Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is known to be a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by synovitis that leads to cartilage and bone erosion. RA is caused by a variety of complex environmental and genetic factors that induced early immune perturbation in both the innate and adaptive compartments and subsequent chronic inflammation.
Creative Bioarray focuses on drug research and development services and helps customers evaluate the drug efficacy and study the pathological mechanisms of rheumatoid arthritis by associated models.
 Figure.1. Rheumatoid arthritis
Figure.1. Rheumatoid arthritis
Creative Bioarray offers you Rheumatoid arthritis models including but not limited to:
- Collagen-Induced Arthritis (CIA) Models
- Collagen Antibody-Induced Arthritis (CAIA) Model
- Adjuvant Arthritis Models
- Spontaneous Arthritis Models
- K/BxN spontaneous mouse model
- TNF-α transgenic mouse model
- SKG model
- Human DR4-CD4 mouse model
- Human/SCID chimeric mouse model
- Pristane-Induced Arthritis Model
- Zymosan-Induced Arthritis Model
Our Capabilities
- We use Rheumatoid arthritis models to test the efficacy of drug candidates against Rheumatoid arthritis.
- We assess the severity of rheumatoid arthritis in animals by clinical scoring system.
- We evaluate various biomarkers and cytokines through WB, IHC, ELISA, etc.
Assays available
- Clinical score
- Histopathology
- Biomarker analysis
- Cytokine analysis
- PK/PD blood analysis
- Paw volume
- Ankle thickness
With extensive experience in the field of RA, we are confident to help you to overcome any upcoming challenges. Our experts are fully capable of customizing our protocols and assays to meet your specific needs. With our help, we wish to facilitate your research with high efficiency.
Study examples
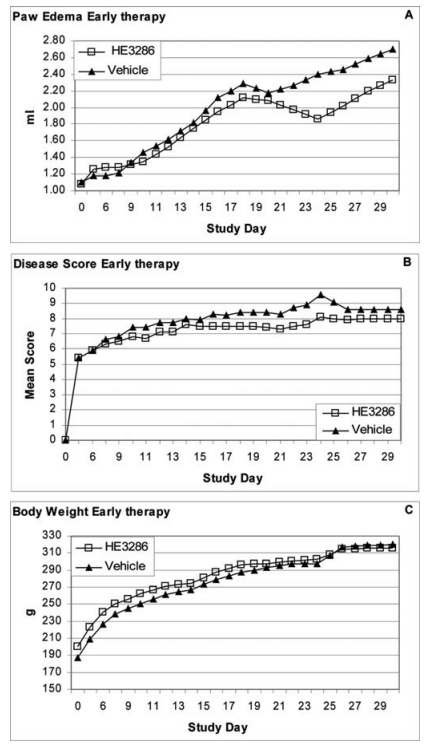 Figure. 2. Effect of early therapeutic treatment with HE3286 in the rat modelof AIA. Arthritis was induced in male Lewis rats (10 per group) by a single (s.c.) injection (0.1 ml) of heat-killed Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Ra (0.3 mg) in Freund's incomplete adjuvant into the base of the tail. On day 8 (post-immunization to induce AIA), when the rats showed clinical signs of arthritis, twice-daily treatments (gavage) began with either HE3286 (25 mg/kg) or vehicle alone (125 μl) and were continued for 15 consecutive days. Paw edema and disease score were assessed daily as described in Materials and methods. Data are expressed as median paw edema (A) and median disease score per animal (B) ± standard deviation. (C) The body weight variation during the study period.
Figure. 2. Effect of early therapeutic treatment with HE3286 in the rat modelof AIA. Arthritis was induced in male Lewis rats (10 per group) by a single (s.c.) injection (0.1 ml) of heat-killed Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Ra (0.3 mg) in Freund's incomplete adjuvant into the base of the tail. On day 8 (post-immunization to induce AIA), when the rats showed clinical signs of arthritis, twice-daily treatments (gavage) began with either HE3286 (25 mg/kg) or vehicle alone (125 μl) and were continued for 15 consecutive days. Paw edema and disease score were assessed daily as described in Materials and methods. Data are expressed as median paw edema (A) and median disease score per animal (B) ± standard deviation. (C) The body weight variation during the study period.
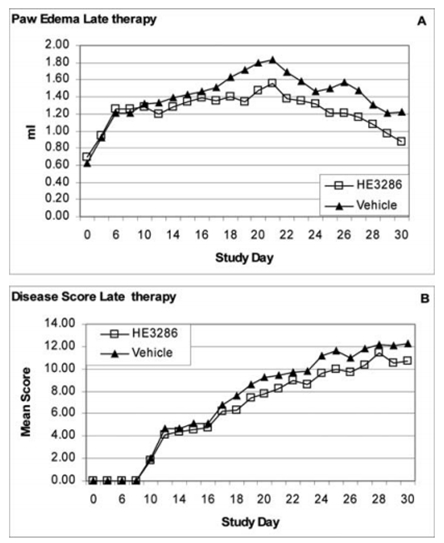 Figure. 3. Effect of late therapeutic treatment with HE3286 in the rat model of AIA. Arthritis was induced in male Lewis rats (10 per group) by a single (s.c.) injection (0.1 ml) of heat-killed Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Ra (0.3 mg) in Freund ' s incomplete adjuvant into the base of the tail. On day 15 (post-immunization to induce AIA), when the rats showed clinical signs of well-established arthritis, twice-daily treatments (gavage) began with either HE3286 (25 mg/kg) or vehicle alone (125 μl) and were continued for 15 consecutive days. Paw edema and disease score were assessed daily as described in Materials and methods. Data are expressed as median paw edema (A) and median disease score per animal (B) ± SD.
Figure. 3. Effect of late therapeutic treatment with HE3286 in the rat model of AIA. Arthritis was induced in male Lewis rats (10 per group) by a single (s.c.) injection (0.1 ml) of heat-killed Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Ra (0.3 mg) in Freund ' s incomplete adjuvant into the base of the tail. On day 15 (post-immunization to induce AIA), when the rats showed clinical signs of well-established arthritis, twice-daily treatments (gavage) began with either HE3286 (25 mg/kg) or vehicle alone (125 μl) and were continued for 15 consecutive days. Paw edema and disease score were assessed daily as described in Materials and methods. Data are expressed as median paw edema (A) and median disease score per animal (B) ± SD.
Quotation and ordering
If you have any special needs or questions regarding our services, please feel free to contact us. We look forward to cooperating with you in the future.
Reference
Auci D L et al. Oral treatment with HE3286 ameliorates disease in rodent models of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 2010, 25(4):625-633.