UGT Induction
- Service Details
- Features
- FAQ
- Explore Other Options
UGT-catalyzed glucuronidation is a major phase II elimination pathway for a large number of drugs and endogenous substrates (e.g., bilirubin). UGT expression (induction) can be modulated by concomitant medications, resulting in increased clearance of glucuronidated drugs and clinically significant DDIs or altered exposure. Regulatory guidance now explicitly references UGTs along with CYPs and transporters with respect to DDI evaluation and recommends standardized in vitro endpoints (mRNA and/or catalytic activity readouts in human hepatocytes) to inform clinical interaction study requirements.
Our UGT Induction Service provides the essential, regulatory-compliant data you need to fully characterize your drug candidate's DDI profile and mitigate late-stage development risk.
Our UGT Induction Assay Service
Workflow
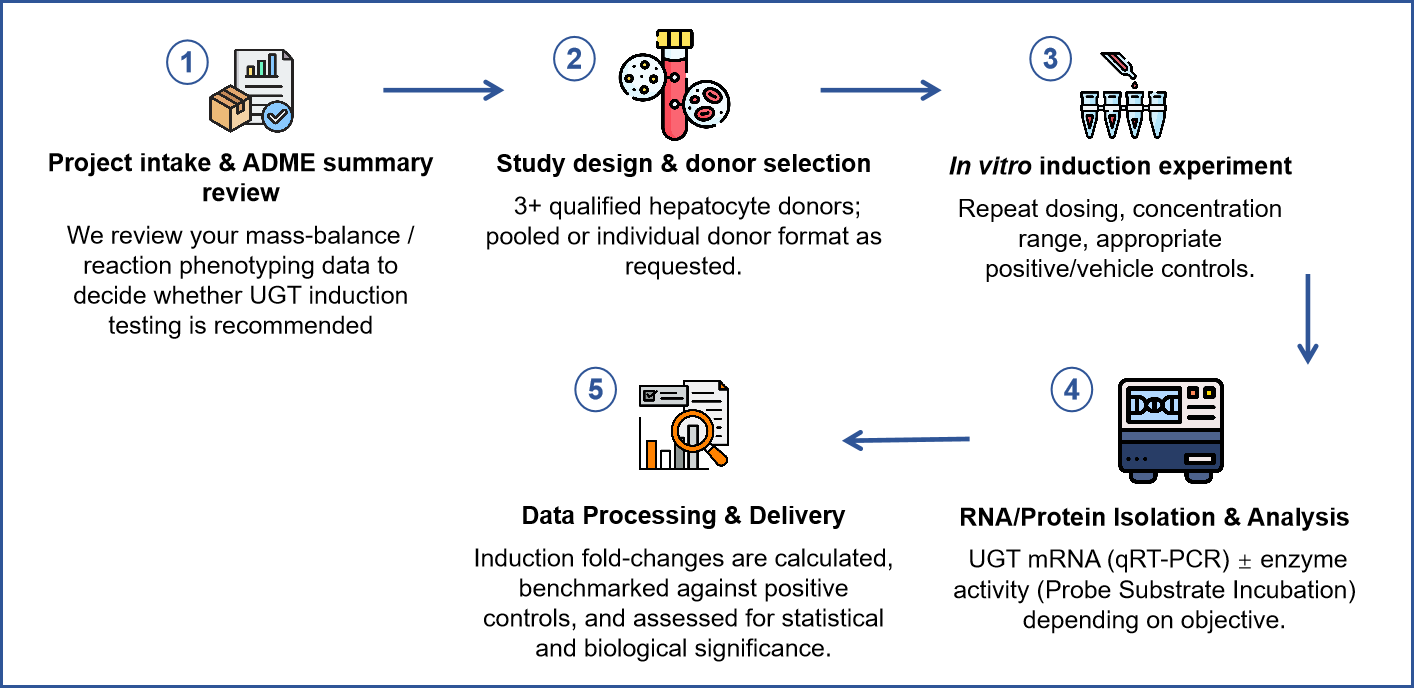
Protocol
| Parameters | Details |
| Test System | Primary Human Hepatocytes (multiple donors) |
| Test Concentration | 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 5, 10, 25μM |
| Enzymes | UGT1A1, UGT1A4, UGT1A9, UGT2B7, UGT2B15 |
| Time Points | 48–72 h (typical 3-day repeat dosing) |
| Replicates | 3 |
| Analysis Method | Enzymatic activity: LC-MS/MS or fluorescent quantification mRNA levels: qPCR |
| Data Delivery | mRNA Fold-Change, Activity Fold-Change, EC50/Emax (if applicable) |
Why Choose US?

Dual Endpoints for Reliable Assessment
We measure both mRNA (qPCR) and enzyme activity (LC-MS/MS) to deliver a comprehensive and regulator-aligned evaluation.

Qualified Human Hepatocytes
Only induction-verified cryopreserved human hepatocyte lots are used, ensuring consistent and responsive results.
Integrated ADME Support
UGT induction testing can be combined with metabolism, transporter, and CYP450 studies for a complete DDI and safety assessment.
FAQ
When should I request UGT induction testing?
Consider UGT induction testing when: (a) reaction phenotyping or clearance data indicates a large fraction of drug eliminated by glucuronidation, (b) major metabolites or concomitant medications raise a plausible risk of transcriptional modulation, or (c) regulatory strategy warrants early de-risking of DDI concerns. Regulators expect to see in vitro data early enough in development to inform clinical trial design and exclusion criteria.
Why is UGT induction assay important if I already test for CYP induction?
UGTs are an independent enzyme system and clearance pathway distinct from CYPs. A compound can be a strong UGT inducer without having an effect on any CYP. Failure to consider UGT induction risks leaving a large and potentially clinical DDI liability untested, especially for drugs with high rates of glucuronidation (e.g., drugs metabolized by UGT1A1).
Which UGT isoforms are required for testing?
Based on current regulatory guidance, we prioritize the major inducible isoforms: UGT1A1, UGT1A4, and UGT2B7. We can readily customize the panel to include other isoforms (e.g., UGT1A9) based on your drug's specific metabolism profile.
Explore Other Options