Methods of Parallel Artificial Membrane Permeability Assays
Parallel artificial membrane permeability assay (PAMPA) has emerged as a valuable tool in pharmaceutical research for evaluating the permeability of drug compounds. Through various methods, PAMPA has been employed to assess gastrointestinal permeability (GIT-PAMPA), skin permeability (skin-PAMPA), and blood-brain barrier permeability (BBB-PAMPA).
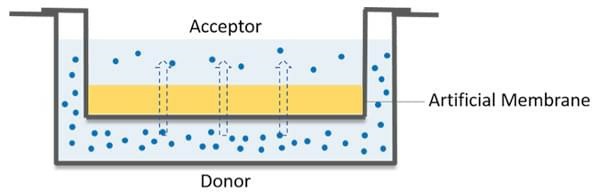 Fig. 1 The schematic diagram of the PAMPA model.
Fig. 1 The schematic diagram of the PAMPA model.
Gastrointestinal Permeability (GIT-PAMPA)
Gastrointestinal permeability (GIT-PAMPA) is critical in predicting oral absorption and bioavailability of pharmaceutical compounds. GIT-PAMPA involves the use of artificial membranes that mimic the physiological conditions of the gastrointestinal tract, including the pH gradient and barrier properties, to assess the permeation of drug compounds.
The assessment of gastrointestinal permeability is essential for understanding the behavior of drugs in the digestive system and predicting their oral absorption. Through GIT-PAMPA, researchers and pharmaceutical companies can identify potential candidates for oral drug delivery and optimize the development of pharmaceutical formulations for improved gastrointestinal permeability and bioavailability.
Skin Permeability (Skin-PAMPA)
The assessment of skin permeability is crucial in understanding dermal absorption and predicting the ability of drug compounds to penetrate the skin barrier. Through Skin-PAMPA, researchers gain insights into the behavior of drug compounds in the context of transdermal delivery, allowing for the identification of promising candidates for topical drug delivery systems.
Skin-PAMPA methods facilitate the rapid screening of a wide range of drug compounds to evaluate their skin permeation characteristics. This high-throughput screening approach accelerates the identification of lead compounds with favorable skin permeability, contributing to the development of innovative transdermal and topical pharmaceutical formulations.
Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability (BBB-PAMPA)
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable border that separates the circulating blood from the brain and extracellular fluid in the central nervous system. It plays a crucial role in protecting the brain from potentially harmful substances while allowing essential nutrients and medicines to enter. Evaluating the permeability of drug compounds across the BBB is critical for the development of therapeutics targeting neurological disorders and diseases.
The BBB-PAMPA is a method specifically designed to assess the ability of drug candidates to cross the BBB and reach the central nervous system. This in vitro assay utilizes an artificial lipid membrane to mimic the properties of the BBB, allowing researchers to measure the passive permeability of drug compounds through this synthetic membrane system. BBB-PAMPA provides a high-throughput and cost-effective means of evaluating brain permeability, enabling researchers to predict the ability of drug candidates to penetrate the BBB and reach their intended targets within the central nervous system.
Creative Bioarray Relevant Recommendations
Creative Bioarray is a reliable PAMPA provider, offering various PAMPA assay kits that allow clients to design and optimize their drug discovery studies according to their research conditions.
| Cat. No. | Product Name |
| DPK-YS001 | SuperQuick® GIT-PAMPA Kit |
| DPK-YS002 | SuperQuick® Skin-PAMPA Kit |
| DPK-YS003 | SuperQuick® BBB-PAMPA Kit |