PDO-based Drug Screening Services

Inter-patient heterogeneity remains one of the major challenges in oncology drug development and clinical translation. Conventional two-dimensional cancer cell lines and animal models often fail to adequately reflect the complex tumor architecture, genetic diversity, and heterogeneous treatment responses observed in patients. Patient-derived organoids (PDOs) have emerged as a clinically relevant ex vivo platform that faithfully preserves patient-specific histopathological characteristics, genomic alterations, and functional drug response profiles, providing a more predictive model for translational drug evaluation.
Our PDO-based drug screening platform bridges the gap between traditional cell lines and in vivo models, offering a more predictive tool for evaluating drug efficacy, resistance mechanisms, and personalized treatment strategies.
Our PDO-Based Drug Screening Services with High Throughput Screening (HTS)
We provide an end-to-end PDO-based Drug Screening service, enabling rapid establishment, large-scale expansion, and personalized drug response profiling of patient-derived tumor organoids. Our platform is designed to support both hypothesis-driven studies and large-scale screening campaigns.
Coverage of 20+ Solid Tumor Types
We support PDO generation and drug screening for over 20 solid tumor types, including but not limited to:
- Colorectal cancer
- Pancreatic cancer
- Breast cancer
- Lung cancer
- Head and neck cancer
- Endometrial cancer
- Cervical cancer
- Esophageal cancer
- Gastric cancer
All PDO models undergo histological and molecular validation to ensure high concordance with the originating patient tumors.
Broad Compound Library Compatibility
Our screening platform supports a wide range of compound libraries:
- Natural Product Library (1,000–4,000 compounds)
- FDA-Approved Drug Library (2,000–3,000 approved drugs)
- Drug Repurposing Library (~4,000 compounds)
- Metabolism-Focused Compound Library (800–5,000 compounds)
- Customized or Client-Provided Libraries
Flexible assay formats allow screening of small molecules, targeted agents, and combination regimens.
Drug Screening Assay Types
We offer multiple PDO-based screening strategies tailored to different research objectives:
Single-Agent Sensitivity Screening
- Dose–response testing across multiple concentrations
- Determination of IC₅₀ / EC₅₀ values
- Identification of sensitive and resistant PDO subpopulations
Drug Combination Screening
- Evaluation of synergistic, additive, or antagonistic effects
- Support for rational combination strategies
- Synergy analysis using established mathematical models
High-Throughput Screening (HTS)
- Medium- to large-scale compound screening
- Automated workflows compatible with 96-, 384-, and 1536-well formats
- Suitable for lead identification and prioritization studies
Standard Workflow
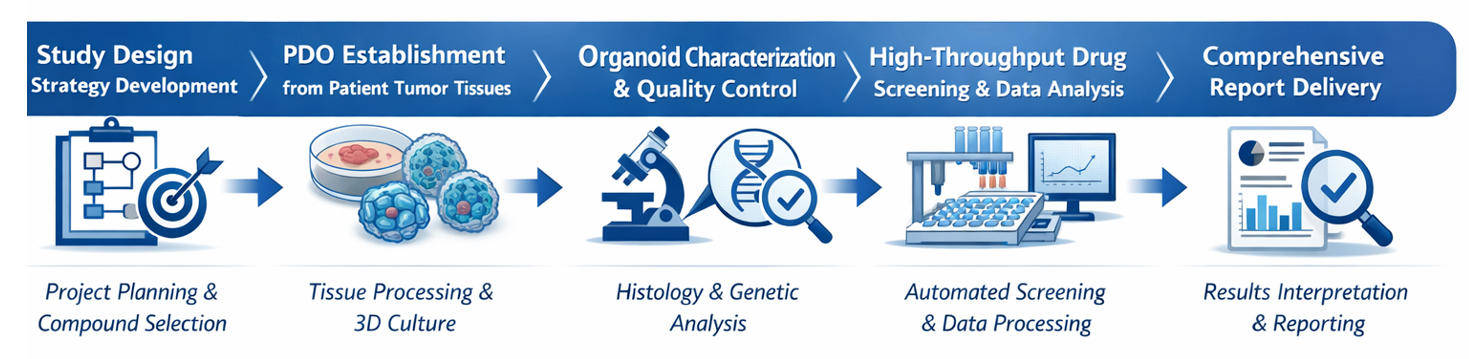
Technical Advantages

End-to-end, standardized platform
Harmonized SOPs ensure consistent and reproducible workflows from sample intake to data analysis.
Scale and automation
Automated handling supports high-throughput screening across multiple formats and study designs.

High-fidelity patient models
Comprehensive pathological and molecular characterization confirms strong concordance with original tumors.
Adaptable microenvironment
Tumor-specific 3D culture systems with optional co-culture models enable more physiologically relevant studies.
Advanced analytics
Robust data analysis, synergy modeling, and biomarker association deliver actionable insights for downstream R&D.
Applications
Our PDO-based drug screening services support a broad range of research and development needs, including:
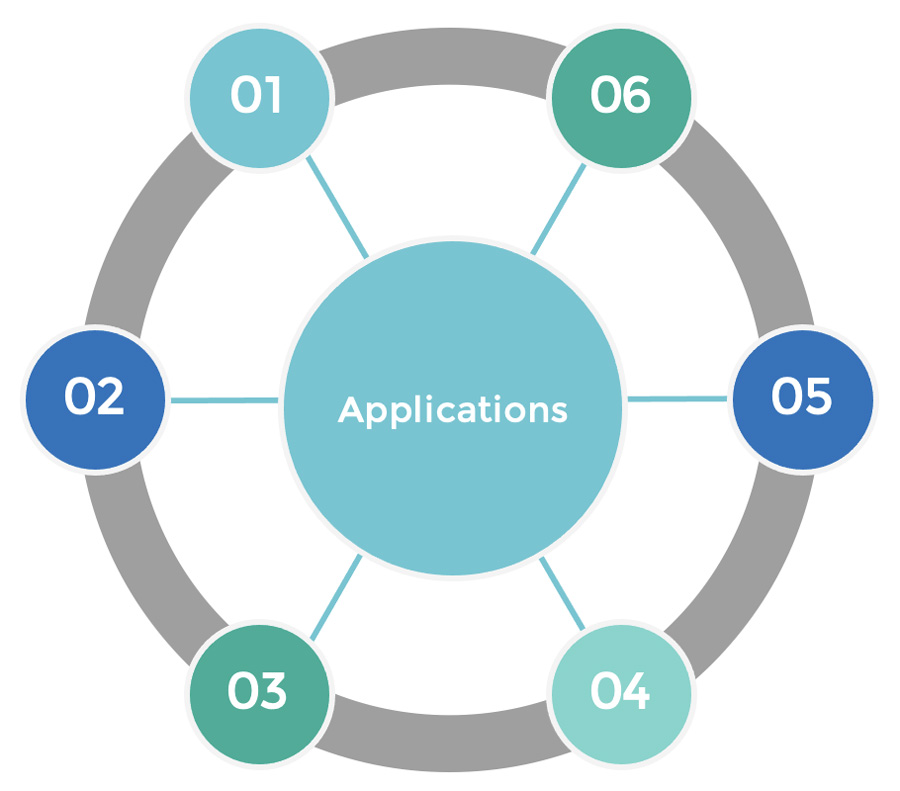
Oncology drug discovery and lead optimization
Drug resistance mechanism studies
Biomarker discovery
Drug repurposing and indication expansion
Rational combination therapy development
Translational research and precision oncology programs
FAQ
1. Can client-provided compounds be screened?
Yes. We support customized screening using client-provided compounds or proprietary libraries.
2. How do you ensure the quality and authenticity of the organoid models?
Each organoid model undergoes rigorous histological and genetic validation to confirm its identity and match with the patient-derived tumor tissue. We also implement strict quality control measures at every stage of the cultivation and screening process to maintain the highest standards.
Explore Other Options