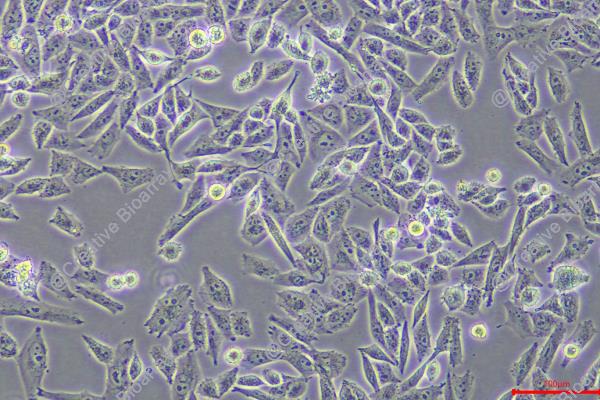
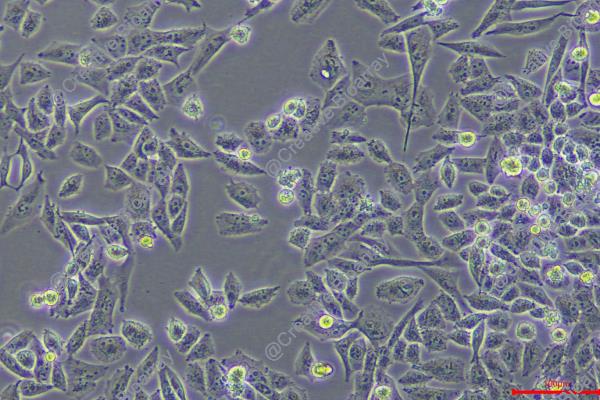
MIA PaCa-2
Cat.No.: CSC-C9492L
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Pancreas
Morphology: Epithelial-like
Culture Properties: monolayer with floating cells
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
CSF1PO: 10
D13S317: 12,13
D16S539: 10,13
D5S818: 12,13
D7S820: 12,13
THO1: 9,10
TPOX: 9
vWA: 15
The MIA PaCa-2 cell line is a foundational and extensively utilized human model of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), established in the 1970s from a primary pancreatic tumor in a 65-year-old male patient. It is classified as an epithelial cell line with a notable spindle-shaped, fibroblastoid morphology, indicative of a pronounced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) phenotype, which correlates with its high invasive potential. Genetically, MIA PaCa-2 harbors the cardinal mutations that define PDAC: a homozygous activating mutation in codon 12 of the KRAS oncogene (c.35G>A, p.G12D) and a homozygous inactivating mutation in the TP53 tumor suppressor gene (c.733G>A, p.G245S). This genetic profile drives constitutive proliferative signaling and defective cell cycle control. A distinguishing biochemical feature is its lack of detectable expression of mucins (MUC1, MUC5AC), making it a "null" model for mucin-related studies and differentiating it from other lines like PANC-1 or Capan-2.
The Anti-Cancer Effects of Tilia Species (Linden) Exert on MIA PaCa-2 Cells
This study investigated the anti-cancer effects of the chemically characterized Tilia species (linden) on MIA PaCa-2 cells by analyzing various cancer-triggering mechanisms, including oxidative stress and inflammation status. Extracts from the flowers, bracts, and inflorescences of T. cordata,T. platyphyllos,T. rubra, and T. tomentosa were evaluated for antioxidant activity; subsequently, their ability to mitigate inflammation was assessed through in vitro nitrite assays in LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. The anticancer potentials of the extracts against MIA PaCa-2 pancreatic cancer cells were investigated in 2D (cytotoxic effect) and 3D (effect on spheroid growth) models in vitro.
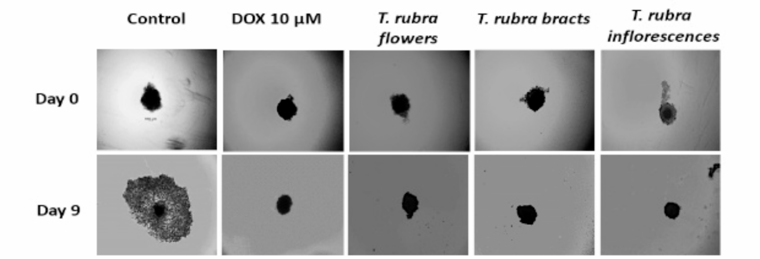
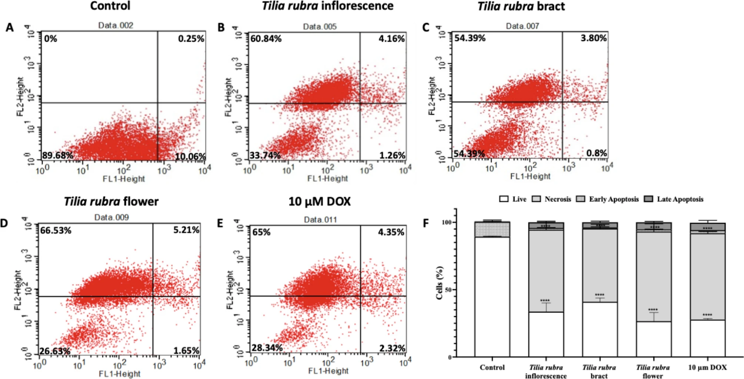
All investigated Tilia species displayed remarkable antioxidant activity and significantly inhibited LPS-induced nitrite, IL-6, and PGE2 production. Extract from T. rubra bracts showed the highest cytotoxic activity against MIA PaCa-2 cells with an IC50 value of 0.16 mg/mL, as well as the most significant delay on spheroid growth, which was further confirmed through the arrest in cell cycle. In the Annexin V cell death assays of T. rubra, cells treated with the flower extract exhibited the highest rate of necrotic population with 66.53%.
Overall, the results highlight a potential use for Tilia extracts, particularly T. rubra, in pancreatic cancer treatment by modulating cell death.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells