41 times more sensitive than standard FISH.
- Low background interference: By utilizing HRP-catalyzed tyramide fluorescence labeling, background fluorescence is minimized while signal stability is maximized.
- Wide application range: Suitable for a variety of environmental samples such as soil, water bodies, sediments, and medical pathogens. It targets microbial rRNA, mRNA, and DNA.
- Single-cell level analysis: Provides detailed insights into physiological, metabolic information, and microbial activity at the single-cell level.
Our CARD-FISH can detect microorganisms including, but not limited to:
- Soil microorganisms: Assess the diversity and function of microbial communities in soil ecosystems, evaluating soil health and fertility.
- Aquatic microorganisms: Monitor water quality and assess pollution levels and ecological health.
- Gut microbiota: Analyze the microbial communities and functional genes in the gut to aid in the prevention and treatment of gastrointestinal diseases.
- Bioremediation: Monitor and evaluate the dynamic changes in microbial communities during remediation processes.
Creative Bioarray's CARD-FISH Services Include
- Sample collection and processing:
We offer on-site sampling guidance for varied environments like water bodies, soil, and sediments, ensuring microbial cell integrity and viability through professional pre-processing. - Probe preparation:
We design and synthesize highly specific oligonucleotide probes targeting microorganisms, labeled with horseradish peroxidase (HRP). - CARD-FISH execution:
Hybridization using specific oligonucleotide probes with target microbial nucleic acid sequences. - Signal amplification:
Enhanced fluorescence signal through catalytic reporter deposition, allowing effective detection of low-abundance microorganisms. - Microscopic visualization:
Employ advanced microscopy for precise identification and quantification of labeled microbial cells. - Data analysis:
Deliver detailed analytical reports customized to meet your specific requirements.
Why choose for Creative Bioarray's CARD-FISH Services?
- High precision and sensitivity: Creative Bioarray's CARD-FISH can detects extremely low abundance target microorganisms with high accuracy.
- In situ analysis: Maintains microorganisms in their natural environmental context, revealing true distribution and interactions.
- Tailored guidance: We Offer flexible experimental planning for both common and rare microorganisms, aligning with your research objectives.
- Rapid turnaround: Our efficient team and advanced equipment ensure prompt project initiation and completion.
FAQ
1. What information is needed to customize CARD-FISH services?
To tailor CARD-FISH services, you need to provide your research objectives, sample types, and the specific microorganisms or functional genes you wish to detect. Our technical team will design an experimental plan based on your requirements.
2. What are the advantages of CARD-FISH over traditional FISH?
CARD-FISH significantly improves detection sensitivity through catalytic signal amplification, particularly advantageous for detecting low-abundance microorganisms. It also retains the in situ analysis capabilities of microorganisms, offering more accurate environmental data.
3. How many microbial species can CARD-FISH detect in a single sample?
The number of detectable microbial species depends on the number of probes used and the complexity of the sample. Typically, multiple complementary probes can be used simultaneously to detect various species.
4. How long does your CARD-FISH process take?
The timeframe depends on the sample complexity and the project's scope, usually ranging from a few weeks to a few months. We will maintain close communication to ensure timely project completion.
5. Can I request custom probes tailored to specific targets for my samples?
Absolutely. We provide custom probe design services, targeting specific microbial sequences according to your research needs.
Quotation and Ordering
For more information or to discuss how our CARD-FISH services can assist in your research needs, please feel free to contact our team.
Explore Other Options