Mesothelioma Cells
- Background
- Applications
- Scientific Data
- FAQ
Mesothelioma cells are unique in their origins, stemming from the mesothelial lining surrounding vital organs, such as the lungs, heart, and abdomen. These cells possess remarkable adaptability, allowing them to thrive under environmental stressors, particularly exposure to asbestos fibers. One of the hallmarks of mesothelioma cells is their ability to evade apoptosis, the programmed cell death that serves as a natural safeguard against uncontrolled proliferation. Through intricate genetic and molecular alterations, mesothelioma cells have developed sophisticated mechanisms to bypass this critical checkpoint, leading to unchecked growth and spreading throughout the affected tissues.
Characteristics of Mesothelioma Cells
- Genetic and molecular alterations. Mesothelioma cells harbor a distinct mutational profile, with alterations in key tumor suppressor genes, such as BAP1, NF2, and CDKN2A. These genetic changes disrupt critical cellular pathways, leading to uncontrolled cell division, evasion of apoptosis, and enhanced survival. Furthermore, mesothelioma cells exhibit dysregulation of signaling cascades that govern cell growth, migration, and invasion. Pathways like the PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis and the Hippo-YAP/TAZ pathway are often hyperactivated in these cells, conferring them with a distinct advantage in terms of proliferative capacity and metastatic potential.
- Metabolic adaptations. Mesothelioma cells have also been observed to undergo remarkable metabolic adaptations, allowing them to thrive even in the face of environmental stressors and resource limitations. Through the process of aerobic glycolysis, commonly known as the "Warburg effect," these cells prioritize the conversion of glucose to lactate, even in the presence of oxygen. This metabolic shift not only provides a steady supply of energy but also generates building blocks for rapid cell division and expansion.
- Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Mesothelioma cells undergo a process known as EMT. This dynamic transformation allows the cells to shed their epithelial features, such as cell-cell adhesion and apical-basal polarity, and acquire a more mesenchymal phenotype characterized by increased motility and invasiveness.
Pathogenesis and Disease Modeling
By studying mesothelioma cells, researchers can create accurate disease models that replicate the human condition. These models are essential for understanding the pathogenesis of mesothelioma and for testing new hypotheses in a controlled setting.
Biomarker Discovery
The analysis of mesothelioma cells has led to the identification of biomarkers that can be used for diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment stratification. For instance, the expression levels of mesothelin, a cell surface protein, are being evaluated as a potential biomarker for mesothelioma.
Drug Discovery and Development
Mesothelioma cell lines and animal models derived from these cells are essential in the preclinical phase of drug discovery. These models allow researchers to test the efficacy and toxicity of new drugs or combinations of drugs. This process helps to prioritize the most promising candidates for further development and clinical trials.
Immunotherapy Research
The immune system's interaction with mesothelioma cells is a significant area of research. Mesothelioma cells can be used to develop and test immunotherapies, such as checkpoint inhibitors, cancer vaccines, and adoptive cell transfer therapies. These treatments aim to enhance the body's ability to recognize and eliminate mesothelioma cells.
Glutamine Depletion Reduces the Mesothelioma Cancer Phenotype
Glutamine addiction is an important property of various cancer types that can be exploited therapeutically. A major goal of this study is to assess the response of mesothelioma cancer cells to glutamine restriction. To assess the role of glutamine in maintaining the mesothelioma cancer cell phenotype, Meso-1 cells were grown in a medium containing 0 or 2 mM glutamine and monitored the impact on cancer endpoints. A marked reduction in cell proliferation (Fig. 1A), spheroid formation (Fig. 1B), invasion through matrigel (Fig. 1C), and migration (Fig. 1D) in glutamine-free conditions. To confirm that the cells require glutamine to maintain the aggressive cancer phenotype, V-9302 was treated, which inhibits SLC1A5, a plasma membrane transporter that imports glutamine, and CB-839 which inhibits GLS, the enzyme that converts glutamine to glutamate. Treatment with V-9302 produces a dose-dependent decrease in cell proliferation (Fig. 1E), inhibits spheroid formation (Fig. 1F), and reduces invasion through matrigel (Fig. 1G). Treatment with CB-839 also reduces these cancer cell characteristics (Fig. 1H, I, J). The impact of SLC1A5 knockdown was measured on the cancer phenotype. Treatment of Meso-1 cells with SLC1A5-siRNA reduced cell proliferation and invasion. These findings strongly suggest that mesothelioma cancer cells require glutamine to maintain the aggressive cancer phenotype and are glutamine addicted.
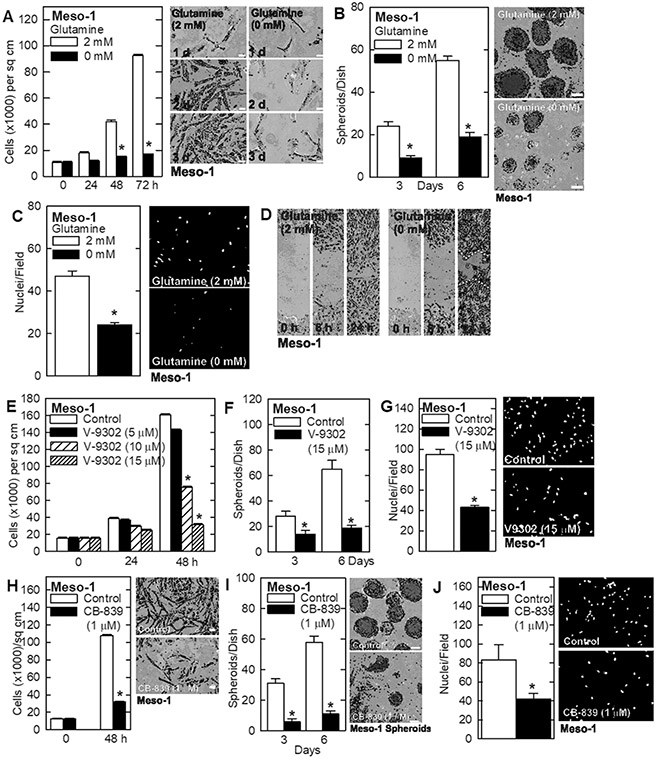 Fig.
1 Glutamine is essential to maintain an aggressive mesothelioma cell phenotype. (Adhikary G, et al,
2023)
Fig.
1 Glutamine is essential to maintain an aggressive mesothelioma cell phenotype. (Adhikary G, et al,
2023)
BAP1 and BRCA1 Are Required for Accurate Mitotic Progression in Mesothelioma Cells
Fluorescence microscopy was performed on cells fixed and stained for DNA to analyze the relative proportion of cells in different stages of mitosis. This revealed that depletion of either BAP1 or BRCA1 increased the proportion of mitotic cells in late mitosis, i.e. anaphase and telophase, compared to mock-depleted cells (Fig. 2A). However, BRCA1 led to most mitotic cells being present in telophase, BAP1 depletion led to the highest proportion of mitotic cells being in anaphase. This suggests that while BAP1 and BRCA1 are both important for the normal mitotic progression of mesothelioma cells, they are likely to have at least in part distinct functions.
Further analysis of these mitotic cells by immunofluorescence microscopy revealed that depletion of either BAP1 or BRCA1 led to chromosome congression errors with an increase in the frequency of misaligned chromosomes in metaphase (Fig. 2B). The frequency of misaligned chromosomes was similar whether cells were depleted of BAP1 or BRCA1. Depletion of either BAP1 or BRCA1 also led to a substantial increase in the number of interphase cells that contained multiple nuclei or micronuclei (Fig. 2C, D). Staining with the centromere marker, CENP-A, revealed the presence of centromeres within these micronuclei indicating that they were likely the result of chromosome segregation errors rather than fragments of broken chromosomes arising due to DNA repair defects.
Since previous data had shown that BRCA1 controls SAC activity by regulating the expression of MAD2L1, a key SAC component, the protein levels of MAD2L1 were examined in cells depleted of BAP1. In comparison to mock-depleted cells, there was a marked reduction in MAD2L1 protein upon depletion of either BAP1 or BRCA1 in MSTO-211H cells or depletion of BAP1 in NCI-H2452 cells (Fig. 2E). The expression and localization of another SAC component, BUBR1, were analyzed in mitotic cells. Although there was no difference in expression of BUBR1 protein as determined by Western blotting upon BAP1 or BRCA1 depletion in MSTO-211H cells, there was reduced association with kinetochores upon depletion of either BAP1 or BRCA1 in MSTO-211H and NCI-H2542 cells arrested in prometaphase with vinorelbine (Fig. 2F). These data indicate that BAP1 is likely to regulate the SAC similarly to BRCA1 through control of MAD2L1 expression and recruitment of BUBR1 to kinetochores.
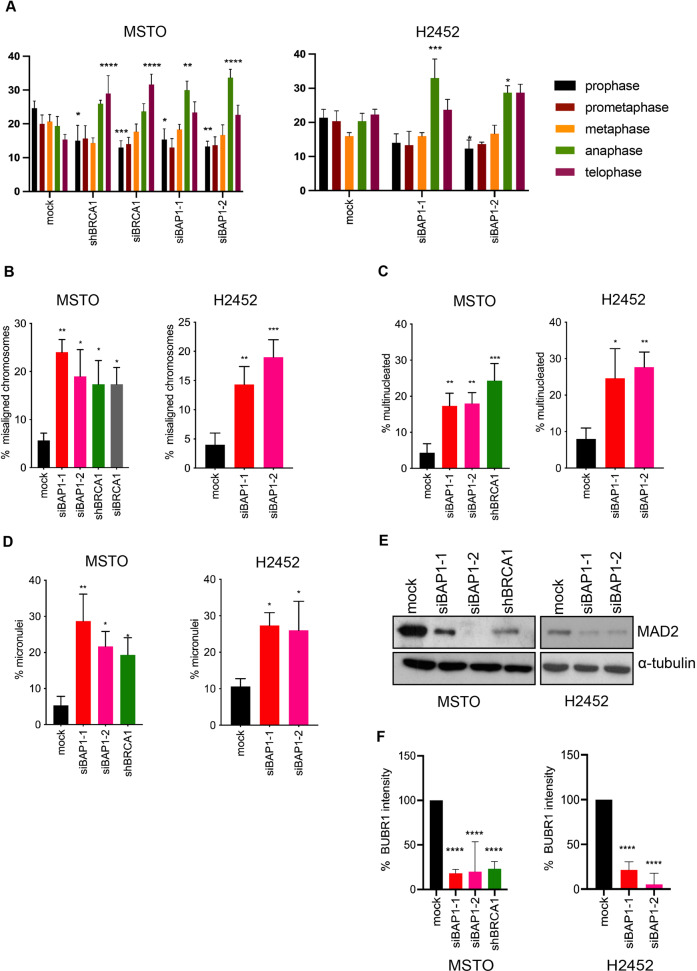 Fig.
2 BAP1 depletion leads to mitotic progression defects and loss of SAC integrity. (Singh A, et al.,
2023)
Fig.
2 BAP1 depletion leads to mitotic progression defects and loss of SAC integrity. (Singh A, et al.,
2023)
Mesothelioma cells are malignant cells that develop from the mesothelial cells lining the body's internal organs, such as the lungs and abdominal cavity. These cells can transform into cancerous cells following exposure to asbestos or other carcinogens, leading to the development of mesothelioma.
Mesothelioma cells exhibit remarkable metabolic adaptations, including the process of aerobic glycolysis (the "Warburg effect"), where they prioritize the conversion of glucose to lactate, even in the presence of oxygen. This metabolic shift provides a steady supply of energy and generates building blocks for rapid cell division. Mesothelioma cells also demonstrate increased dependence on glutamine metabolism, utilizing this amino acid as a source of carbon and nitrogen for biosynthesis and energy production, enabling them to adapt and survive in the often nutrient-deprived tumor microenvironment.
The primary cause of mesothelioma cell proliferation is exposure to asbestos fibers. Other factors may include genetic predisposition, radiation exposure, and certain viral infections, although asbestos remains the most significant risk factor.
Filters Clear all filters
Species
- African clawed frog (1)
- American mink (1)
- Asian tiger mosquito (1)
- Atlantic salmon (1)
- Bluegill (2)
- Bluestriped grunt (1)
- Bovine (7)
- Brazilian free-tailed bat (1)
- Brown bullhead (2)
- Cabbage looper (1)
- Cabbage moth (6)
- Cat (4)
- Central mudminnow (1)
- Chicken (3)
- Chinese hamster (5)
- Chinook salmon (2)
- Chum salmon (1)
- Coho salmon (1)
- Common carp (2)
- Cotton-top tamarin (1)
- Dog (2)
- Fall armyworm (3)
- Fathead minnow (2)
- Fruit fly (1)
- Gilthead sea bream (2)
- Golden hamster (7)
- Goldfish (6)
- Gray dwarf hamster (1)
- Green monkey (2)
- Gypsy moth (1)
- Horse (1)
- Human (998)
- Japanese eel (1)
- Japanese rice fish (7)
- Koi carp (1)
- Mouse (315)
- Mouse x Gray dwarf hamster (1)
- Mouse x Rat (20)
- Northern pike (1)
- Pig (3)
- Rabbit (2)
- Rainbow trout (3)
- Rat (115)
- Rhesus macaque (1)
- Salt marsh moth (1)
- Sheep (2)
- Snakehead murrel (2)
- Sockeye salmon (1)
- Vervet monkey (2)
- Zebrafish (2)
Source
- Abdomen (1)
- Abdomen Metastasis (2)
- Adipose (2)
- Adrenal Gland (8)
- Adrenal Gland Metastasis (2)
- Aorta (4)
- Artery (1)
- Ascites (28)
- Ascites Metastasis (37)
- Bile Duct (3)
- Bladder (25)
- Bladder Metastasis (1)
- Blastocyst (1)
- Blastula (1)
- Blood (127)
- Bone (27)
- Bone Marrow (57)
- Bone Marrow Metastasis (18)
- Bone Metastasis (6)
- Brain (55)
- Brain Metastasis (8)
- Breast (30)
- Bronchus (1)
- Caudal Peduncle (1)
- Caudal Trunk (2)
- Cecum (3)
- Cerebrospinal Fluid (1)
- Cerebrospinal Fluid Metastasis (1)
- Cervix (32)
- Colon (90)
- Connective Tissue (7)
- Cornea (3)
- Cutaneous Metastasis (1)
- Dermis (2)
- Duodenum (1)
- Embryo (29)
- Endometrium (17)
- Esophagus (44)
- Eye (12)
- Eye Socket (5)
- Fetus (3)
- Fin (9)
- Foreskin (4)
- Gallbladder (1)
- Gingiva (2)
- Globe (2)
- Glomerulus (2)
- Groin (1)
- Head Kidney (2)
- Heart (4)
- Hemolymph (1)
- Hypodermis Metastasis (5)
- Ileum (1)
- Intestine (94)
- Jejunum (1)
- kidney (1)
- Kidney (27)
- Liver (35)
- Liver Metastasis (17)
- Lung (58)
- Lung Metastasis (8)
- Lymph Node (7)
- Lymph Node Metastasis (59)
- Muscle (7)
- Muscle Metastasis (2)
- Nose (2)
- Omentum Metastasis (2)
- Oral Cavity (10)
- Ovary (21)
- Ovary Metastasis (2)
- Pancreas (19)
- Pelvic Wall Metastasis (1)
- Pelvis (1)
- Perianal Space Metastasis (1)
- Pericardial Effusion (1)
- Pericardial Effusion Metastasis (2)
- Perineus (1)
- Peripheral Blood (126)
- Peripheral Nervous System (21)
- Peritoneal Effusion (2)
- Peritoneum (1)
- Peritoneum Metastasis (1)
- Pharynx (3)
- Pituitary Gland (7)
- Pleural Effusion (54)
- Pleural Effusion Metastasis (46)
- Prostate (7)
- Rectum (15)
- Renal Pelvis (1)
- Retroperitoneal Space (2)
- Salivary Gland (2)
- Skeletal Muscle (5)
- Skin (32)
- Skin Metastasis (3)
- Small Intestine (4)
- Small Intestine Metastasis (1)
- Smooth Muscle (2)
- Soft Tissue (1)
- Soft Tissue Metastasis (1)
- Spinal Cord (2)
- Stomach (4)
- Testis (15)
- Thoracic Cavity Metastasis (6)
- Thymus (5)
- Thyroid Gland (16)
- Thyroid Gland Metastasis (1)
- Tongue (5)
- Trachea (1)
- Umbilical Cord (1)
- Umbilical Cord Blood (1)
- Urachus (1)
- Ureter (1)
- Uterus (54)
- Uvea (2)
- Vagina (2)
- Vulva (1)
Disease
- Acute Biphenotypic Leukemia (1)
- Acute Erythroid Leukemia (4)
- Acute Megakaryoblastic Leukemia (4)
- Acute Monocytic Leukemia (9)
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (25)
- Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia (2)
- Adrenal Gland Neuroblastoma (11)
- Adult B Acute Lymphoblastic leukemia (1)
- Adult B Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (6)
- Adult T Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (6)
- Adult T Lymphoblastic Lymphoma (2)
- Adult T-Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma (1)
- Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma (4)
- Alveolar Ridge Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Amelanotic Melanoma (3)
- Ampulla of Vater Adenocarcinoma (1)
- Ampulla of Vater Adenosquamous Carcinoma (3)
- Anaplastic Astrocytoma (3)
- Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (7)
- Askin Tumor (1)
- Astrocytoma (5)
- B Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (2)
- B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (5)
- Bare Lymphocyte Syndrome Type 2 (1)
- Barrett Adenocarcinoma (2)
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (1)
- Bladder Carcinoma (14)
- Bladder Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Bovine Leukemia (2)
- Breast Adenocarcinoma (4)
- Breast Carcinoma (9)
- Breast Ductal Carcinoma (2)
- Burkitt Lymphoma (17)
- Canavan Disease (1)
- Canine Histiocytic Sarcoma (1)
- Cecum Adenocarcinoma (3)
- Central Nervous System Lymphoma (2)
- Cervical Adenocarcinoma (2)
- Cervical Adenosquamous Carcinoma (2)
- Cervical Small Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma (2)
- Chicken Bursal Lymphoma (2)
- Childhood B Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (13)
- Childhood T Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (16)
- Childhood T Lymphoblastic Lymphoma (1)
- Cholangiocarcinoma (2)
- Chronic Eosinophilic Leukemia (1)
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (2)
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (23)
- Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma (2)
- Colon Adenocarcinoma (55)
- Colon Carcinoma (34)
- Colorectal Adenocarcinoma (1)
- Colorectal Carcinoma (1)
- Congenital Pure Red Cell Aplasia (1)
- Cutaneous Melanoma (10)
- Dedifferentiated Chondrosarcoma (1)
- Desmoplastic Melanoma (1)
- Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (28)
- Down Syndrome (2)
- EBV-Related Burkitt Lymphoma (12)
- Embryonal Carcinoma (3)
- Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma (3)
- Endometrial Adenocarcinoma (13)
- Endometrial Adenosquamous Carcinoma (2)
- Endometrial Carcinoma (2)
- Endometrioid Stromal Sarcoma (1)
- Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma (1)
- Epithelioid Sarcoma (3)
- Esophageal Adenocarcinoma (6)
- Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (41)
- Essential Thrombocythemia (1)
- Ewing Sarcoma (2)
- Extraskeletal Myxoid Chondrosarcoma (1)
- Fanconi Anemia (1)
- Fibrosarcoma (1)
- Follicular Lymphoma (2)
- Gallbladder Carcinoma (2)
- Gallbladder Undifferentiated Carcinoma (2)
- Gastric Adenocarcinoma (6)
- Gastric Adenosquamous Carcinoma (1)
- Gastric Carcinoma (5)
- Gastric Choriocarcinoma (1)
- Gastric Fundus Carcinoma (1)
- Gastric Signet Ring Cell Adenocarcinoma (1)
- Gastric Small Cell Carcinoma (2)
- Gastric Tubular Adenocarcinoma (5)
- Gastroesophageal Junction Adenocarcinoma (1)
- Gestational Choriocarcinoma (1)
- Gingival Squamous Cell Carcinoma (2)
- Glioblastoma (18)
- Gliosarcoma (1)
- Goldfish Erythrophoroma (4)
- Hairy Cell Leukemia (1)
- Hamster Kidney Tumor (1)
- Hamster Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (1)
- Hamster Uterine Leiomyosarcoma (1)
- Hepatoblastoma (2)
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma (6)
- Hepatosplenic T-Cell Lymphoma (2)
- Hereditary Thyroid Gland Medullary Carcinoma (1)
- High Grade B-Cell Lymphoma (1)
- High Grade Ovarian Serous Adenocarcinoma (8)
- Hodgkin Lymphoma (9)
- Hypopharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (2)
- Infectious Mononucleosis (1)
- Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma (6)
- Invasive Breast Carcinoma of No Special Type (12)
- Invasive Breast Lobular Carcinoma (1)
- Kidney Neoplasm (1)
- Kidney Rhabdoid Tumor (1)
- Krukenberg Tumor (1)
- Liposarcoma (1)
- Lung Adenocarcinoma (17)
- Lung Giant Cell Carcinoma (8)
- Lung Large Cell Carcinoma (9)
- Lung Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma (1)
- Lung Non-Small Cell Carcinoma (2)
- Lung Small Cell Carcinoma (25)
- Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma (9)
- Lymphoblastic Lymphoma (1)
- Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor (1)
- Mantle Cell Lymphoma (5)
- Mature Gastric Teratoma (1)
- Maxillary Sinus Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Medaka Hepatoma (2)
- Medulloblastoma (3)
- Melanoma (24)
- Meningioma (2)
- Minimally Invasive Lung Adenocarcinoma (1)
- Monophasic Synovial Sarcoma (1)
- Mouse Bladder Transitional Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Mouse Chondrosarcoma (1)
- Mouse Colon Adenocarcinoma (3)
- Mouse Ependymoma (2)
- Mouse Erythroid Leukemia (13)
- Mouse Fibrosarcoma (5)
- Mouse Glioblastoma (1)
- Mouse Hemangioendothelioma (1)
- Mouse Hepatocellular Carcinoma (1)
- Mouse Insulinoma (3)
- Mouse Intestinal Tract Neuroendocrine Adenoma (1)
- Mouse Islet Cell Adenoma (1)
- Mouse Kidney Carcinoma (1)
- Mouse Leukemia (10)
- Mouse Leydig Cell Tumor (1)
- Mouse Lymphoma (8)
- Mouse Mammary Gland Malignant Neoplasm (23)
- Mouse Melanoma (9)
- Mouse Multiple Myeloma (5)
- Mouse Myeloid Leukemia (3)
- Mouse Neoplasm (1)
- Mouse Neuroblastoma (21)
- Mouse Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Mouse Osteosarcoma (3)
- Mouse Pituitary Gland Neoplasm (1)
- Mouse Plasmacytoma (1)
- Mouse Precursor T Cell Lymphoblastic Lymphoma/Leukemia (2)
- Mouse Pulmonary Adenoma (1)
- Mouse Pulmonary Malignant Tumor (3)
- Mouse Pulmonary Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Mouse Rectum Carcinoma (2)
- Mouse Reticulum Cell Sarcoma (2)
- Mouse Sarcoma (1)
- Mouse Teratocarcinoma (8)
- Mouse Thymic Lymphoma (3)
- Mycosis Fungoides (1)
- Myelodysplastic Syndrome (1)
- Myxofibrosarcoma (1)
- Natural Killer Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma (2)
- Neuroblastoma (26)
- Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma (15)
- Osteoid Osteoma (1)
- Osteosarcoma (15)
- Ovarian Carcinoma (1)
- Ovarian Clear Cell Adenocarcinoma (1)
- Ovarian Endometrioid Adenocarcinoma (4)
- Ovarian Granulosa Cell Tumor (1)
- Ovarian Mucinous Adenocarcinoma (2)
- Ovarian Serous Adenocarcinoma (2)
- Ovarian Serous Cystadenocarcinoma (2)
- Ovarian Small Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma (13)
- Pancreatic Carcinoma (5)
- Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (12)
- Papillomavirus-Independent Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Papillomavirus-Related Cervical Adenocarcinoma (7)
- Papillomavirus-Related Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma (4)
- Papillomavirus-Related Endocervical Adenocarcinoma (16)
- Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (3)
- Pharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Plasma Cell Myeloma (15)
- Pleural Epithelioid Mesothelioma (5)
- Pleural Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma (2)
- Poorly Differentiated Thyroid Gland Carcinoma (1)
- Primary Cutaneous T-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (1)
- Primary Effusion Lymphoma (7)
- Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor (1)
- Prostate carcinoma (1)
- Prostate Carcinoma (9)
- Rat C-Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Rat Cholangiocarcinoma (1)
- Rat Colon Adenocarcinoma (5)
- Rat Digestive System Neoplasm (1)
- Rat Fibrosarcoma (1)
- Rat Hepatocellular Carcinoma (20)
- Rat Histiocytic Sarcoma (1)
- Rat Insulinoma (2)
- Rat Leukemia (1)
- Rat Leydig Cell Adenoma (1)
- Rat Lung Carcinoma (1)
- Rat Malignant Glioma (4)
- Rat Malignant Meningioma (1)
- Rat Malignant Oligodendroglioma (2)
- Rat Malignant Thymoma (3)
- Rat Mammary Gland Adenocarcinoma (10)
- Rat Neuroblastoma (3)
- Rat Osteosarcoma (2)
- Rat Pituitary Gland Neoplasm (6)
- Rat Prostate Adenocarcinoma (3)
- Rat Rhabdomyosarcoma (1)
- Rat Sarcoma (2)
- Rat Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Rat Urinary Bladder Transitional Cell Carcinoma (2)
- Rat Urinary System Neoplasm (6)
- Rectal Adenocarcinoma (13)
- Rectosigmoid Adenocarcinoma (1)
- Recurrent Bladder Carcinoma (1)
- Renal Cell Carcinoma (7)
- Renal Pelvis Urothelial Carcinoma (1)
- Retinoblastoma (11)
- Sacral Chordoma (1)
- Sacrococcygeal Teratoma (1)
- Salivary Gland Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Sezary Syndrome (1)
- Shwachman-Diamond Syndrome (1)
- Skin Squamous Cell Carcinoma (2)
- Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma (1)
- Testicular Embryonal Carcinoma (8)
- Testicular Teratoma (2)
- Testicular Yolk Sac Tumor (1)
- Thyroid Gland Anaplastic Carcinoma (10)
- Thyroid Gland Follicular Carcinoma (4)
- Thyroid Gland Papillary Carcinoma (3)
- Thyroid Gland Sarcoma (1)
- Thyroid Gland Squamous Cell Carcinoma (2)
- Tongue Adenosquamous Carcinoma (1)
- Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma (6)
- Type I Endometrial Adenocarcinoma (1)
- Ureter Urothelial Carcinoma (1)
- Uterine Carcinosarcoma (2)
- Uterine Corpus Leiomyosarcoma (1)
- Uterine Corpus Sarcoma (2)
- Uveal Melanoma (2)
- Vaginal Melanoma (2)
- Vulvar Melanoma (1)
- Vulvar Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
Description: Species: human, Caucasian male adult; Tissue: skin; Tumor: melanoma
Description: Species: human, Caucasian male adult; Tissue: skin; Tumor: melanoma
Description: Species: human, Caucasian male adult; Tissue: skin; Tumor: melanoma
Description: Species: human male; Tissue: subcutaneous metastasis; Tumor: melanoma, metastatic
Description: established from the pleural effusion of a 70- year- old Caucasian woman with pleural epithelioid ...
Description: established from the pleural effusion of a 71- year- old Caucasian man with pleural epithelioid ...
Description: Species: human male 67 years old; Tissue: pleural effusion; Tumor: mesothelioma
Description: Established from a pleural biopsy of a 62-year-old man with malignant mesothelioma
Description: Established from the untreated malignant epithelioid mesothelioma of the pleura of a 54-year-old ...
Description: Established in 2003 from the untreated malignant mesothelioma of the pleura of a 78-year-old man ...