Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model
- Service Details
- Features
- FAQ
- Explore Other Options
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a disorder caused by the uncontrolled growth of liver fat that occurs without alcohol, which is one of the most widespread forms of liver disease in the world. The pathology can vary from plain fatty liver to metabolic dysfunction-associated non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (MASH, formerly NASH) and evolve into liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) or liver failure. Today, there are as many as 29.62% cases of NAFLD across Asia and there is currently no effective FDA-approved therapy, so new therapeutic options are desperately needed.
As we attempt to investigate the causes and targets of NAFLD and MASH, animal models become an indispensable and valuable resource. It is particularly important to use useful preclinical models to mimic human pathology and investigate drug activity. Nowadays, the most commonly adopted animal models are diet-induced, chemical-induced and gene-editing models. With such mouse models, scientists can study how diseases are created in greater detail and create new drugs faster.
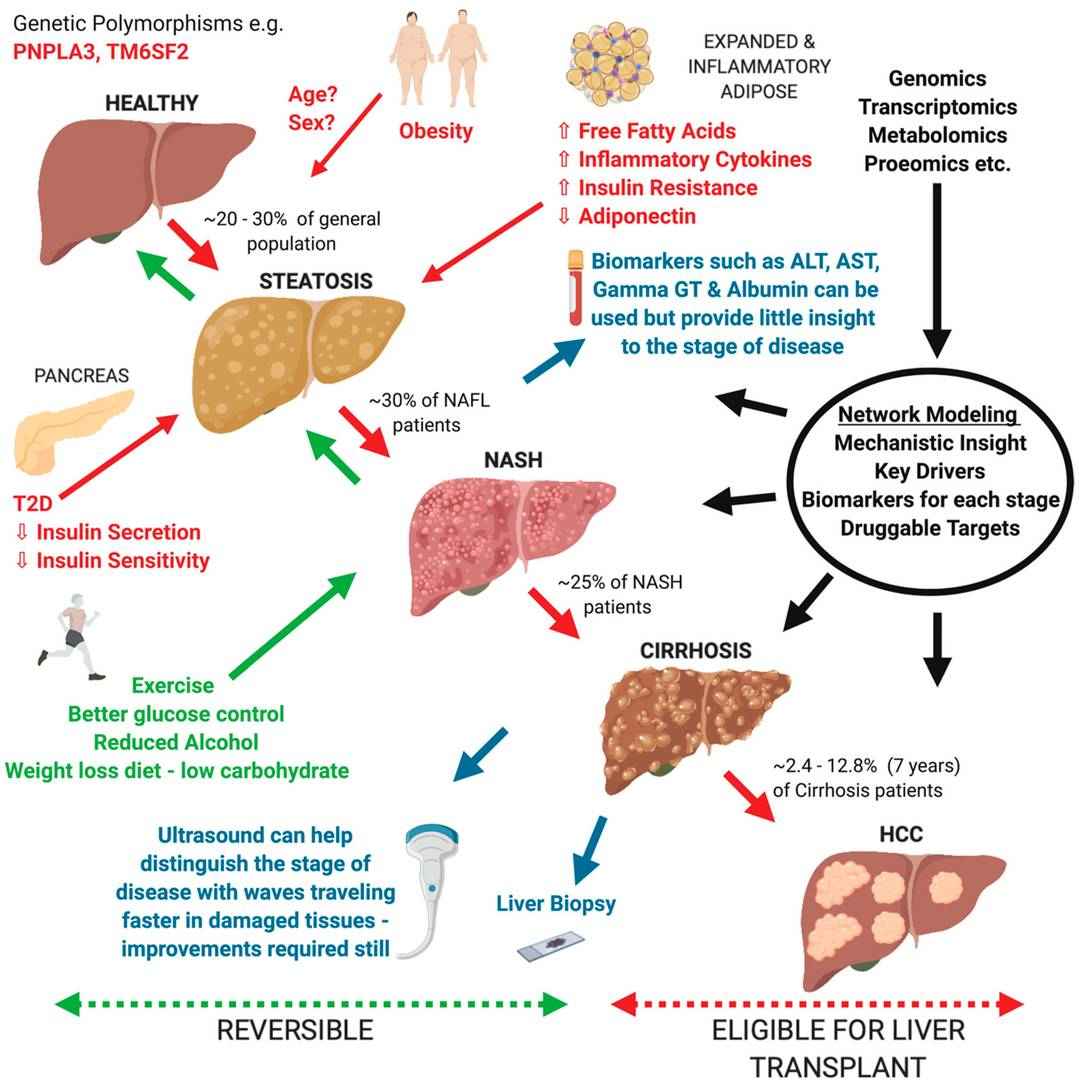 Fig. 1. Overview of current understanding of Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) progression from a healthy liver to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (Blencowe M, Karunanayake T., et al., 2019).
Fig. 1. Overview of current understanding of Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) progression from a healthy liver to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) (Blencowe M, Karunanayake T., et al., 2019).
Creative Bioarray's Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Models Include but not Limited to:
Diet models
- Methionine and Choline Deficient (MCD) Diet-Induced NAFLD Model
Mechanism: Methionine is an amino acid that provides methyl groups to create choline in the body. Choline is found in molecules such as phosphatidylcholine and acetylcholine. The lack of choline reduces liver phospholipid production and slows down lipoprotein (specifically very low-density lipoprotein VLDL) production, leading to liver triglyceride buildup and fat accumulation.
The induction involves feeding experimental animals with high-sucrose (approx. 40%) and high-fat (approx. 10%) but methionine- and choline-deficient diets over a 3-4 weeks period. The animal models may exhibit glucose metabolism changes without insulin resistance. This model is frequently used for early drug screening and ferroptosis research. - Choline-Deficient L-Amino Acid Defined (CDAA) Diet-Induced NAFLD Model
Mechanism: Similar to the MCD diet model, the lack of choline leads to triglyceride accumulation within the liver, resulting in fatty liver.
Animals are fed a high-sugar and high-fat L-amino acid mixture lacking choline. The modeling process can last from weeks to months as animals maintain body weight but develop insulin resistance and significantly elevated lipid levels. - High-Fat Diet (HFD) Induced NAFLD Model
Mechanism: HFD contains abundant precursors for lipid synthesis, promoting hepatic lipid accumulation leading to fatty liver.
Animals are provided with high-fat feed. The modeling period spans 16-20 weeks, effectively simulating early human NAFLD pathological features, including lipid metabolism disorders, liver fat accumulation, and insulin resistance. - Gubra-Amylin NASH (GAN) Diet-Induced NAFLD Model
Mechanism: GAN diet, composed of 40% kcal from high-fat sources, 22% fructose, 10% sucrose, and 2% cholesterol, mimics key aspects of human disease by replicating a dietary profile high in fats and sugars. This composition promotes excessive hepatic lipid accumulation, leading to the development of fatty liver and progressing towards features characteristic of NAFLD.
Animals are fed the GAN diet to induce NAFLD, effectively simulating early human NAFLD pathological features, including obesity, lipid metabolism disorders, hepatic fat accumulation, and insulin resistance.
Chemically induced model
- Carbon Tetrachloride (CCl4) Induced NAFLD Model
Mechanism: CCl4 is hepatotoxic and generates radicals and promotes liver peroxidation, leading to rapid liver steatosis, lipid peroxidation and hepatocyte membrane destruction. These changes produce excessive ECM synthesis and fibrosis. It is possible for metabolites to activate Kupffer cells and drive inflammation and hepatocyte destruction, in a manner similar to NAFLD.
CCl4 is dissolved in vegetable oil and administered via oral gavage, intraperitoneal, or subcutaneous injection. This short-duration model, usually about 8 weeks, results in clear pathological alterations in fatty liver.
Transgenic model
- Lepob/ Lepob/ (ob/ob) Mouse Model
ob/ob mice exhibit spontaneous mutation in the ob gene, hindering normal synthesis of leptin, an appetite-suppressing hormone. This defect precipitates metabolic disorders such as overeating, obesity, hyperinsulinemia, hyperlipidemia, and significant hyperglycemia. Consequently, these imbalances disrupt hepatic fat intake and output, leading to fatty liver, progressing towards NASH, liver fibrosis, and potentially cirrhosis.
Endpoints & Readouts
Histological examination
Assessment of fat degeneration, inflammation, and fibrosis severity in hepatic tissues.
Biochemical markers
Serum liver enzyme levels, such as ALT, AST, and GGT, along with triglycerides and cholesterol as indicators of liver damage.
Imaging
ultrasound, CT, MRI, or MRS to evaluate liver morphology, size, and fat content.
Metabolic syndrome indicators
Determine if models demonstrate metabolic syndrome characteristics similar to human NAFLD, such as insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, and hypertension.
Available Services
- Animal model construction.
- Pathological analysis: Comprehensive histopathological assessments including steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis evaluation.
- Metabolic phenotyping: Analysis of body weight, glucose, lipids, and insulin sensitivity.
- Data reporting and technical support.
Available Species
- Mouse
- Rat
Features
Employ multiple construction methods to precisely simulate human NAFLD pathophysiological processes
Maintain strict experimental controls to ensure model stability and reproducibility, enhancing experimental efficiency and data reliability.

Comprehensive model evaluation standards confirm the effectiveness of animal models.

Provide customized analysis services and plans based on client research needs.
FAQ
1. How to select the appropriate model?
When choosing the right NAFLD model, clarify your research objectives. For early disease effects, diet-induced models are effective in rapidly inducing hepatic steatosis. For studies involving genetic factors, gene-edited models are suitable for mimicking human genetic susceptibility. If evaluating drug therapeutic effects, composite models that closely reflect human disease complexity and pathology are preferable. Contact our team with your specific needs for guidance in selecting the ideal model.
2. What are the applicable ranges of your models?
Our NAFLD models have broad applications, supporting basic research, drug screening, mechanistic exploration, and evaluation of potential treatment efficacy and safety. These models serve as crucial platforms for scientific research and can assist the pharmaceutical industry in accelerating new drug development and optimizing disease treatment strategies.
3. Are your models suitable for drug testing?
Yes, our NAFLD models are applicable for drug testing. Utilizing our animal models, researchers can observe the hepatic targeting effects of drugs, evaluate their metabolic pathways and assess effectiveness and safety via relevant biomarkers. Our service team provides professional guidance and data support to ensure smooth progress of your drug testing studies.
Reference
- Blencowe M, Karunanayake T, et al. Network Modeling Approaches and Applications to Unravelling Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Genes. 2019. 10(12), 966.