3D Hepatotoxicity Service
- Features
- Workflow
- Applications
- Study examples
- Explore Other Options
Accurate prediction of human drug-induced liver injury (DILI) remains one of the most critical challenges in preclinical safety assessment. Despite extensive reliance on animal studies and conventional 2D in vitro assays, nearly half of the compounds that later demonstrate hepatotoxicity in humans show no comparable toxicity in non-clinical models. This disconnect is largely driven by species-specific differences in drug-metabolizing enzymes, limited representation of human liver microenvironments, and the inability of traditional models to capture long-term or idiosyncratic toxicities. As a result, hepatotoxicity continues to be a leading cause of clinical trial failure and post-marketing drug withdrawal.
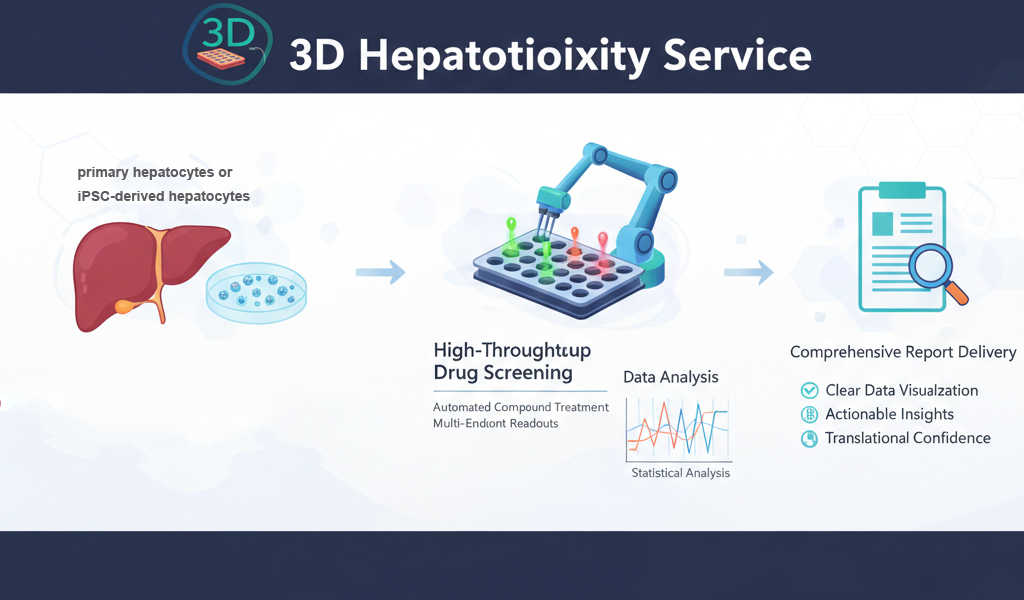 Fig. 1 The RNAscope principle. (Gross-Thebing T, et al., 2014)
Fig. 1 The RNAscope principle. (Gross-Thebing T, et al., 2014)
In contrast to 2D cultures, 3D liver systems (spheroids, organoids, scaffold-based cultures, bioreactors, and microfluidic liver-on-chip) exhibit higher metabolic competence, long-term functionality, and recapitulate the human liver microenvironment more closely. Restoration of critical cell–cell interactions in three dimensions and the ability to assess these long-term in 3D platforms allow for more accurate prediction of human-relevant hepatotoxic response.
Our 3D Hepatotoxicity Service leverages 3D spheroids platforms to deliver higher translational confidence, enabling earlier de-risking, mechanistic insight, and more informed decision-making throughout drug development.
Creative Bioarray's 3D Hepatotoxicity Testing Services
Our 3D liver spheroids are primary hepatocytes or iPSC-derived hepatocytes in co-culture with non-parenchymal cells. The 3D spheroids retain physiologically relevant architecture, long-term CYP activity, and stable metabolic and functional phenotype for more accurate modeling of chronic, low-dose and mechanistic hepatotoxicity not possible with 2D cultures.
Advantages
- Providing novel approaches to in vitro drug safety assessment that overcomes many limitations of existing models.
- Several physiologic model systems are available by using primary cells, hepatic cell lines or iPSC.
- Our liver toxicity tests cover most endpoints.
- The detection includes both acute and chronic toxicity.
- Spheroids of hepatocytes co-cultured with non-parenchymal cells better mimic the complex structure of human liver.
| Category | Details |
| Cell Models Available | Primary human hepatocytes iPSC-derived hepatocytes Multi-cell co-culture spheroids Other models and custom models available upon request |
| Key Endpoints | Cell viability (ATP, LDH) Apoptosis (caspase activity, annexin V) ROS Mitochondrial function lipid accumulation (steatosis) oxidative stress glutathione levels Inflammation & Fibrosis DILI biomarkers |
| Analysis Method | Plate reading (luminescence/fluorescence/colorimetric) High content imaging Biochemical assays Metabolite profiling (optional) |
| Test Article Concentration | custom concentrations available upon request |
| Number of Replicates | 3 replicates per concentration |
| Time points | Single or multiple time points |
| Data Delivery | Dose–response curves IC50 values Margin of safety Optional mechanistic endpoints |
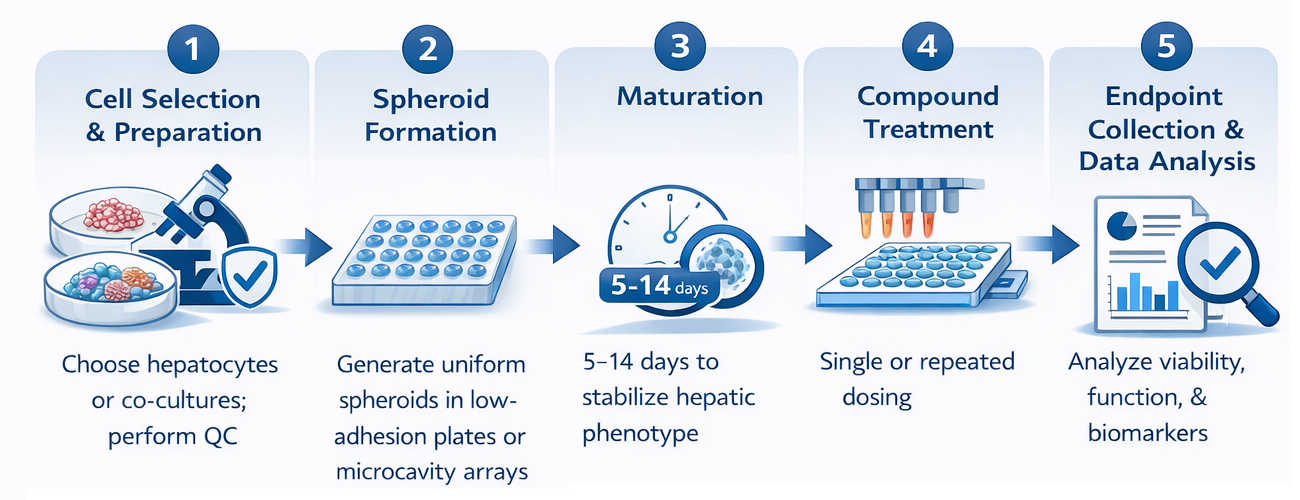
Workflow
Applications
Our 3D liver spheroid platform supports a wide range of research and safety assessment needs:
Early hepatotoxicity screening and compound ranking
Mechanistic toxicity evaluation (mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, steatosis, apoptosis)
Repeated-dose and chronic toxicity assessment
Metabolism-dependent toxicity and bioactivation studies
DILI risk assessment and safety margin estimation
Inflammation and fibrosis modeling using multi-cell spheroids
Study examples
 Figure. 2 The representative data analysis for the measurements of tissue ATP and the secreted factor albumin when compared 2D culture to 3D culture.
Figure. 2 The representative data analysis for the measurements of tissue ATP and the secreted factor albumin when compared 2D culture to 3D culture.
Quotations and ordering
Our customer service representatives are available 24hr a day!
References
- Bachmann, A., et al. 3D Cultivation Techniques for Primary Human Hepatocytes. Microarrays. 2015, 4.1: 64-83.
- Nguyen, D. G., et al. Bioprinted 3D primary liver tissues allow assessment of organ-level response to clinical drug induced toxicity in vitro. PLoS One. 2016, 11.7: e0158674.
- Gunness, P., et al. 3D organotypic cultures of human HepaRG cells: a tool for in vitro toxicity studies. Toxicological sciences. 2013, 133.1: 67-78.
Explore Other Options