hERG Safety Assay
- Service Details
- Features
- FAQ
- Explore Other Options
Accurate and early assessment of hERG liability is a critical component of cardiac safety in drug development today. Our hERG Safety Assay Service delivers regulatory-aligned, high-quality electrophysiology data to help clients identify cardiac risks early and select safer lead compounds. Using high-throughput QPatch platforms complemented by GLP-compliant manual patch clamp assays, we provide precise, reproducible, and publication-grade hERG inhibition results suitable for both discovery and preclinical evaluation.
Understanding hERG and Its Role in Cardiac Safety
The human Ether-à-go-go-Related Gene (hERG / KCNH2) is the gene that encodes the Kv11.1 voltage-gated potassium channel. This channel mediates the rapid delayed rectifier current (IKr) and is a key contributor to the repolarization phase of the cardiac action potential. The pore structure and gating properties of hERG, which include rapid activation, fast inactivation, and slow deactivation, make it prone to off-target drug binding. Inhibition of this channel can prolong the QT interval and trigger life-threatening arrhythmias such as Torsade de Pointes.
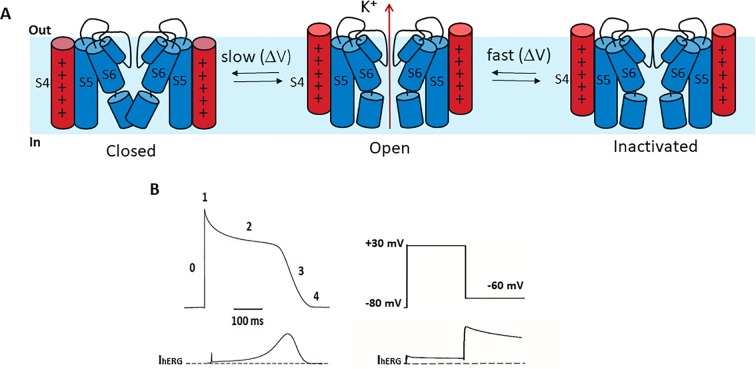 Fig. 1. hERG channel gating (Shi YP, Thouta S, et al. 2020).
Fig. 1. hERG channel gating (Shi YP, Thouta S, et al. 2020).
Given these risks, hERG assessment is a central component of global cardiac safety guidelines. ICH S7B and ICH E14 specify the non-clinical and clinical requirements for evaluating delayed repolarization, with recent updates emphasizing the importance of high-quality in vitro patch-clamp data in integrated risk assessment. Historical cases, including numerous market withdrawals tied to QT prolongation, highlight the necessity of early and reliable hERG liability screening during drug development.
Our hERG Safety Assay Service
Automated hERG sreening platform
Our hERG Safety Assessment integrates both manual and automated patch clamp platforms (QPatch) with biochemical and fluorescence polarization assays, offering a tiered strategy for cardiac risk mitigation:
- pA-Level Sensitivity: Direct measurement of native hERG currents in physiological saline (>1 GΩ seal, no additives).
- Dynamic Exposure Simulation: 0.5-sec microfluidic gradient perfusion for precise in vivo PK simulation (Cmax peak).
- High-Throughput Precision: 48-channel parallel detection (200+ samples/day) with >95% concordance to manual patch clamp (R²).
- Temperature Control Options: Recordings performed at room or physiological temperature as required.

Core Readouts
- Percent inhibition of hERG current
- Concentration-response curves
- IC50 and Hill slope
GLP-compliant manual patch clamp validation
For small number of compounds or compounds requiring deeper mechanistic understanding or regulatory-grade validation, we offer conventional whole-cell patch clamp assays performed by experienced electrophysiologists.
Manual patch clamp provides the highest resolution in ion channel studies, enabling:

- Precise control of voltage protocols
- State-dependent kinetics (open vs. inactivated block)
- Analysis of gating parameters
- Extended stability for slow-acting compounds
Workflow
Step 1: Compound Reception and Preparation
Compounds provided by the client will undergo quality verification and stock solution preparation.
Step 2: Experiment Setup
Recover hERG cells and set the inhibition test concentration according to the experimental design.
Step 3: Electrophysiology Recording
Compounds are tested using standardized cumulative or non-cumulative exposure protocols on QPatch or manual patch clamp systems.

Step 4: Data Processing & Modeling
All electrophysiological data—including raw traces, peak currents, concentration–response curves, IC50 values, Hill coefficients, and kinetic parameters—are analyzed using standardized methods
Step 5: Report Generation
Provide a detailed experimental report and data interpretation.
Protocol
| Parameter | Standard Protocol | Customizable Options |
| Instrument | Manual or QPatch Automated Patch Clamp System | Manual patch clamp (GLP-compliant) |
| Analysis Method | Whole-cell voltage clamp mode | Custom voltage protocols |
| Cell Line | CHO-hERG, HEK293-hERG | iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes (pre-assessment required) |
| Test Concentration Range | 0.1, 0.3, 1, 3, 10 μM | Client-specified concentrations or extended ranges |
| Sample Requirements | 100 μL of 10 mM DMSO solution | Special handling for low-solubility compounds |
| Data Delivery | - Raw current traces & concentration-response curves - Mean inhibition rate ± SEM - IC50 calculation (four-parameter logistic fit) |
Full raw data files, custom analysis formats |
Features

High-Throughput Screening
Quickly process a large number of compounds, ideal for large-scale screening projects.

Experienced Team
Our scientific team has extensive experience in hERG research and can provide professional advice to clients.
Comprehensive Support
Provide full-service support from detection to result analysis, meeting the needs of different clients.
FAQ
1. Why is the study of hERG inhibition important?
Studying hERG inhibition is crucial because the hERG potassium channel is essential for cardiac repolarization. Inhibition of this channel can prolong the QT interval on an electrocardiogram, potentially leading to life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias such as Torsade de Pointes. Identifying compounds that inhibit hERG early in drug development helps prevent late-stage clinical failures and ensures the cardiac safety of new pharmaceuticals.
2. What is the relationship between in vitro hERG inhibition and in vivo cardiac toxicity?
The purpose of in vitro hERG inhibition assays is to forecast whether a compound might extend the QT interval in living organisms leading to cardiac toxicity. When scientists conduct tests on compounds using in vitro methods they determine how those compounds interact with hERG channels and can forecast potential cardiac side effects in humans. The correlation of in vitro results with in vivo effects represents an essential step in the assessment of a drug's safety profile before starting clinical trials.
3. How does hERG support drug development?
During the drug discovery phase hERG screening helps drug development by pinpointing cardiac safety risks at an early stage. Researchers can select drug candidates with minimal safety risks by analyzing their interactions with the hERG channel which decreases the chance of failures during later development stages. Additionally, insights from hERG research direct medicinal chemistry strategies to enhance compound safety which facilitates the development of safer therapeutic drugs.
4. Does showing inhibition in the hERG Safety Assay mean the compound cannot proceed to clinical trials?
Not necessarily. While hERG inhibition is a potential marker for cardiac toxicity, it must be evaluated in conjunction with other experimental data (such as in vivo studies and preclinical pharmacological research). In some cases, cardiac toxicity risk can be reduced through structural optimization or adjustments to the dosing regimen.
Reference
- Shi YP, Thouta S, et al. Modulation of hERG K+ Channel Deactivation by Voltage Sensor Relaxation. Front Pharmacol. 2020. 11:139.
Explore Other Options