HUVEC;Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells
Cat.No.: CSC-C4076X
Species: Human
Source: Umbilical Cord; Vein
Cell Type: Endothelial Cell
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVEC) are derived from the umbilical vein within the umbilical cord, which is one of the main blood vessels connecting the fetus to the mother. The umbilical cord has two umbilical arteries and one umbilical vein. These cells grow as a monolayer in vitro and have a polygonal shape with tight intercellular connections. It has a central nucleus, rich organelles, and unclear boundaries. HUVEC is a vascular endothelial cell with typical features and plays an important role in physiological functions such as angiogenesis, inflammation, thrombosis, and material exchange. As such, it has become an important cell model in the research of vascular diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and tumor angiogenesis. It also expresses a variety of cell surface receptors and signal transduction pathways, such as C1q receptor, c-kit receptor, and P450 enzyme system involved in cell signaling and metabolism.
HUVEC has been widely used in the fields of drug screening, gene expression, and cell signaling pathways research because of its easy collection, stable culture, and rich functions. It has also become an important model in the research of cardiovascular diseases, vascular biology, tumor angiogenesis, and inflammatory response.
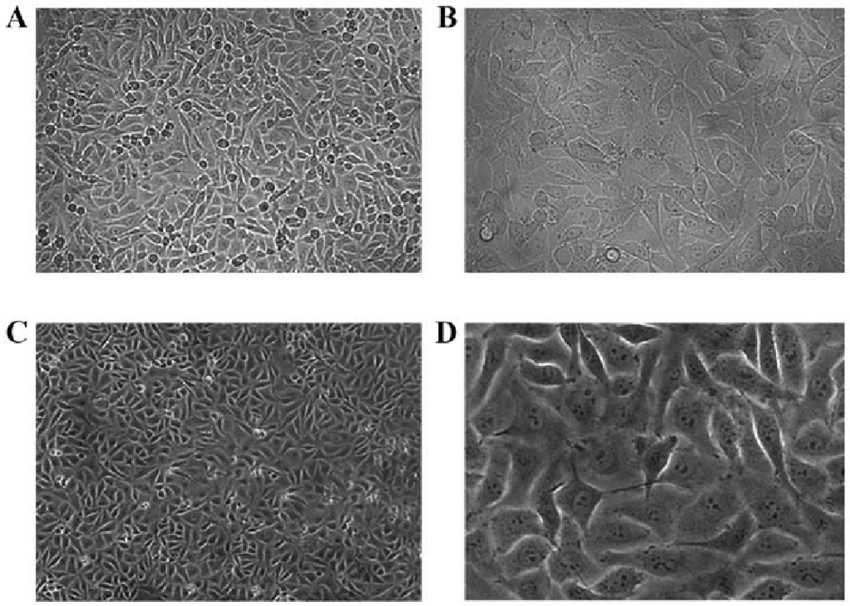 Fig. 1. HUVEC morphology
under light microscopy (Peng M, Yang M Y, et al., 2017).
Fig. 1. HUVEC morphology
under light microscopy (Peng M, Yang M Y, et al., 2017).
Interaction between PS-NPs and Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells
Nanoplastics (NPs) are ubiquitous in the environment and can enter the human body by different routes of exposure, which may potentially lead to adverse health effects. In this study, Lu's team explored the interaction and autophagy of polystyrene nanoplastics (PS-NPs) (100 and 500 nm) on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). The autophagic flux level in PS-NPs–treated HUVECs was assessed using a dual fluorescent LC3 lentiviral reporter assay.
Interaction of PS-NPs with target cells is pivotal for their toxicity. The flow cytometry assay showed that 100 nm PS-NPs could be taken up by almost all the HUVECs at 5-25 μg/mL and were accumulated in a time-dependent manner (Fig. 1A-B). Similar interactions were observed in HUVECs with 500 nm PS-NPs (Fig.1C-D). Moreover, both 100 and 500 nm PS-NPs (10/25 μg/mL) increased the cells' fluorescence intensity significantly within 10 min (Fig. 1E-F). The fluorescence intensity was positively correlated with PS-NPs' concentration and lasted in a sustained manner for 10 min-3 h (Fig. 1E-F). These data indicated that PS-NPs interacted with HUVECs in a time- and concentration-dependent manner.
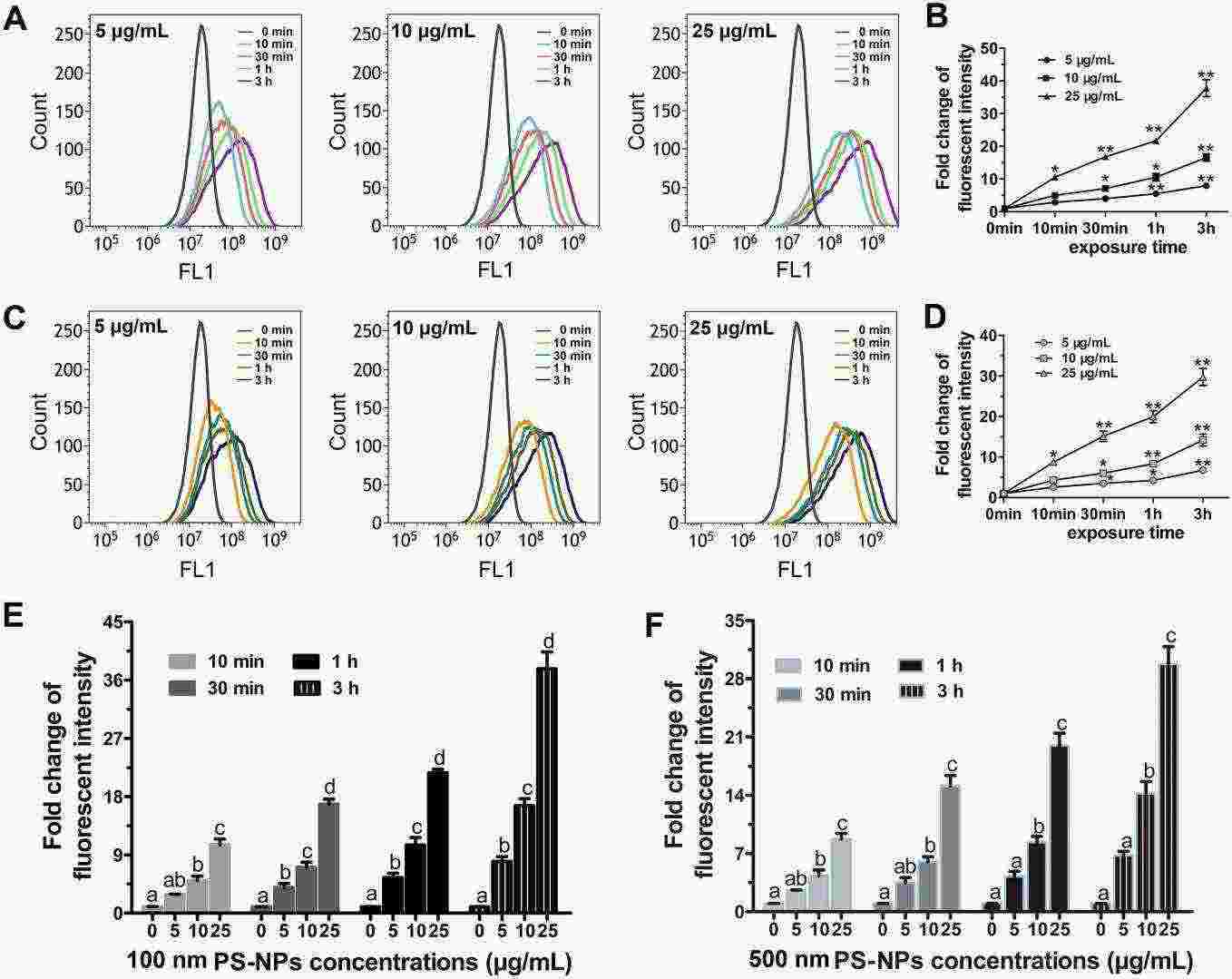 Fig.
1. The effect of exposure time and concentration on PS-NPs internalization in HUVECs (Lu Y Y, Li H Y, et al., 2022).
Fig.
1. The effect of exposure time and concentration on PS-NPs internalization in HUVECs (Lu Y Y, Li H Y, et al., 2022).
Activation of Piezo1 by Ultrasonic Stimulation and Its Effect on The Permeability of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells
Ultrasound produces acoustic radiation forces which generate shear stress in the acoustic field. Shear stress can be sensed by a mechanosensitive ion channel protein Piezo1 and transduced into downstream signalling. In this study, Zhang's team employed ultrasonic stimulation to investigate Piezo1 sensitivity and its downstream biological functions in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs).
To understand the impact of ultrasonic stimulation on Piezo1, HUVECs were transfected with Piezo1 siRNA or negative control siRNA, and they were named as CP1.si and CNc.si cells, respectively. RT-qPCR and Western blot showed that Piezo1 was effectively knocked down in CP1.si cells (Fig. 2a, b). To identify optimal ultrasonic stimulation parameters, CBlank cells with endogenous Piezo1 were stimulated with 1 W or 0.2 W ultrasound for 10 s, and then calcium fluorescence imaging was performed. As shown in Fig. 3, 1 W and 0.2 W ultrasound both led to a significant increase in intracellular calcium. However, 1 W ultrasound damaged cells (Fig. 3b). Thus, 0.2 W was determined as the appropriate power.
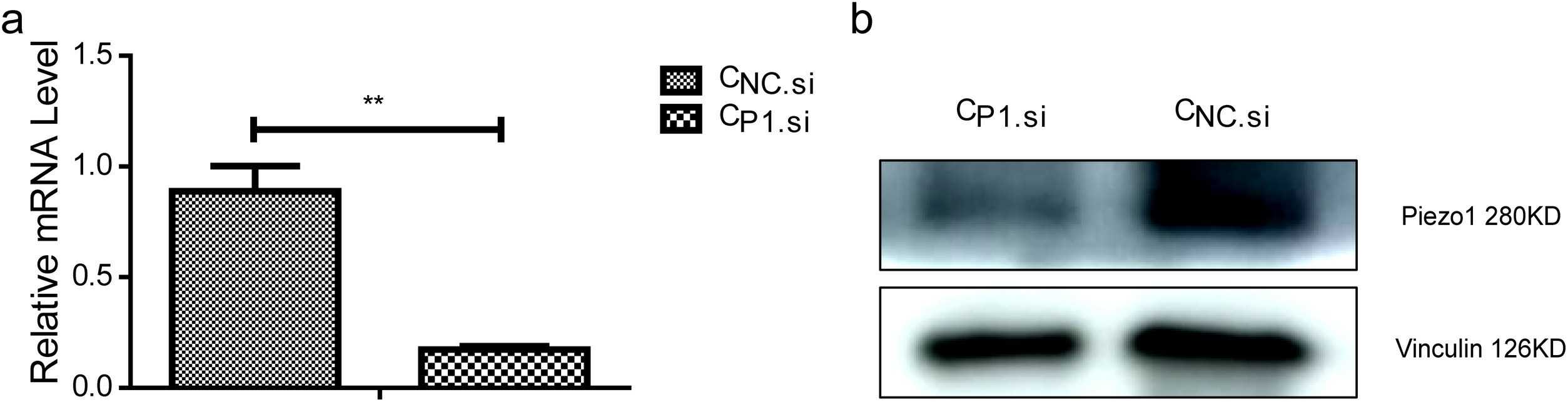 Fig. 2.
(a) Relative expression of Piezo1 analyzed using real-time PCR; (b) Expression of Piezo1 analyzed using Western
blotting (Zhang L G, Liu X J, et al., 2020).
Fig. 2.
(a) Relative expression of Piezo1 analyzed using real-time PCR; (b) Expression of Piezo1 analyzed using Western
blotting (Zhang L G, Liu X J, et al., 2020).
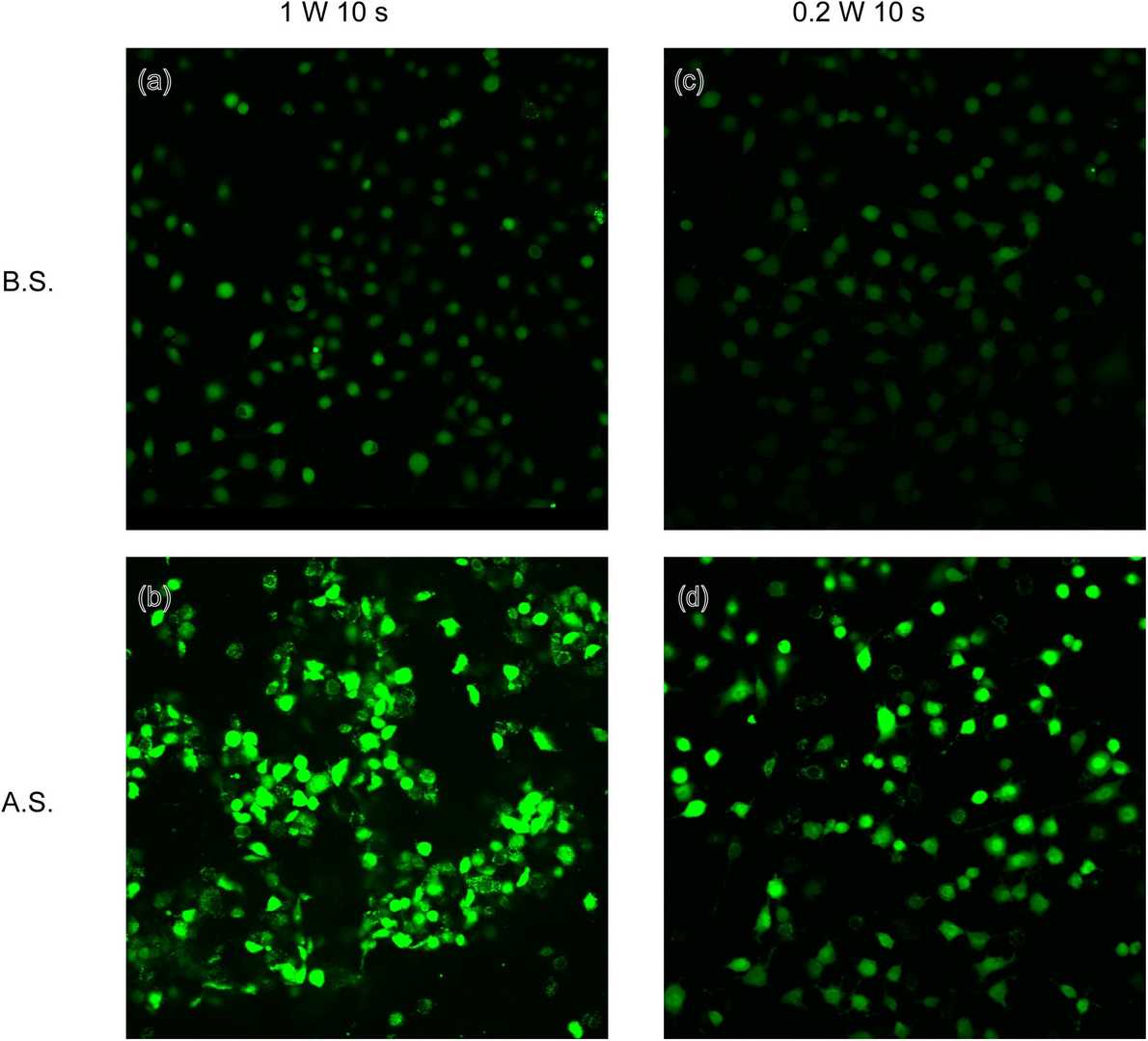 Fig. 3.
Calcium fluorescent images of CBlank subjected to ultrasound stimulation at 1 W and 0.2 W (Zhang L G, Liu
X J, et al., 2020).
Fig. 3.
Calcium fluorescent images of CBlank subjected to ultrasound stimulation at 1 W and 0.2 W (Zhang L G, Liu
X J, et al., 2020).
Passage 1, Passage 3.
Cell lines are authenticated using DNA profiling techniques such as short tandem repeat (STR) analysis and tested for mycoplasma contamination to ensure their identity and purity.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 5.0 | 1 Scientist has reviewed this product
High-quality
The quality of the tumor cells is exceptional and has allowed us to carry out precise experiments.
09 July 2022
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review