High-Fat Diet-Induced Atherosclerosis Model
Creative Bioarray offers a well-established atherosclerosis model induced by a high-fat diet, available to customers worldwide. With our state-of-the-art technology and experienced experts, we ensure our global clients receive the most reliable service at the most competitive price. Our team of professional scientists is dedicated to helping clients and expediting their preclinical research programs.
Atherosclerosis is the pathology of numerous cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), posing a persistent threat despite the widespread adoption of lipid-lowering medications, interventional therapies, and other conventional treatments. It remains the world's leading cause of mortality, exacerbated by chronic exposure to cardiovascular risk factors including hyperlipidemia, hypertension, smoking, and diabetes. To advance our understanding and treatment of this condition, high-fat diet-induced atherosclerosis has become indispensable. This model offers a critical research platform, enabling scientists to rigorously assess the efficacy of novel drug candidates in the battle against atherosclerosis and its associated CVDs.
Our High-Fat Diet-Induced Atherosclerosis Model
- Available Animal
- Rat
- Mouse
- Modeling Method
1) Apoe-/- Mouse: Apoe-/- mice are fed with high-fat diet for 12-16 weeks to induce atherosclerosis model.
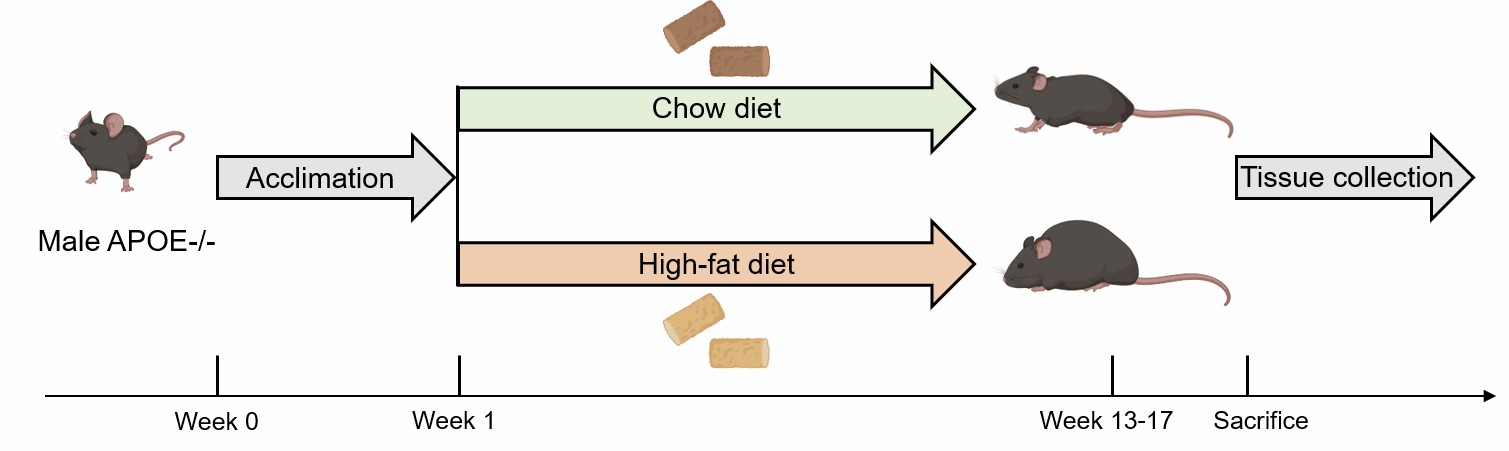 Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of the method of atherosclerosis modeling in Apoe-/- mice.
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of the method of atherosclerosis modeling in Apoe-/- mice.
2) Rat: Atherosclerosis is induced in rats by feeding them a high-fat diet for 13 weeks, with intraperitoneal injection of vitamin D3 administered at intervals of 1 week, 3 weeks, 6 weeks, and 9 weeks.
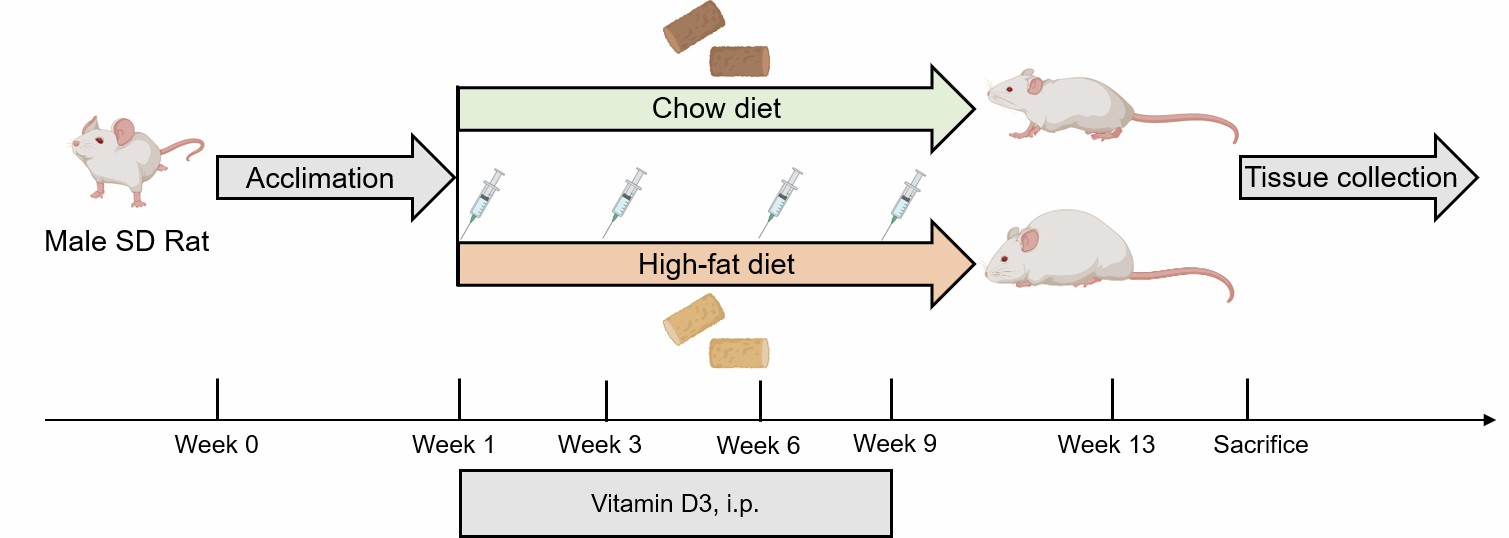 Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of the method of atherosclerosis modeling in rat.
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of the method of atherosclerosis modeling in rat.
- Endpoints
- Atherosclerotic plaques observation
- Histology analysis: H&E staining, Oil Red O staining, Masson staining, Sirius Red staining, IHC
- Serum analysis: TG, TC, HDL-C, LDL-C
- Body weight
- qPCR or Western blot
- Other customized endpoints: available upon request
Example Data
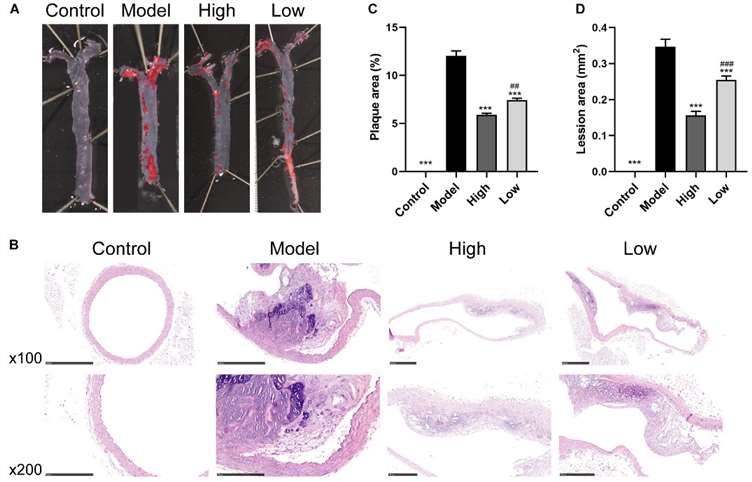 Fig. 3 Berberine attenuates HFD-induced atherosclerosis. (A) Representative images of en face Oil Red O staining of aorta. (B) H&E staining of aortic root. (C and D) Quantitative analysis of plaque area in aorta and lesion size in the aortic root. (Wu et al. 2020)
Fig. 3 Berberine attenuates HFD-induced atherosclerosis. (A) Representative images of en face Oil Red O staining of aorta. (B) H&E staining of aortic root. (C and D) Quantitative analysis of plaque area in aorta and lesion size in the aortic root. (Wu et al. 2020)
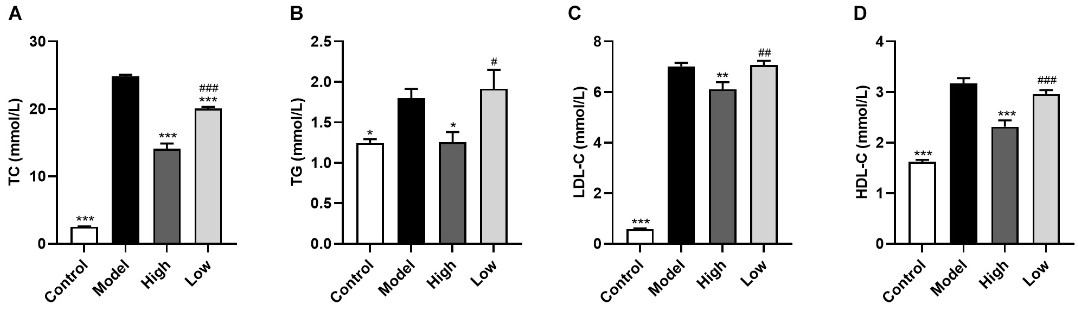 Fig. 4 Berberine ameliorates serum lipid levels in HFD-fed ApoE–/– mice. (A) Total cholesterol, (B) triglyceride, (C) low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, (D) high density lipoprotein cholesterol. (Wu et al. 2020)
Fig. 4 Berberine ameliorates serum lipid levels in HFD-fed ApoE–/– mice. (A) Total cholesterol, (B) triglyceride, (C) low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, (D) high density lipoprotein cholesterol. (Wu et al. 2020)
Quotation and Ordering
Creative Bioarray is dedicated to creating a wide range of disease models to support and enhance preclinical research programs. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us at any time or submit an inquiry to us directly.
Reference
- Wu, M., et al. Effect of berberine on atherosclerosis and gut microbiota modulation and their correlation in high-fat diet-fed ApoE−/− mice. Frontiers in pharmacology, 2020, 11: 223.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Oral Mucositis Model
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
- Graft-versus-host Disease (GvHD) Models
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Schizophrenia Model
- Depression Models
- Pain Models
-
Metabolic Disease Models
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Animal Model of Hyperuricemia
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model
- High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Methionine and Choline Deficient (MCD) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Gubra-Amylin NASH (GAN) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Model
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer (DFU) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthotopic Kidney Transplantation Model
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Model
- Peritoneal Fibrosis Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
- Otology Disease Models