Thyroid Tumor Cells
- Background
- Applications
- Scientific Data
The thyroid gland, a master regulator of metabolism, plays a pivotal role in maintaining physiological homeostasis. However, the transformation of thyroid cells into tumor cells poses a significant health concern. The thyroid gland consists of follicular and parafollicular cells, each with distinct functions. Follicular cells are responsible for thyroid hormone synthesis, while parafollicular cells, also known as C cells, secrete calcitonin. The transformation of these cells into tumor cells is a multifaceted process involving genetic mutations, epigenetic alterations, and environmental factors.
The Biology of Thyroid Tumor Cells
- Genetic alterations. Mutations in key genes such as BRAF, RAS, and RET are implicated in the pathogenesis of thyroid cancer. These mutations disrupt normal cellular signaling pathways, leading to uncontrolled proliferation and tumor formation. For instance, the BRAF V600E mutation is commonly associated with papillary thyroid cancer, the most prevalent thyroid cancer subtype.
- Epigenetic changes. Epigenetic modifications, including DNA methylation and histone modification, also contribute to thyroid tumor development. These changes can silence tumor suppressor genes or activate oncogenes, fostering an environment conducive to cancer growth.
- Tumor heterogeneity. Thyroid tumors exhibit significant heterogeneity, both at the genetic and histopathological levels. This diversity is reflected in the range of thyroid cancer types, including papillary, follicular, medullary, and anaplastic thyroid cancers. Each type presents unique challenges in terms of diagnosis and treatment, necessitating a tailored approach to patient management.
Molecular Testing
Molecular testing of thyroid tumor cells has revolutionized the diagnostic process. Techniques such as next-generation sequencing (NGS) allow for the detection of specific mutations, aiding in the diagnosis and prognosis of thyroid cancer. For example, the presence of the BRAF V600E mutation can indicate a more aggressive tumor phenotype.
Therapeutic Development
Thyroid tumor cells serve as essential models for developing targeted therapies. The unique genetic profile of these cells provides opportunities for precision medicine, where treatments are tailored to the individual's genetic makeup. For example, tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) such as sorafenib and lenvatinib have been approved for advanced thyroid cancers, demonstrating significant improvements in progression-free survival. These agents target key signaling pathways involved in tumor growth and angiogenesis, offering a more personalized approach to treatment.
Model for Cancer Research
Thyroid tumor cells provide a valuable model for studying fundamental aspects of cancer biology. Researchers use these cells to investigate processes such as angiogenesis, metastasis, and tumor immune evasion. Insights gained from these studies contribute to a broader understanding of cancer and may lead to the development of new therapeutic strategies applicable to various cancer types.
NRXN2 Suppressed THCA Cell Proliferation and Metastasis
Thyroid cancer (THCA) is a common endocrine malignant tumor, and the global incidence of THCA has increased significantly. Neurexin 2 (NRXN2) is involved in the progression of some diseases. Fig. 1a presents that, in comparison with adjacent normal tissues, the expression of NRXN2 mRNA was largely reduced in 35 paired tissues of THCA patients (P < 0.05). Besides, Fig. 1b demonstrates a decreased expression of NRXN2 mRNA in CAL-62, BCPAP, TPC-1, and 8505C THCA cell lines, compared to that in human normal thyroid epithelial cell line (Nthy-ori 3-1) (P < 0.05). Our results implied that NRXN2 was probably implicated in THCA initiation and development. The CCK-8 assay was exploited to evaluate the impacts of NRXN2 on the proliferation of NRXN2-overexpressed THCA cells. OVER-NRXN2 expression cassettes were designed for overexpressing NRXN2. Our data exposed that OVER-NRXN2 had a high overexpression efficiency. NRXN2 was overexpressed by transfection with OVER-NRXN2 in CAL-62 and TPC-1 cells (P < 0.001, Fig. 1c, d). Overexpressing NRXN2 greatly retarded THCA cell proliferation (P < 0.05, Fig. 1e, f).
The Transwell assay was performed to verify if NRXN2 could regulate THCA cell migration and invasion in vitro. After overexpressing NRXN2 in CAL-62 and TPC1 cells, cell migration and invasion assays were conducted. The result showed that the number of adhered cells on the lower chamber membrane surface was significantly decreased compared to the control group (Fig. 2a-h). These results indicated that NRXN2 could suppress THCA cell metastasis.
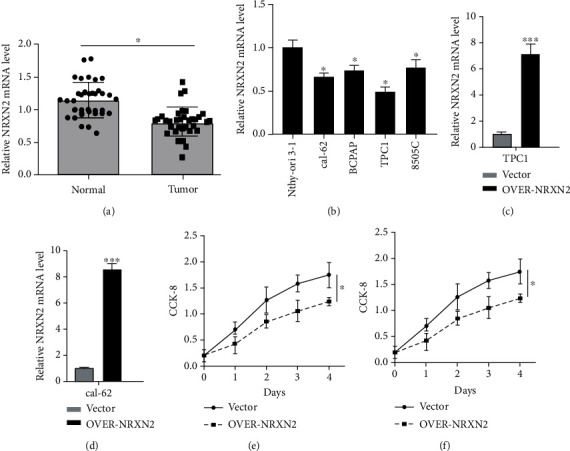 Fig. 1 NRXN2 expression was downregulated in THCA. (a)
Differences in NRXN2 expression between 35 THCA tissues and matched adjacent tissues. (b) Differences in NRXN2
expression between 4 different THCA cell lines (CAL-62, BCPAP, TPC-1, and 8505C) and human thyroid cell lines
(Nthy-ori 3-1). (c, d) Determination of NRXN2 expression level in OVER-NRXN2 transfected TPC1 cell line and
OVER-NRXN2 transfected CAL-62 cell line. (e, f) CCK-8 analysis of the influence of NRXN2 overexpression on TPC1
cell proliferation, and CAL-62 cell proliferation. (Ma C, et al, 2021)
Fig. 1 NRXN2 expression was downregulated in THCA. (a)
Differences in NRXN2 expression between 35 THCA tissues and matched adjacent tissues. (b) Differences in NRXN2
expression between 4 different THCA cell lines (CAL-62, BCPAP, TPC-1, and 8505C) and human thyroid cell lines
(Nthy-ori 3-1). (c, d) Determination of NRXN2 expression level in OVER-NRXN2 transfected TPC1 cell line and
OVER-NRXN2 transfected CAL-62 cell line. (e, f) CCK-8 analysis of the influence of NRXN2 overexpression on TPC1
cell proliferation, and CAL-62 cell proliferation. (Ma C, et al, 2021)
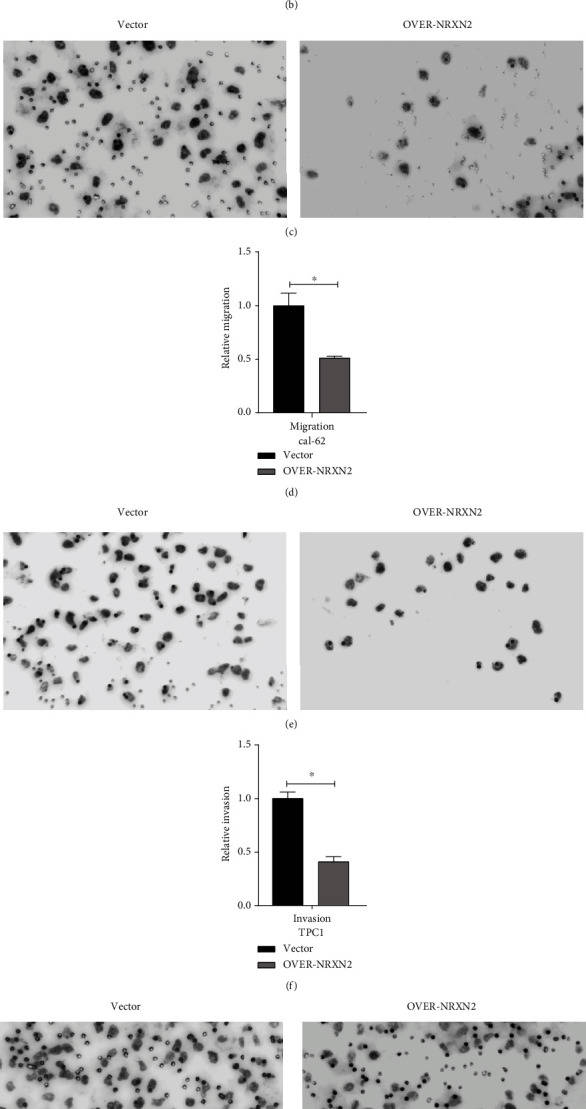 Fig. 2 NRXN2 decreased cell metastasis in THCA cells.
(a, b) Transwell assay analysis of the impacts of NRXN2 overexpression on TPC1 cell invasion. (c, d) Transwell
assay analysis of the impacts of NRXN2 overexpression on TPC1 cell migration. (e, f) Transwell assay analysis of
the impacts of NRXN2 overexpression on CAL-62 cell invasion. (g, h) Transwell assay analysis of the impacts of
NRXN2 overexpression on CAL-62 cell migration. (Ma C, et al, 2021)
Fig. 2 NRXN2 decreased cell metastasis in THCA cells.
(a, b) Transwell assay analysis of the impacts of NRXN2 overexpression on TPC1 cell invasion. (c, d) Transwell
assay analysis of the impacts of NRXN2 overexpression on TPC1 cell migration. (e, f) Transwell assay analysis of
the impacts of NRXN2 overexpression on CAL-62 cell invasion. (g, h) Transwell assay analysis of the impacts of
NRXN2 overexpression on CAL-62 cell migration. (Ma C, et al, 2021)
Expression of Stc1 in Normal Thyroid and Thyroid Tumor Cells
Stanniocalcin (STC) is a secreted glycoprotein known to regulate serum calcium and phosphate homeostasis. Two STCs, STC1 and STC2, are present in fish and mammals and are expressed in a wide variety of tissues, including the heart, lung, liver, adrenal gland, kidney, prostate, and ovary for STC1, and pancreas, spleen, kidney, and skeletal muscle for STC2. In recent years, the relationship of STC expression to cancer was described in various tissues including the colon, breast, ovary, liver, and esophagus. The higher expression levels of STC1 and STC2 are generally correlated with poor prognostic outcomes of cancers.
STC1 expression was examined in four human FTC-derived cell lines, FTC133, FTC236, FTC238, and RO82-W-1, and one anaplastic thyroid carcinoma-derived cell line, 8305C, by qRT-PCR (Fig. 3A). No mouse thyroid cancer-derived cell lines were available. The three human FTC lines were derived from the same patient; the higher the number, the more distant the metastasis was, which can be considered less differentiated. The expression levels of STC1 mRNA increased as the number became larger in FTC lines of cells, while STC1 expression was lower in RO82-W-1 derived from the metastasis of differentiated follicular carcinoma cells than FTC236, and 8305C obtained from the undifferentiated thyroid carcinoma, had similar STC1 expression level to FTC236. Levels of STC1 mRNA expression in FTC236, FTC238, RO82-W-1, and 8305C were all significantly higher than that of FTC133. STC1 mRNA expression of normal human thyroid was obtained at similar levels to that of RO82-W-1. Western blotting demonstrated the highest protein expression found for FTC238 cells (Fig. 3B). Thus, it appears that both mRNA and protein expression levels for STC1 are roughly correlated with each other and that the expression is roughly inversely correlated with the differentiation status of cells.
Immunohistochemistry was carried out to determine the pattern of STC1 expression in mouse and human thyroids. The results showed that the STC1 antigen was weakly detected in nuclei of many normal mouse thyroid cells with occasional strong expression (Fig. 4A). Focal strong STC1 staining was observed mainly in the cytoplasm of mouse thyroid adenoma tissues (Fig. 4B). Normal human thyroid follicular epithelium was often, but not always, immunoreactive in the nucleus (Fig. 4C). Some human thyroid carcinomas and a thyroid carcinoma cell line had focal strong STC1 immunoreactivity in the nucleus (Fig. 4D-F).
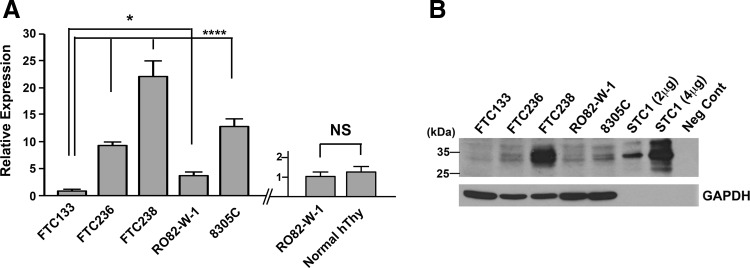 Fig. 3 Analysis of STC1 expression in thyroid
cancers. (A) qRT-PCR analysis of STC1 expression in human thyroid carcinoma derived FTC133, FTC236,
FTC238, RO82-W-1, and 8305C cells (left). qRT-PCR analysis of STC1 expression in the RO82-W-1 thyroid
carcinoma cell line and normal human thyroid tissue (right). (B) Representative Western blotting of STC1 protein
expression using a whole cell lysate of the aforementioned cells. (Hayase S, et al., 2015)
Fig. 3 Analysis of STC1 expression in thyroid
cancers. (A) qRT-PCR analysis of STC1 expression in human thyroid carcinoma derived FTC133, FTC236,
FTC238, RO82-W-1, and 8305C cells (left). qRT-PCR analysis of STC1 expression in the RO82-W-1 thyroid
carcinoma cell line and normal human thyroid tissue (right). (B) Representative Western blotting of STC1 protein
expression using a whole cell lysate of the aforementioned cells. (Hayase S, et al., 2015)
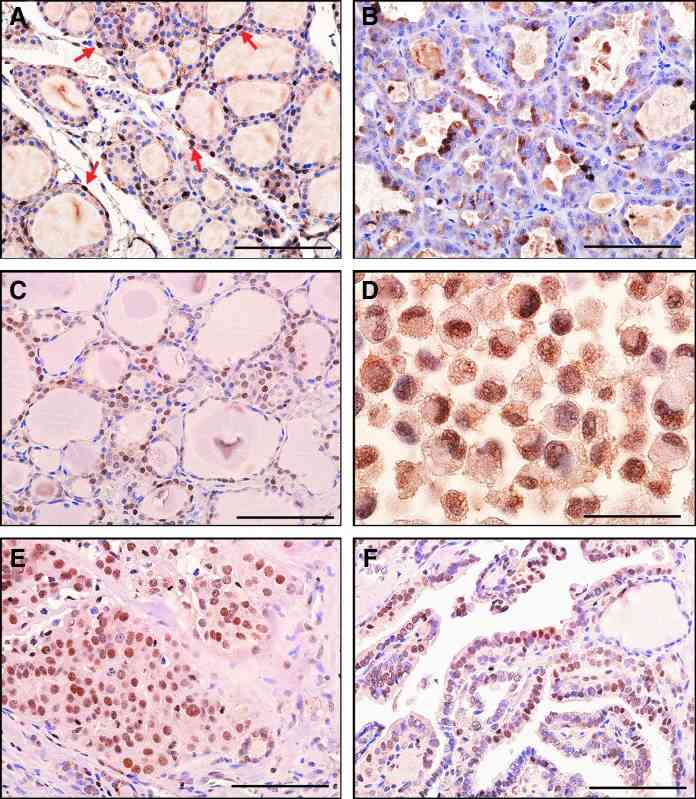 Fig. 4 STC1 antigen/protein expression in
thyroid tissues. (A) Histology of normal mouse thyroid. (B) Mouse thyroid adenoma showing focal cytoplasmic
staining. (C) Histology of normal human thyroid. Note nuclear staining. (D) Human RO82-W-1 thyroid carcinoma
cell line (cell pellet) showing nuclear staining. (E) Human thyroid follicular carcinoma. (F) Human papillary
thyroid carcinoma showing weak nuclear staining. (Hayase S, et al., 2015)
Fig. 4 STC1 antigen/protein expression in
thyroid tissues. (A) Histology of normal mouse thyroid. (B) Mouse thyroid adenoma showing focal cytoplasmic
staining. (C) Histology of normal human thyroid. Note nuclear staining. (D) Human RO82-W-1 thyroid carcinoma
cell line (cell pellet) showing nuclear staining. (E) Human thyroid follicular carcinoma. (F) Human papillary
thyroid carcinoma showing weak nuclear staining. (Hayase S, et al., 2015)
Filters Clear all filters
Species
- African clawed frog (1)
- American mink (1)
- Asian tiger mosquito (1)
- Atlantic salmon (1)
- Bluegill (2)
- Bluestriped grunt (1)
- Bovine (7)
- Brazilian free-tailed bat (1)
- Brown bullhead (2)
- Cabbage looper (1)
- Cabbage moth (6)
- Cat (4)
- Central mudminnow (1)
- Chicken (3)
- Chinese hamster (5)
- Chinook salmon (2)
- Chum salmon (1)
- Coho salmon (1)
- Common carp (2)
- Cotton-top tamarin (1)
- Dog (2)
- Fall armyworm (3)
- Fathead minnow (2)
- Fruit fly (1)
- Gilthead sea bream (2)
- Golden hamster (7)
- Goldfish (6)
- Gray dwarf hamster (1)
- Green monkey (2)
- Gypsy moth (1)
- Horse (1)
- Human (998)
- Japanese eel (1)
- Japanese rice fish (7)
- Koi carp (1)
- Mouse (315)
- Mouse x Gray dwarf hamster (1)
- Mouse x Rat (20)
- Northern pike (1)
- Pig (3)
- Rabbit (2)
- Rainbow trout (3)
- Rat (115)
- Rhesus macaque (1)
- Salt marsh moth (1)
- Sheep (2)
- Snakehead murrel (2)
- Sockeye salmon (1)
- Vervet monkey (2)
- Zebrafish (2)
Source
- Abdomen (1)
- Abdomen Metastasis (2)
- Adipose (2)
- Adrenal Gland (8)
- Adrenal Gland Metastasis (2)
- Aorta (4)
- Artery (1)
- Ascites (28)
- Ascites Metastasis (37)
- Bile Duct (3)
- Bladder (25)
- Bladder Metastasis (1)
- Blastocyst (1)
- Blastula (1)
- Blood (127)
- Bone (27)
- Bone Marrow (57)
- Bone Marrow Metastasis (18)
- Bone Metastasis (6)
- Brain (55)
- Brain Metastasis (8)
- Breast (30)
- Bronchus (1)
- Caudal Peduncle (1)
- Caudal Trunk (2)
- Cecum (3)
- Cerebrospinal Fluid (1)
- Cerebrospinal Fluid Metastasis (1)
- Cervix (32)
- Colon (90)
- Connective Tissue (7)
- Cornea (3)
- Cutaneous Metastasis (1)
- Dermis (2)
- Duodenum (1)
- Embryo (29)
- Endometrium (17)
- Esophagus (44)
- Eye (12)
- Eye Socket (5)
- Fetus (3)
- Fin (9)
- Foreskin (4)
- Gallbladder (1)
- Gingiva (2)
- Globe (2)
- Glomerulus (2)
- Groin (1)
- Head Kidney (2)
- Heart (4)
- Hemolymph (1)
- Hypodermis Metastasis (5)
- Ileum (1)
- Intestine (94)
- Jejunum (1)
- kidney (1)
- Kidney (27)
- Liver (35)
- Liver Metastasis (17)
- Lung (58)
- Lung Metastasis (8)
- Lymph Node (7)
- Lymph Node Metastasis (59)
- Muscle (7)
- Muscle Metastasis (2)
- Nose (2)
- Omentum Metastasis (2)
- Oral Cavity (10)
- Ovary (21)
- Ovary Metastasis (2)
- Pancreas (19)
- Pelvic Wall Metastasis (1)
- Pelvis (1)
- Perianal Space Metastasis (1)
- Pericardial Effusion (1)
- Pericardial Effusion Metastasis (2)
- Perineus (1)
- Peripheral Blood (126)
- Peripheral Nervous System (21)
- Peritoneal Effusion (2)
- Peritoneum (1)
- Peritoneum Metastasis (1)
- Pharynx (3)
- Pituitary Gland (7)
- Pleural Effusion (54)
- Pleural Effusion Metastasis (46)
- Prostate (7)
- Rectum (15)
- Renal Pelvis (1)
- Retroperitoneal Space (2)
- Salivary Gland (2)
- Skeletal Muscle (5)
- Skin (32)
- Skin Metastasis (3)
- Small Intestine (4)
- Small Intestine Metastasis (1)
- Smooth Muscle (2)
- Soft Tissue (1)
- Soft Tissue Metastasis (1)
- Spinal Cord (2)
- Stomach (4)
- Testis (15)
- Thoracic Cavity Metastasis (6)
- Thymus (5)
- Thyroid Gland (16)
- Thyroid Gland Metastasis (1)
- Tongue (5)
- Trachea (1)
- Umbilical Cord (1)
- Umbilical Cord Blood (1)
- Urachus (1)
- Ureter (1)
- Uterus (54)
- Uvea (2)
- Vagina (2)
- Vulva (1)
Disease
- Acute Biphenotypic Leukemia (1)
- Acute Erythroid Leukemia (4)
- Acute Megakaryoblastic Leukemia (4)
- Acute Monocytic Leukemia (9)
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (25)
- Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia (2)
- Adrenal Gland Neuroblastoma (11)
- Adult B Acute Lymphoblastic leukemia (1)
- Adult B Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (6)
- Adult T Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (6)
- Adult T Lymphoblastic Lymphoma (2)
- Adult T-Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma (1)
- Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma (4)
- Alveolar Ridge Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Amelanotic Melanoma (3)
- Ampulla of Vater Adenocarcinoma (1)
- Ampulla of Vater Adenosquamous Carcinoma (3)
- Anaplastic Astrocytoma (3)
- Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (7)
- Askin Tumor (1)
- Astrocytoma (5)
- B Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (2)
- B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (5)
- Bare Lymphocyte Syndrome Type 2 (1)
- Barrett Adenocarcinoma (2)
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (1)
- Bladder Carcinoma (14)
- Bladder Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Bovine Leukemia (2)
- Breast Adenocarcinoma (4)
- Breast Carcinoma (9)
- Breast Ductal Carcinoma (2)
- Burkitt Lymphoma (17)
- Canavan Disease (1)
- Canine Histiocytic Sarcoma (1)
- Cecum Adenocarcinoma (3)
- Central Nervous System Lymphoma (2)
- Cervical Adenocarcinoma (2)
- Cervical Adenosquamous Carcinoma (2)
- Cervical Small Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma (2)
- Chicken Bursal Lymphoma (2)
- Childhood B Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (13)
- Childhood T Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (16)
- Childhood T Lymphoblastic Lymphoma (1)
- Cholangiocarcinoma (2)
- Chronic Eosinophilic Leukemia (1)
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (2)
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (23)
- Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma (2)
- Colon Adenocarcinoma (55)
- Colon Carcinoma (34)
- Colorectal Adenocarcinoma (1)
- Colorectal Carcinoma (1)
- Congenital Pure Red Cell Aplasia (1)
- Cutaneous Melanoma (10)
- Dedifferentiated Chondrosarcoma (1)
- Desmoplastic Melanoma (1)
- Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (28)
- Down Syndrome (2)
- EBV-Related Burkitt Lymphoma (12)
- Embryonal Carcinoma (3)
- Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma (3)
- Endometrial Adenocarcinoma (13)
- Endometrial Adenosquamous Carcinoma (2)
- Endometrial Carcinoma (2)
- Endometrioid Stromal Sarcoma (1)
- Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma (1)
- Epithelioid Sarcoma (3)
- Esophageal Adenocarcinoma (6)
- Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (41)
- Essential Thrombocythemia (1)
- Ewing Sarcoma (2)
- Extraskeletal Myxoid Chondrosarcoma (1)
- Fanconi Anemia (1)
- Fibrosarcoma (1)
- Follicular Lymphoma (2)
- Gallbladder Carcinoma (2)
- Gallbladder Undifferentiated Carcinoma (2)
- Gastric Adenocarcinoma (6)
- Gastric Adenosquamous Carcinoma (1)
- Gastric Carcinoma (5)
- Gastric Choriocarcinoma (1)
- Gastric Fundus Carcinoma (1)
- Gastric Signet Ring Cell Adenocarcinoma (1)
- Gastric Small Cell Carcinoma (2)
- Gastric Tubular Adenocarcinoma (5)
- Gastroesophageal Junction Adenocarcinoma (1)
- Gestational Choriocarcinoma (1)
- Gingival Squamous Cell Carcinoma (2)
- Glioblastoma (18)
- Gliosarcoma (1)
- Goldfish Erythrophoroma (4)
- Hairy Cell Leukemia (1)
- Hamster Kidney Tumor (1)
- Hamster Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (1)
- Hamster Uterine Leiomyosarcoma (1)
- Hepatoblastoma (2)
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma (6)
- Hepatosplenic T-Cell Lymphoma (2)
- Hereditary Thyroid Gland Medullary Carcinoma (1)
- High Grade B-Cell Lymphoma (1)
- High Grade Ovarian Serous Adenocarcinoma (8)
- Hodgkin Lymphoma (9)
- Hypopharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (2)
- Infectious Mononucleosis (1)
- Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma (6)
- Invasive Breast Carcinoma of No Special Type (12)
- Invasive Breast Lobular Carcinoma (1)
- Kidney Neoplasm (1)
- Kidney Rhabdoid Tumor (1)
- Krukenberg Tumor (1)
- Liposarcoma (1)
- Lung Adenocarcinoma (17)
- Lung Giant Cell Carcinoma (8)
- Lung Large Cell Carcinoma (9)
- Lung Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma (1)
- Lung Non-Small Cell Carcinoma (2)
- Lung Small Cell Carcinoma (25)
- Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma (9)
- Lymphoblastic Lymphoma (1)
- Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor (1)
- Mantle Cell Lymphoma (5)
- Mature Gastric Teratoma (1)
- Maxillary Sinus Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Medaka Hepatoma (2)
- Medulloblastoma (3)
- Melanoma (24)
- Meningioma (2)
- Minimally Invasive Lung Adenocarcinoma (1)
- Monophasic Synovial Sarcoma (1)
- Mouse Bladder Transitional Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Mouse Chondrosarcoma (1)
- Mouse Colon Adenocarcinoma (3)
- Mouse Ependymoma (2)
- Mouse Erythroid Leukemia (13)
- Mouse Fibrosarcoma (5)
- Mouse Glioblastoma (1)
- Mouse Hemangioendothelioma (1)
- Mouse Hepatocellular Carcinoma (1)
- Mouse Insulinoma (3)
- Mouse Intestinal Tract Neuroendocrine Adenoma (1)
- Mouse Islet Cell Adenoma (1)
- Mouse Kidney Carcinoma (1)
- Mouse Leukemia (10)
- Mouse Leydig Cell Tumor (1)
- Mouse Lymphoma (8)
- Mouse Mammary Gland Malignant Neoplasm (23)
- Mouse Melanoma (9)
- Mouse Multiple Myeloma (5)
- Mouse Myeloid Leukemia (3)
- Mouse Neoplasm (1)
- Mouse Neuroblastoma (21)
- Mouse Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Mouse Osteosarcoma (3)
- Mouse Pituitary Gland Neoplasm (1)
- Mouse Plasmacytoma (1)
- Mouse Precursor T Cell Lymphoblastic Lymphoma/Leukemia (2)
- Mouse Pulmonary Adenoma (1)
- Mouse Pulmonary Malignant Tumor (3)
- Mouse Pulmonary Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Mouse Rectum Carcinoma (2)
- Mouse Reticulum Cell Sarcoma (2)
- Mouse Sarcoma (1)
- Mouse Teratocarcinoma (8)
- Mouse Thymic Lymphoma (3)
- Mycosis Fungoides (1)
- Myelodysplastic Syndrome (1)
- Myxofibrosarcoma (1)
- Natural Killer Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma (2)
- Neuroblastoma (26)
- Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma (15)
- Osteoid Osteoma (1)
- Osteosarcoma (15)
- Ovarian Carcinoma (1)
- Ovarian Clear Cell Adenocarcinoma (1)
- Ovarian Endometrioid Adenocarcinoma (4)
- Ovarian Granulosa Cell Tumor (1)
- Ovarian Mucinous Adenocarcinoma (2)
- Ovarian Serous Adenocarcinoma (2)
- Ovarian Serous Cystadenocarcinoma (2)
- Ovarian Small Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma (13)
- Pancreatic Carcinoma (5)
- Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (12)
- Papillomavirus-Independent Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Papillomavirus-Related Cervical Adenocarcinoma (7)
- Papillomavirus-Related Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma (4)
- Papillomavirus-Related Endocervical Adenocarcinoma (16)
- Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (3)
- Pharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Plasma Cell Myeloma (15)
- Pleural Epithelioid Mesothelioma (5)
- Pleural Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma (2)
- Poorly Differentiated Thyroid Gland Carcinoma (1)
- Primary Cutaneous T-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (1)
- Primary Effusion Lymphoma (7)
- Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor (1)
- Prostate carcinoma (1)
- Prostate Carcinoma (9)
- Rat C-Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Rat Cholangiocarcinoma (1)
- Rat Colon Adenocarcinoma (5)
- Rat Digestive System Neoplasm (1)
- Rat Fibrosarcoma (1)
- Rat Hepatocellular Carcinoma (20)
- Rat Histiocytic Sarcoma (1)
- Rat Insulinoma (2)
- Rat Leukemia (1)
- Rat Leydig Cell Adenoma (1)
- Rat Lung Carcinoma (1)
- Rat Malignant Glioma (4)
- Rat Malignant Meningioma (1)
- Rat Malignant Oligodendroglioma (2)
- Rat Malignant Thymoma (3)
- Rat Mammary Gland Adenocarcinoma (10)
- Rat Neuroblastoma (3)
- Rat Osteosarcoma (2)
- Rat Pituitary Gland Neoplasm (6)
- Rat Prostate Adenocarcinoma (3)
- Rat Rhabdomyosarcoma (1)
- Rat Sarcoma (2)
- Rat Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Rat Urinary Bladder Transitional Cell Carcinoma (2)
- Rat Urinary System Neoplasm (6)
- Rectal Adenocarcinoma (13)
- Rectosigmoid Adenocarcinoma (1)
- Recurrent Bladder Carcinoma (1)
- Renal Cell Carcinoma (7)
- Renal Pelvis Urothelial Carcinoma (1)
- Retinoblastoma (11)
- Sacral Chordoma (1)
- Sacrococcygeal Teratoma (1)
- Salivary Gland Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Sezary Syndrome (1)
- Shwachman-Diamond Syndrome (1)
- Skin Squamous Cell Carcinoma (2)
- Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma (1)
- Testicular Embryonal Carcinoma (8)
- Testicular Teratoma (2)
- Testicular Yolk Sac Tumor (1)
- Thyroid Gland Anaplastic Carcinoma (10)
- Thyroid Gland Follicular Carcinoma (4)
- Thyroid Gland Papillary Carcinoma (3)
- Thyroid Gland Sarcoma (1)
- Thyroid Gland Squamous Cell Carcinoma (2)
- Tongue Adenosquamous Carcinoma (1)
- Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma (6)
- Type I Endometrial Adenocarcinoma (1)
- Ureter Urothelial Carcinoma (1)
- Uterine Carcinosarcoma (2)
- Uterine Corpus Leiomyosarcoma (1)
- Uterine Corpus Sarcoma (2)
- Uveal Melanoma (2)
- Vaginal Melanoma (2)
- Vulvar Melanoma (1)
- Vulvar Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
Description: FTC-133 was isolated from a lymph node metastasis of a follicular thyroid carcinoma. The morphology ...
Description: Species: human male 42 years old; Tissue: thyroid; Tumor: carcinoma, follicular; Derived from: lung ...
Description: Species: human; Tissue: thyroid; Tumor: carcinoma, follicular
Description: Established from the primary tumor of a 67-year-old woman with primary thyroid carcinoma ...
Description: Established from the sarcoma of the thyroid gland from a 47-year-old woman in 1985
Description: Established from the tumor tissue of a 76-year-old woman with metastasizing papillary thyroid ...
Description: established from the lymph node metastasis of a 63-year-old woman with anaplastic papillary thyroid ...
Description: Established from the sternal metastasis of follicular thyroid carcinoma removed from a 70-year-old ...
Description: Established from the thyroid gland (right lobe) of a 70-year-old woman with thyroid anaplastic ...
Description: ML-1 is one of three celll lines isolated in 1978 from the peripheral blood of a 24 year old male ...
Description: Established from the malignant tumor of a 49-year-old woman with well-differentiated oxyphilic ...
Description: Established in 1996 from the tumor tissue of a 57-year-old Caucasian man with local recurrence of a ...
Description: Established from cancer cells disseminated in the pleural fluid of a 44-year-old woman with ...
Description: Established from the primary tumor of a 78-year-old woman with thyroid carcinoma (undifferentiated ...
Description: established from the thyroid gland from a 66-year-old male patient with thyroid gland anaplastic ...
Description: G-CSF producing thyroidal squamous carcinoma.
Description: Serum-free, protein-free cultured HOTHC cells.
Description: Thyroid tumor. TAF, G-CSF, colloid producing.