Erectile Dysfunction (ED) Models
Creative Bioarray is pleased to introduce our comprehensive Erectile Dysfunction (ED) Models, specifically developed to support researchers in evaluating the efficacy of innovative therapies for ED. Our models provide a reliable platform for advancing scientific understanding and treatment options for this prevalent condition.
What is Erectile Dysfunction (ED)?
ED is a common sexual disorder characterized by the inability to achieve or maintain a satisfactory erection, impacting both the individual and their partner. Its prevalence increases with age and can stem from physiological, psychological, or hormonal disturbances in various systems, including nervous, cardiovascular, and reproductive. ED can be classified as psychogenic, organic (e.g., hormonal or drug-induced), or a combination of both. While PDE5 inhibitors are effective treatments, side effects, cost, and limited efficacy in certain populations highlight the need for better options. Research is focused on developing safer, more effective therapies, including physical therapy and combined approaches, to improve outcomes for ED patients.
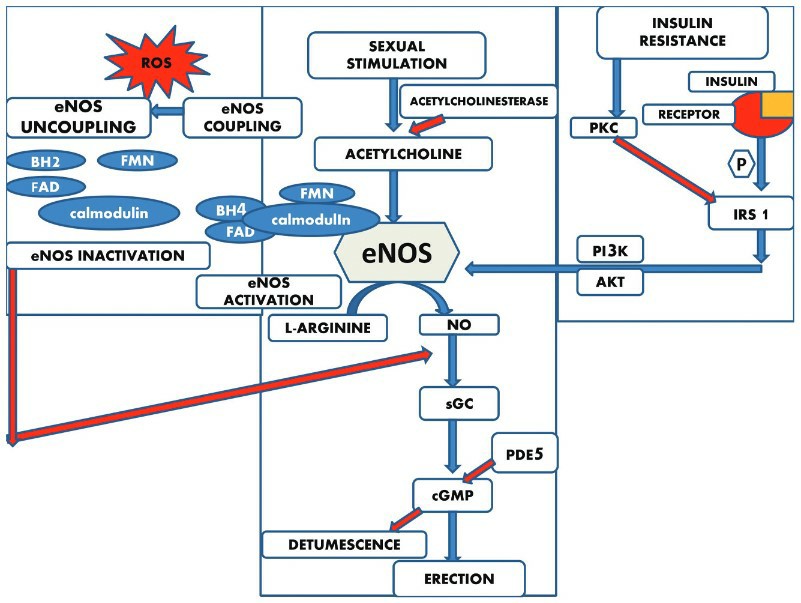 Fig. 1: Mechanisms underlying the pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction. (Saikia et al., 2024)
Fig. 1: Mechanisms underlying the pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction. (Saikia et al., 2024)
Creative Bioarray's Erectile Dysfunction (ED) Models
Available Animal
- SD Rat
Modeling Method
- Vasculogenic ED Model: Induced by bilateral internal iliac artery ligation.
- Neurogenic ED Model: Induced by cavernous nerve clamping.
- Endocrinologic ED Model: Induced through streptozotocin (STZ) injection.
Endpoints
- Apomorphine (APO)-induced erectile response test: Number of erections
- Intracavernosal pressure (ICP)
- Histology analysis: Masson staining
- Custom endpoints tailored to meet your specific research needs
Example Data
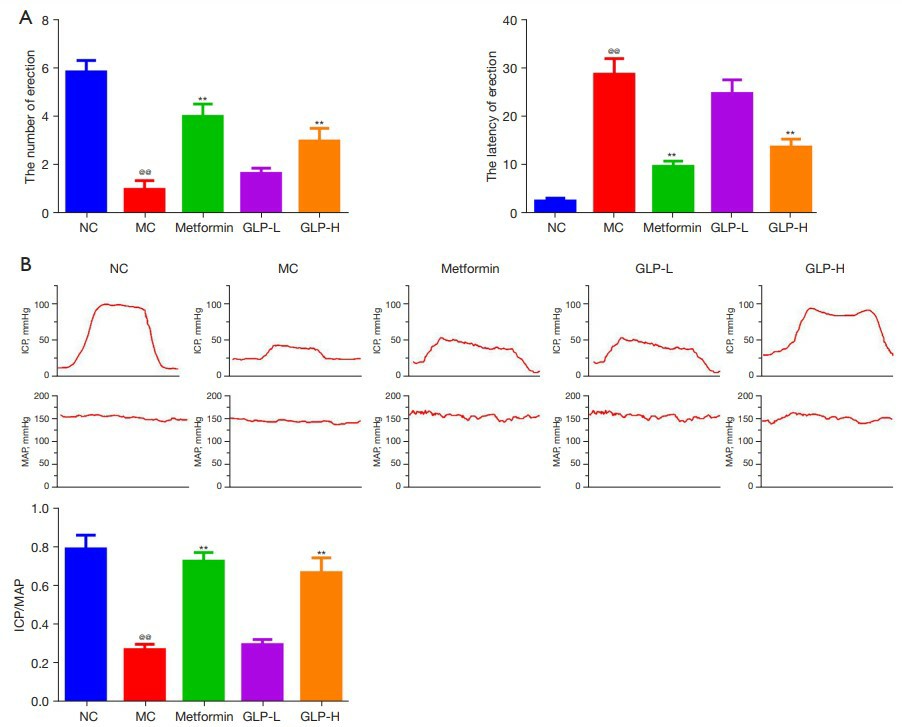 Fig. 2: GLP improved ED in DMED rats. (A) The number and latency of erections after GLP treatment. (B) The representative waves of ICP and MAP as well as the value of ICP/MAP after GLP treatment. (Yao et al., 2022)
Fig. 2: GLP improved ED in DMED rats. (A) The number and latency of erections after GLP treatment. (B) The representative waves of ICP and MAP as well as the value of ICP/MAP after GLP treatment. (Yao et al., 2022)
Quotation and Ordering
If you are interested in learning more about our Erectile Dysfunction (ED) Models or would like to explore our services further, please do not hesitate to contact us. We welcome your inquiries and are dedicated to supporting your research endeavors with high-quality models and expertise.
References
- Saikia, Q., et al. Erectile dysfunction: basics and its management using plant products. Egyptian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 2024, 11(1): 25-41.
- Yao, X., et al. Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide ameliorated diabetes mellitus-induced erectile dysfunction in rats by regulating fibrosis and the NOS/ERK/JNK pathway. Translational Andrology and Urology, 2022, 11(7): 982.