Alcoholic Liver Disease Model
Alcohol consumption, both acute and chronic, is an important health and economic concern worldwide. So far, alcohol abuse has become the fifth leading global cause of preventable morbidity and mortality. Excessive alcohol intake is one of the risk factor for the development of multi-organ pathology, including alcoholic liver disease (ALD).
Alcoholic Liver Disease (ALD) is identified as a spectrum of clinical disorders, which consists of fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis (AH), cirrhosis and even hepatocellular carcinoma. It is reported that 95 percent of heavy drinkers develop fatty liver. Therefore, it is necessary to develop suitable animal models for studying its pathogenesis and test new therapies.
Creative Bioarray focuses on drug research and development as well as helping customers evaluate the efficacy of drug candidates and study the pathological mechanisms through alcoholic liver disease model.
Animal models available
- Lieber-DeCarli liquid diet induced ALD model
- Tsukamoto–French model
- Second-hit models
- EtOH administration with a high fat diet
- EtOH administration with lipopolysaccharide
- Genetically modified models
Species available
- Rat
- Mouse
Our capabilities
- We detect body weight of rodents at different time points.
- Serum and liver ALT, AST, TG, TC, and LDL cholesterol concentrations were determined by colorimetric methods.
- We analyze the hepatic histology by Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) and Oil-Red-O staining.
- We detect associated protein expression and RNA level by Western blot, immunofluorescence staining and RT-qPCR, respectively.
Assays available
- Biochemical analysis
- Pathological evaluation
With extensive experience in the field of ALD, we are confident to help you overcome any upcoming challenges. Our experts are fully capable of customizing our protocols and assays to meet your specific needs. With our help, we wish to facilitate your research with high efficiency.
Study examples
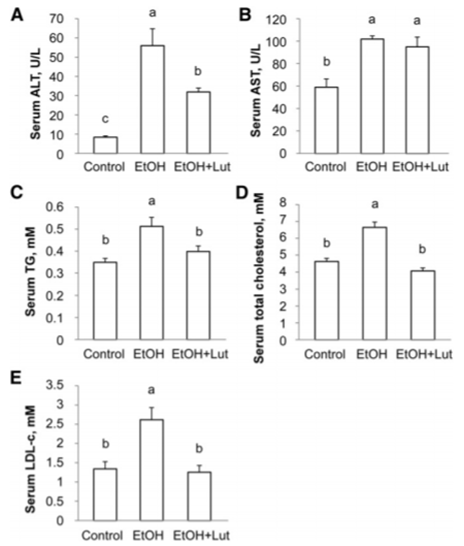 Figure. 1. Serum concentrations of ALT (A), AST (B), TGs (C), total cholesterol (D), and LDL cholesterol (E) in male mice fed a control diet or an ethanol-containing diet with or without luteolin for 2 wk.
Figure. 1. Serum concentrations of ALT (A), AST (B), TGs (C), total cholesterol (D), and LDL cholesterol (E) in male mice fed a control diet or an ethanol-containing diet with or without luteolin for 2 wk.
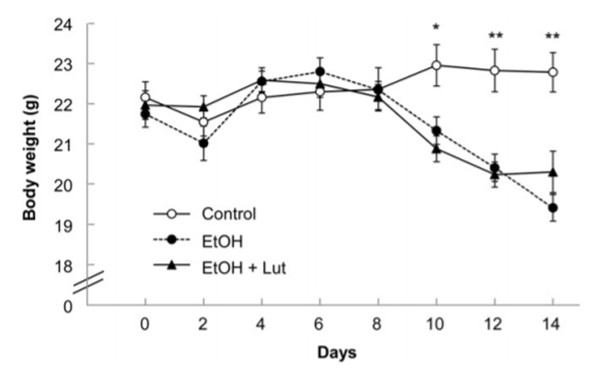 Figure. 2. Body weight of male mice that consumed a control diet or an ethanol-containing diet with or without luteolin for 2 wk.
Figure. 2. Body weight of male mice that consumed a control diet or an ethanol-containing diet with or without luteolin for 2 wk.
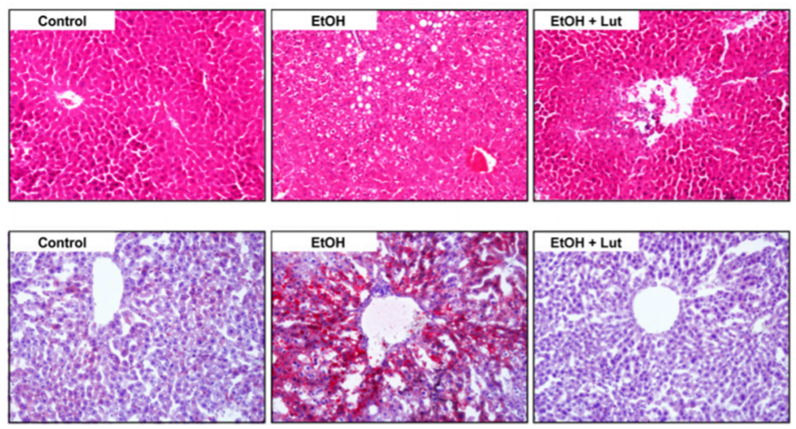 Figure. 3. Hematoxylin and eosin staining and Oil-Red-O staining
Figure. 3. Hematoxylin and eosin staining and Oil-Red-O staining
Quotation and ordering
If you have any special needs or questions regarding our services, please feel free to contact us. We look forward to cooperating with you in the future.
Reference
Liu G , Zhang Y , Liu C , et al. Luteolin Alleviates Alcoholic Liver Disease Induced by Chronic and Binge Ethanol Feeding in Mice[J]. Journal of Nutrition, 2014, 144(7):1009-1015.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Oral Mucositis Model
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
- Graft-versus-host Disease (GvHD) Models
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Schizophrenia Model
- Depression Models
- Pain Models
-
Metabolic Disease Models
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Animal Model of Hyperuricemia
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model
- High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Methionine and Choline Deficient (MCD) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Gubra-Amylin NASH (GAN) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Model
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer (DFU) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthotopic Kidney Transplantation Model
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Model
- Peritoneal Fibrosis Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
- Otology Disease Models