Blood-Brain-Barrier Assay
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is the protective barrier comprised of brain capillary endothelial cells (BCECs) that separates the central nervous system (CNS) from the circulatory system. Tight junctions between cells and specific transporters expressed at the BBB tightly regulate what can enter the brain allowing the maintenance of microenvironment needed for normal brain function and protection from toxins and pathogens. However, the brain tissue faces significant drug delivery obstacles due to the barrier's restrictive selective permeability. Successful penetration evaluation of candidate molecules through the BBB is essential for developing functional therapeutic strategies and delivery systems in CNS disorder treatment.
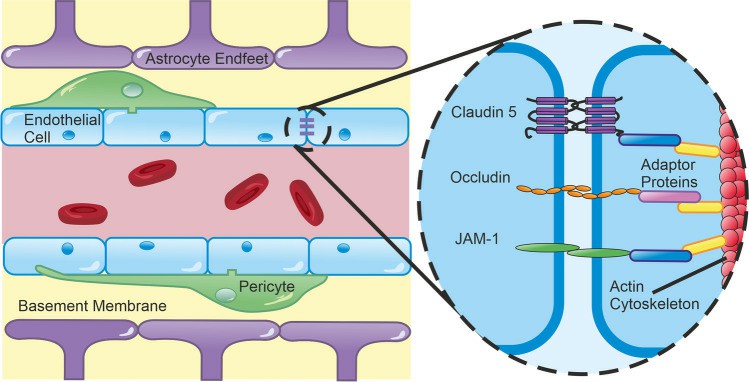 Fig. 1. Structural Elements of the BBB (Harris WJ, Asselin MC, et al., 2023).
Fig. 1. Structural Elements of the BBB (Harris WJ, Asselin MC, et al., 2023).
Creative Bioarray offers a comprehensive portfolio of both in vitro and in vivo BBB assays for measurement of brain penetration, transporter liabilities and more to aid in lead optimization and candidate selection. Our services combine validated animal models, advanced imaging and sampling techniques, and physiologically relevant cell-based models to deliver robust, translational data for small molecules and selected biologics.
Comprehensive Service Portfolio
In vitro blood-brain-barrier assays
Our in vitro assays offer high-throughput, cost-effective screening capabilities for early-stage discovery, allowing for detailed mechanistic studies of drug transport.
Available in vitro BBB models
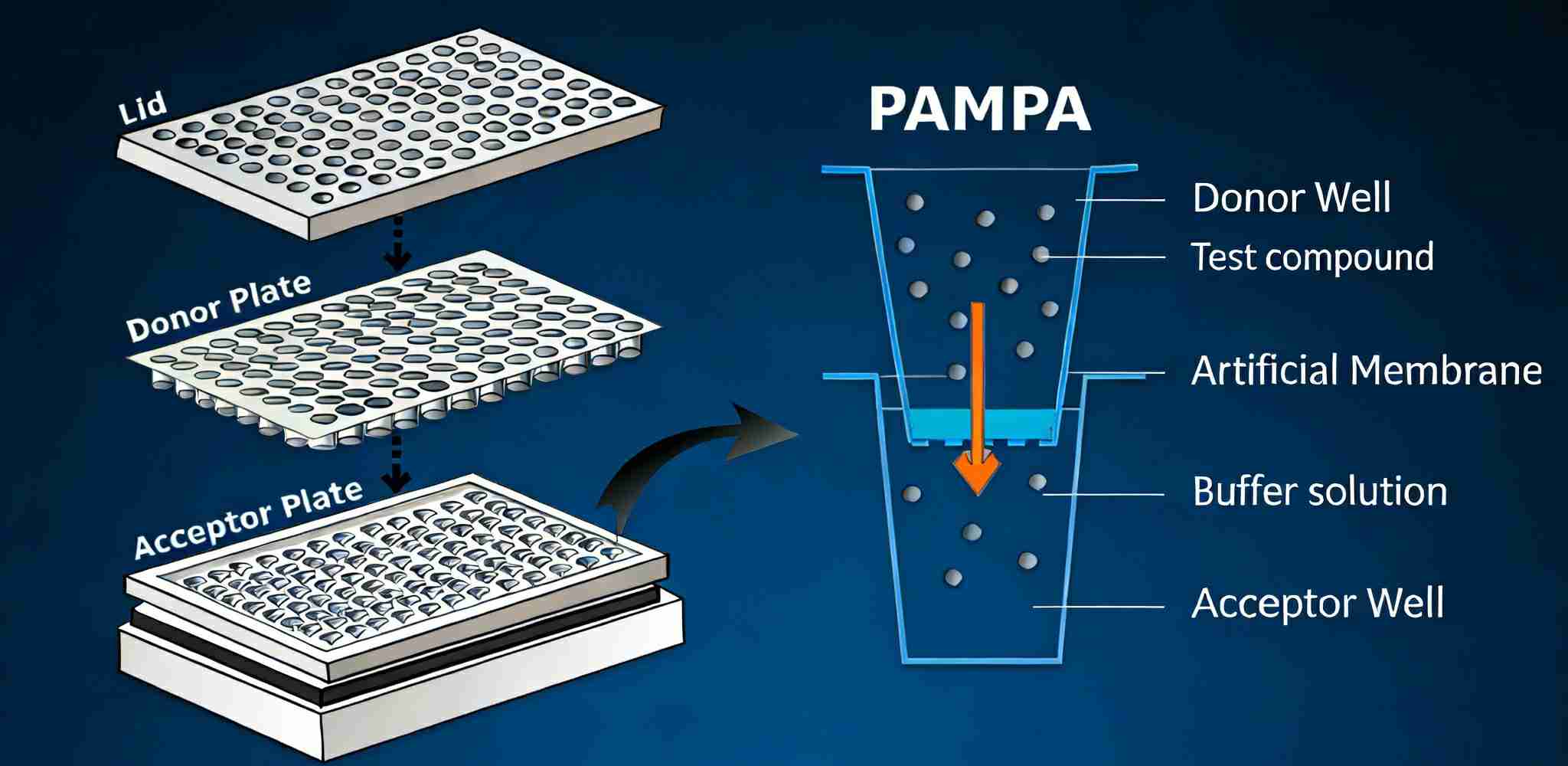
1. BBB PAMPA (Parallel Artificial Membrane Permeability Assay)
A non-cell-based assay designed for rapid assessment of passive BBB permeability. BBB PAMPA is ideally suited for early-stage compound triaging and structure–permeability relationship analysis.
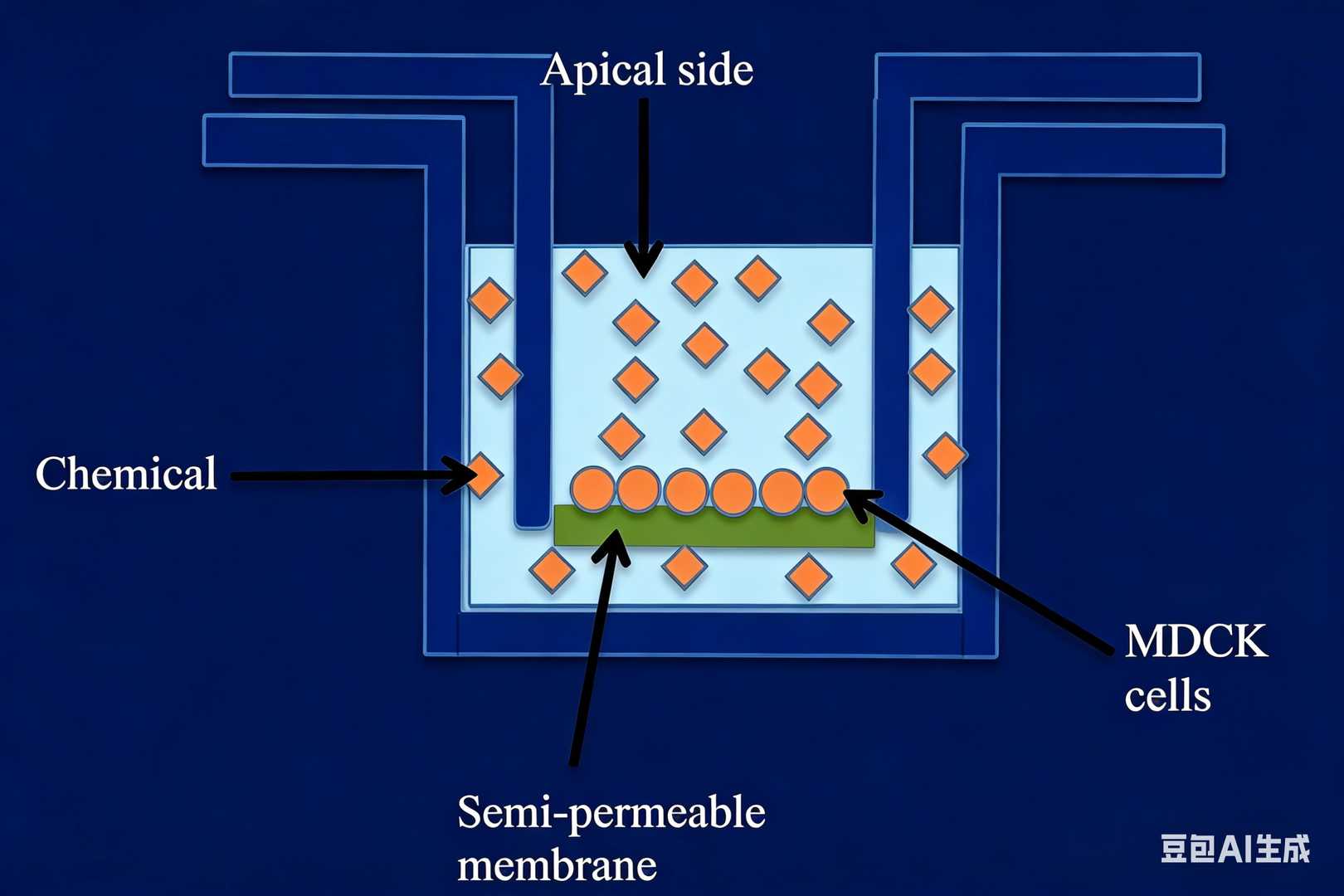
2. MDCK I/II–MDR1 BBB Model
A transporter-expressing epithelial model used to evaluate P-glycoprotein (P-gp/MDR1)-mediated efflux liability.
- Includes both MDCK I–MDR1 and MDCK II–MDR1 formats
- MDCK I–MDR1 offers superior monolayer tightness and lower paracellular leakage
- Suitable for identifying active efflux and ranking CNS penetration potential
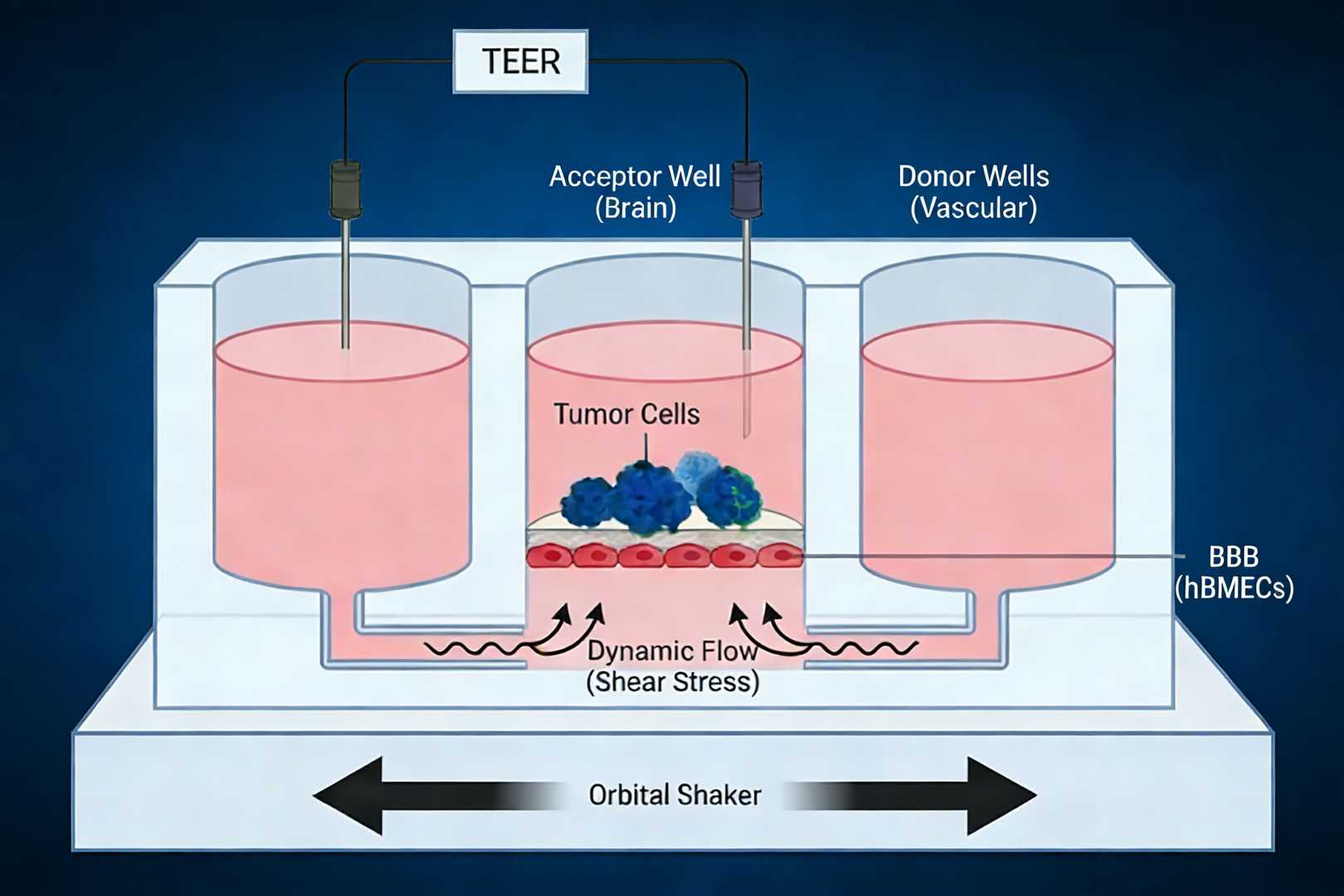
3. Dynamic BMEC BBB Model (Co-culture Compatible)
This advanced model goes beyond static Transwell systems by incorporating controlled fluid dynamics to better mimic in vivo BBB physiology.
- Tricompartmental Design: Features two "Vascular" donor wells and one "Brain" acceptor well.
- Dynamic Flow System: Utilizing an orbital shaker, the system generates a hydrostatic pressure gradient that drives unidirectional flow beneath the BBB cell layer. This flow mimics blood-induced shear stress, which is critical for maintaining a mature, physiologically tight endothelial barrier.
- Versatility: The central acceptor well is seeded with a tight monolayer of hBMEC/D3 cells. It can remain empty for permeability quantification or be seeded with target cells (e.g., tumor cells) to assess drug efficacy post-permeation simultaneously.
Key in vitro endpoints
Permeability: Papp/Pe measurements (A→B and B→A) to assess passive diffusion and active efflux.
Barrier Integrity: TEER monitoring to evaluate tight junction formation and stability.
Paracellular Transport: Flux of tracers (e.g., sodium fluorescein) to check leakage.
Transporter Activity: Functional assessment of P-gp/MDR1 and BCRP using substrates/inhibitors.
Cell Health: Cytotoxicity and morphology check to ensure reliable permeability data.
Workflow
We also offer complementary services to provide a holistic view of compound absorption and distribution, including MDR1-MDCK Permeability Assay and Parallel Artificial Membrane Permeability Assay (PAMPA).
In vivo blood-brain-barrier assays
We provide comprehensive rodent studies to validate CNS exposure in a physiological environment, accounting for blood flow, systemic clearance, and complex tissue binding.
Available in vivo Services

1. Healthy Rodent Models: Standard PK studies in mice and rats.
2. Disease Models: Pathological models for Alzheimer's (AD), cerebral ischemia (stroke), and glioma.
3. Advanced Sampling:
- CSF Sampling: Optional collection of Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) for site-specific exposure analysis.
- Tissue Distribution: Precise brain tissue harvesting and processing.
Key in vivo endpoints
Brain/Plasma Concentration & Free Fraction: Quantitative LC-MS/MS analysis of total and unbound drug in brain (homogenate or microdialysis) to determine CNS exposure.
Brain/Plasma Ratios: Kp and Kp,uu calculations as gold-standard metrics for unbound drug penetration.
BBB Integrity: Tracer extravasation assays (e.g., Evans Blue, fluorescent markers) and histology to assess barrier disruption.
Imaging: Dynamic contrast MRI or PET/SPECT for longitudinal, regional distribution and translational evaluation.
Molecular Analysis: Measure BBB activation markers via gene expression (RT-PCR) and protein levels (Western blot, immunohistochemistry).
Workflow
Why Choose Our BBB Assays?
Integrated Platform:
Our assays provide a streamlined platform that bridges high-throughput in vitro screens (PAMPA/MDCK) to in vivo prediction.
Physiologically Relevant Models:
Utilization of advanced co-culture systems, including human iPSC-derived NVU models, to achieve superior barrier tightness and predictive capacity.
Assay Flexibility:
We will work with you to select the best assays and models to support your small molecule, biologics (antibodies, peptides) and/or gene therapy projects.
High Sensitivity Analytics:
Our experienced scientists will utilize state-of-the-art LC-MS/MS to quantify drug concentrations in plasma and brain for accurate determination of Kp,uu.
FAQ
What compound information is required prior to testing?
Molecule type, MW, purity, pKa, solvent and solubility, LC-MS profile are recommended to optimize dosing and analytical protocols.
How to select appropriate animal models?
While healthy mice are great for initial screening studies, disease models are useful for understanding how the BBB is altered in disease. We will help you decide on the best model(s) to meet your research objectives.
How do you ensure the in vitro BBB model is an intact monolayer?
Barrier integrity is validated by measuring Transendothelial Electrical Resistance (TEER) and ensuring it meets a threshold standard, in addition to ensuring tight junction-impermeable paracellular tracers (e.g. Lucifer Yellow) do not flux.
Which in vitro model best translates to human brain exposure?
Our Dynamic BMEC BBB model has been shown to best translate to brain exposure in humans of all the in vitro models we offer. This model takes into account fluid flow by exposing cells to a physiologically relevant level of shear stress. Exposure to fluid flow has been shown to upregulate brain endothelial cell maturation and promote tight junction formation and expression of functional transporters making this model more predictive of the in vivo BBB compared to static models.
When should I run in vivo BBB studies?
In vivo studies are conducted once the lead compounds have been prioritized (post in vitro ADME and transporter screens) or once dosing regimens and estimates of brain exposure are needed to conduct efficacy studies and PK/PD modeling.
Reference
- Harris WJ, Asselin MC, et al. In vivo methods for imaging blood-brain barrier function and dysfunction. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2023. 50(4):1051-1083.
Explore Other Options