In Vitro Mammalian Chromosomal Aberration Test (OECD 473)
- Service Details
- Features
- FAQ
- Explore Other Options
Many human genetic diseases are caused by chromosomal aberrations. Chromosomal damages in somatic cells that involve alterations in oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes are also related to tumor formation in humans and animals. Therefore, in vitro mammalian chromosomal aberration test is one of the recommended in vitro tests for mutagen assessment.
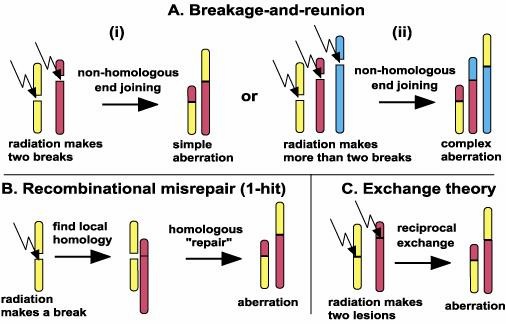 Fig. 1. Chromosomal Aberration (Paul K and Paul D, 2015).
Fig. 1. Chromosomal Aberration (Paul K and Paul D, 2015).
Creative Bioarray provides in vitro mammalian chromosomal aberration test follows the current OECD guideline Test No. 473. This test aims to identify substances that cause structural chromosomal aberrations in cultured mammalian cells (Chinese Hamster Ovary cell line CHO-K1, other cells upon request). Our test is available under either GLP (Good Laboratory Practice) or Non-GLP conditions.
Creative Bioarray's In Vitro Mammalian Chromosomal Aberration Test (OECD 473)
Workflow
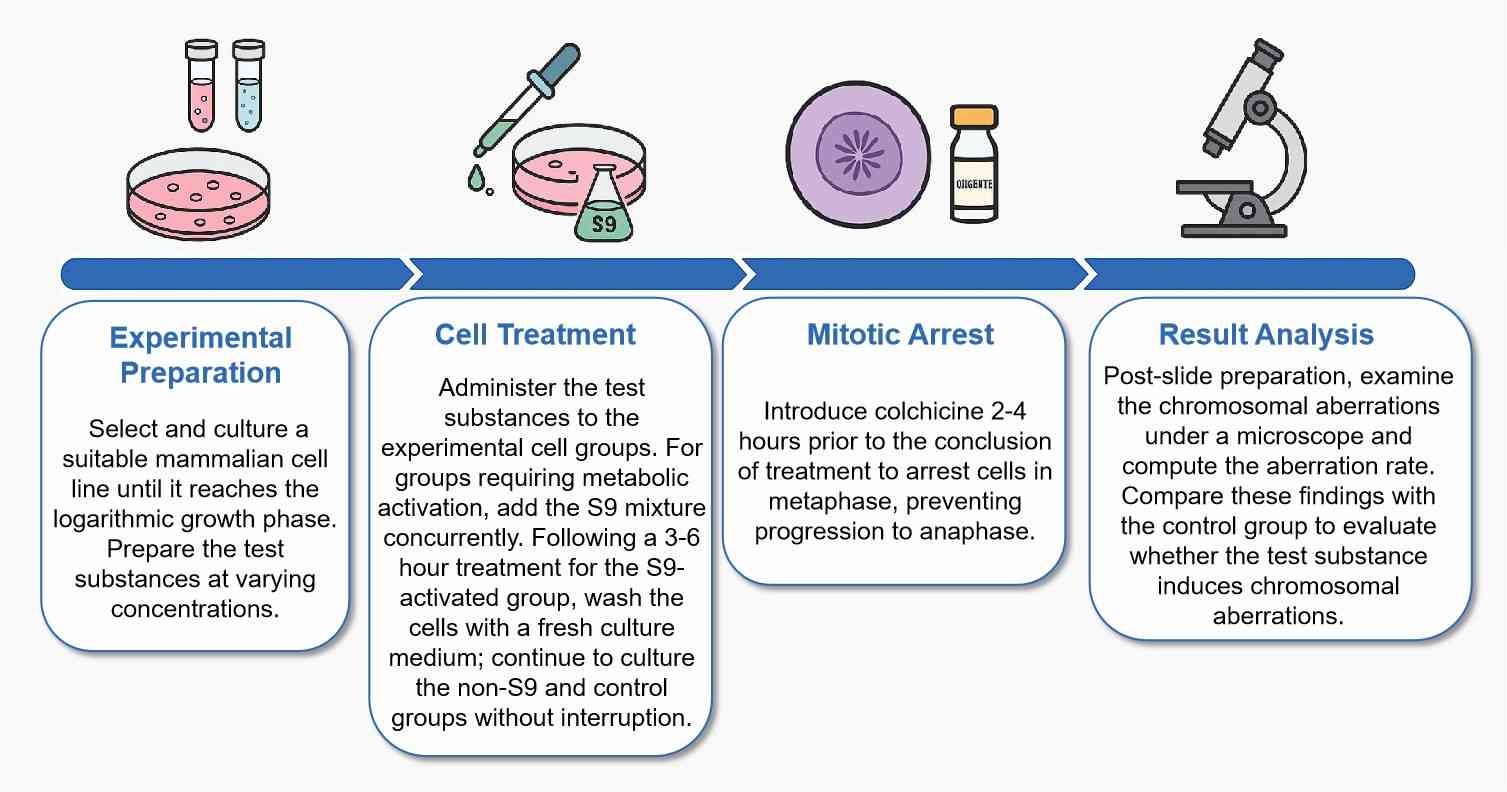
Protocol
| In vitro mammalian chromosomal aberration test | Details |
| Cell types |
|
| Concentration | ≥3 effective concentrations + negative control/positive control |
| Exposure Time |
|
| Metabolic system | Aroclor-1254 induced rat liver S9 |
| Compound requirements | 100 μL DMSO* solution, at 200-fold highest concentration, kept at 0.5% DMSO or equivalent solid compound amount |
Our Core Advantages

Stringent Quality Control
All experiments strictly adhere to OECD 473 guidelines and Good Laboratory Practice (GLP).

Flexible Customization
Supports non-standard study designs, such as combined exposure and time-dose effect studies.

Expertise
Our team comprises experienced genetic toxicologists who ensure high-quality and reliable results.

Advanced Infrastructure
We utilize the latest technologies and equipment for accurate analysis.
FAQ
1. What is the chromosomal aberration test and its applications?
The chromosomal aberration test is a method used at the cellular level to detect changes in the structure or number of chromosomes caused by chemical substances or physical factors. It is an integral component of genetic toxicity testing, aimed at assessing the potential of chemical substances to induce genetic damage. Its applications include:
- Drug Development and Safety Assessment: Used to screen for the mutagenicity of new drugs.
- Chemical Safety Evaluation: Helps determine the safety of industrial chemicals, food additives, cosmetics, etc.
- Environmental Monitoring: Evaluates the genetic toxicity of environmental pollutants, such as heavy metals and radiation.
2. What causes chromosomal aberrations?
Chromosomal aberrations can be induced by various factors, including:
- Chemical Agents: Such as mutagenic drugs, industrial chemicals, and pesticides.
- Physical Factors: Such as ionizing radiation and ultraviolet exposure.
- Biological Factors: Such as viral infections.
- Genetic Factors: Certain genetic mutations can also affect chromosomal stability.
3. How to interpret test results?
- Positive Results: If the chromosomal aberration frequency in the test substance-treated group is significantly higher than in the control group and exhibits a dose-response relationship, it indicates the substance has genetic toxicity.
- Negative Results: If there is no significant difference in the chromosomal aberration frequency between the test substance-treated group and the control group, and no noticeable increase in aberration frequency is observed across various dose levels, it can be preliminarily concluded that the substance does not have genetic toxicity.
Reference
- Paul Karthika, and D Paul. Genotoxicity: A real concern of the pharmaceutical industry." WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES 4.2(2015):1124-1153.
Explore Other Options