Immortalized Mouse Microglia (BV2)
Cat.No.: CSC-I2227Z
Species: Mouse
Morphology: Morphology microglial
Culture Properties: Adherent/suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
The role of microglia in neurodegenerative diseases, toxicology, and immunology is an ever-growing area of biomedical research. Traditional studies often rely on animal models, necessitating many animals for experimentation. However, using a microglia-like cell line, such as BV2 cells, offers a promising alternative by providing a continuous and reproducible source of microglia.
BV2 cells are a unique type of microglial cells derived from C57/BL6 murine, a widely used laboratory mouse strain. These cells are immortalized using the v-raf/v-myc carrying J2 retrovirus, resulting in a stable cell line with unique characteristics.
One of the key advantages of BV2 cells is their ability to retain the morphological and functional characteristics of microglia, the resident immune cells of the central nervous system. Due to the expression of v-raf/v-myc, BV2 cells exhibit an accelerated metabolic and proliferation rate compared to other microglia, making them an ideal tool for various research applications. The expression of nuclear v-myc and cytoplasmic v-RAF oncogene products and the env gp70 antigen on the surface of BV2 cells establish them as a suitable model for studying macrophages. These cells possess morphological, phenotypical, and functional markers similar to macrophages, expanding their potential applications in immunology research.
BV2 cells have proven to be a valid substitute for primary microglia in various experimental settings, facilitating research on neurodegeneration, toxicology, immunity, and cell-cell interactions.
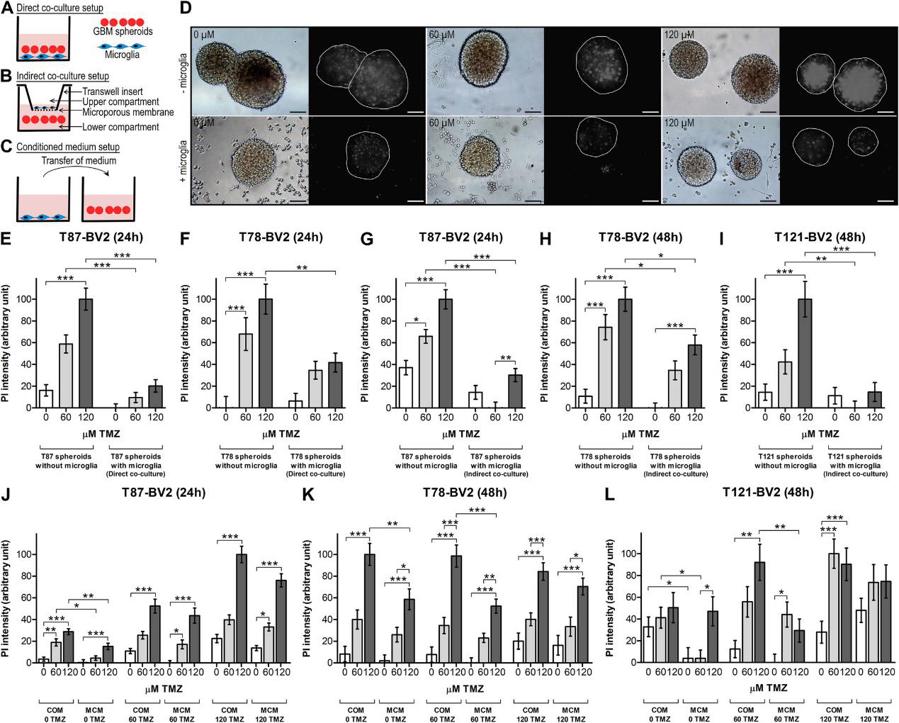
Microglia Increase TMZ Resistance of Glioblastoma Cells
Glioblastoma is the most malignant primary brain tumor. Even with standard treatment comprising surgery followed by radiation and concomitant temozolomide (TMZ) chemotherapy, glioblastoma remains incurable. Glioblastomas are densely infiltrated with tumor-associated microglia and macrophages (TAMs). These immune cells affect the tumor cells in experimental studies and are associated with poor patient survival in clinical studies. The aim of the study was to investigate the impact of microglia on glioblastoma chemo-resistance.
We co-cultured patient-derived glioblastoma spheroids with microglia at different TMZ concentrations and analyzed cell death. Co-culture experiments showed that microglia significantly increased TMZ resistance in glioblastoma cells.
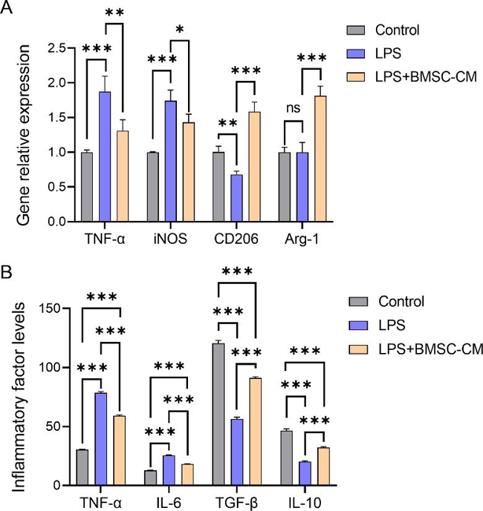
Conditioned Culture Medium of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promotes Phenotypic Transformation of Microglia by Regulating Mitochondrial Autophagy
To study the mechanism by which conditioned medium of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs-CM) facilitates the transition of pro-inflammatory polarized microglia to an anti-inflammatory phenotype.
BV2 cells, a mouse microglia cell line, were transformed into a pro-inflammatory phenotype using lipopolysaccharide (LPS). After co-culture with BMSCs-CM, the expression of pro-inflammatory microglia-related markers decreased, whereas that of anti-inflammatory microglia markers (CD206 and Arg-1) increased significantly (Fig. 2A). The expression levels of inflammatory factors TNF-α and IL-6 were inhibited, whereas those of anti-inflammatory factors TGF-β and IL-10 were increased (Fig. 2B).
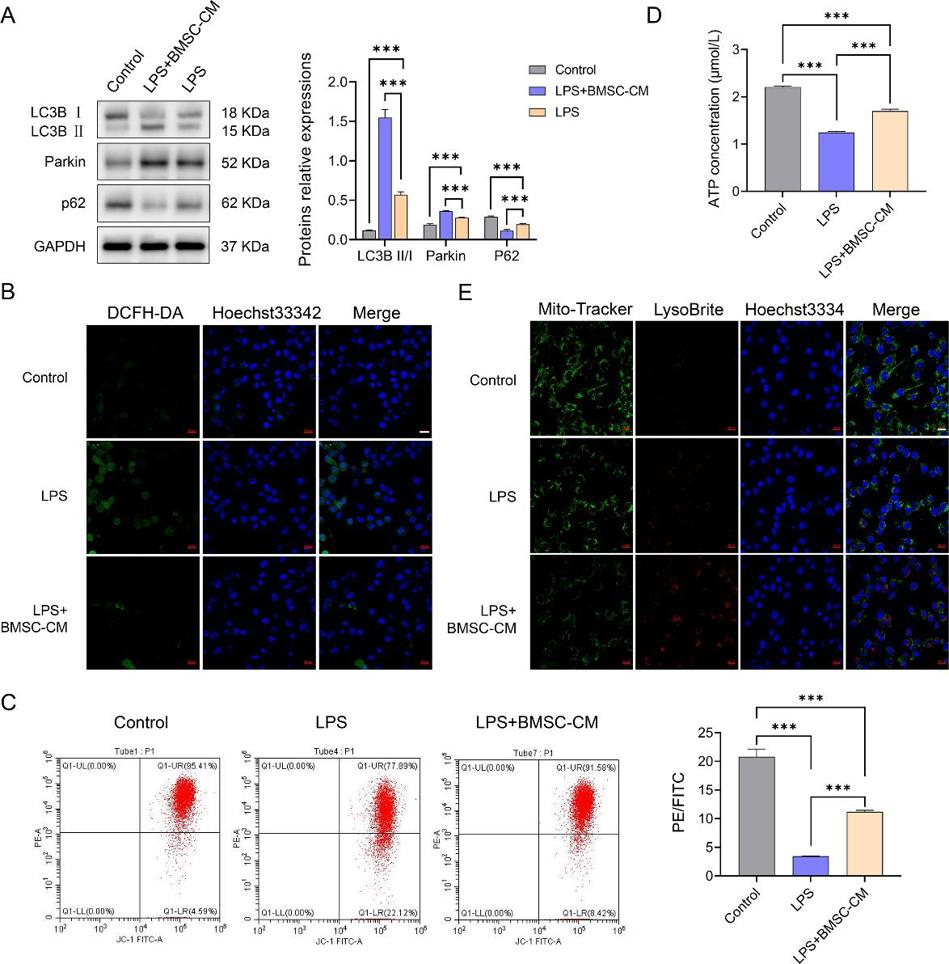
Furthermore, co-culture with BMSCs-CM increased mitophagy-associated protein expression, ATP levels, mitochondrial and lysosomal co-localization in these cells and decreased reactive oxygen species levels (Fig. 3A–3E).
The BV2 cell line consists of mouse microglial cells that have been immortalized to enable indefinite proliferation. These cells retain many of the functional properties of primary microglia and are widely used as a model for studying microglial behavior in various research contexts.
Yes, we offer a range of custom services, including:
Genetic modification (e.g., knockout or knock-in projects).
High-volume cell production for large-scale studies.
Development of custom assays to suit specific research objectives.
Tailored media formulations to enhance specific cellular behaviors.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells
