Allergic Rhinitis (AR) Model
Boasting a wealth of expertise honed through years of rigorous research, Creative Bioarray proudly introduces our specialized rodent disease model tailored for allergic rhinitis (AR), alongside a comprehensive array of complementary services. Our dedicated team of scientists strives to enable groundbreaking discoveries and drive advancements in drug development through our offerings.
AR is caused by reactions to inhaled allergens mediated by immunoglobulin E (IgE). It is a common chronic condition worldwide and often occurs alongside asthma and conjunctivitis. AR is a global health problem that causes significant burden and disability. During the sensitization phase, allergens are taken up by dendritic cells in the nasal mucosa. This process leads to the production of allergen-specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) by plasma cells. The IgE binds to mast cells, basophils, memory allergen-specific type 2 T helper cells (TH2 cells), and IgE+ B cells. In individuals sensitized to the allergen, subsequent exposure triggers the activation of mast cells and basophils in the nasal mucosa. This activation results in the release of allergic mediators, causing acute symptoms of allergic rhinitis. Memory allergen-specific TH2 cells also produce cytokines, which lead to an inflammatory response characterized by eosinophil recruitment within a few hours. This inflammatory response causes more symptoms and changes in the functional aspects of the nasal mucosa, resembling chronic rhinitis.
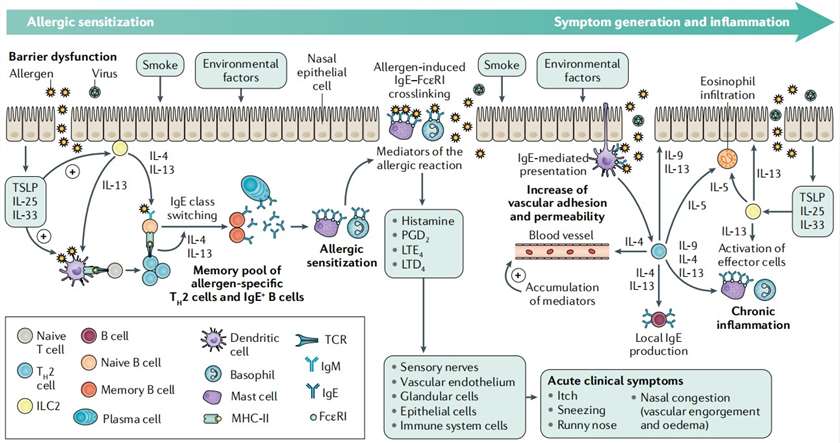 Fig. 1 Pathophysiology of allergic rhinitis. (Bousquet et al. 2020)
Fig. 1 Pathophysiology of allergic rhinitis. (Bousquet et al. 2020)
Our Allergic Rhinitis Model
- Available Animal
Balb/c mouse
- Modeling Method
Mice are sensitized to ovalbumin (OVA) on days 0, 7, and 14 by an intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection. One week after the last injection, on day 21, the mice are challenged with OVA in the bilateral nasal cavities.
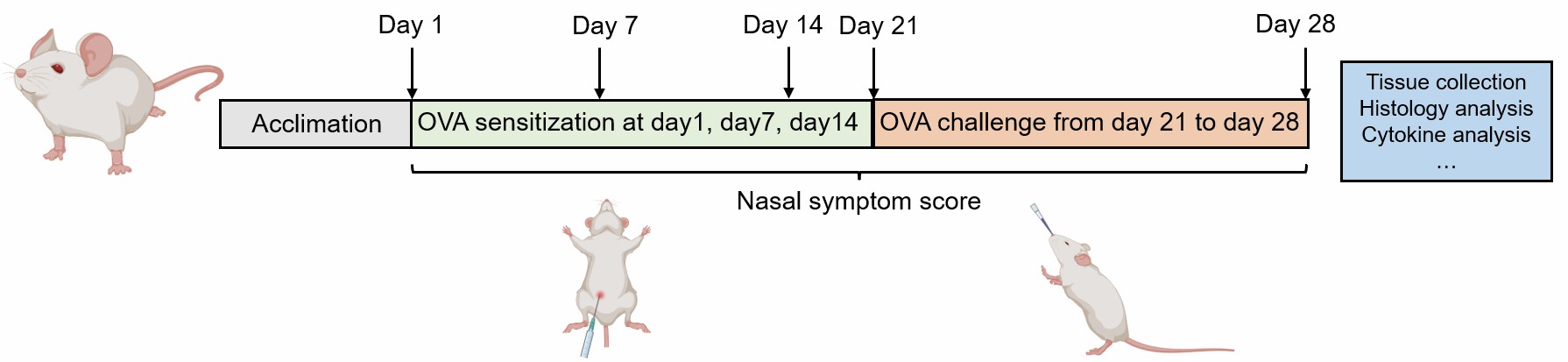 Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of OVA-induced allergic rhinitis model
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of OVA-induced allergic rhinitis model
- Endpoints
- Nasal symptom score
- Cytokine analysis: IL-4, IL-5, IL-13 etc.
- Histology analysis: H&E staining, IHC
- OVA-specific IgE analysis
- qPCR or Western blot
- Other customized endpoints
Example Data
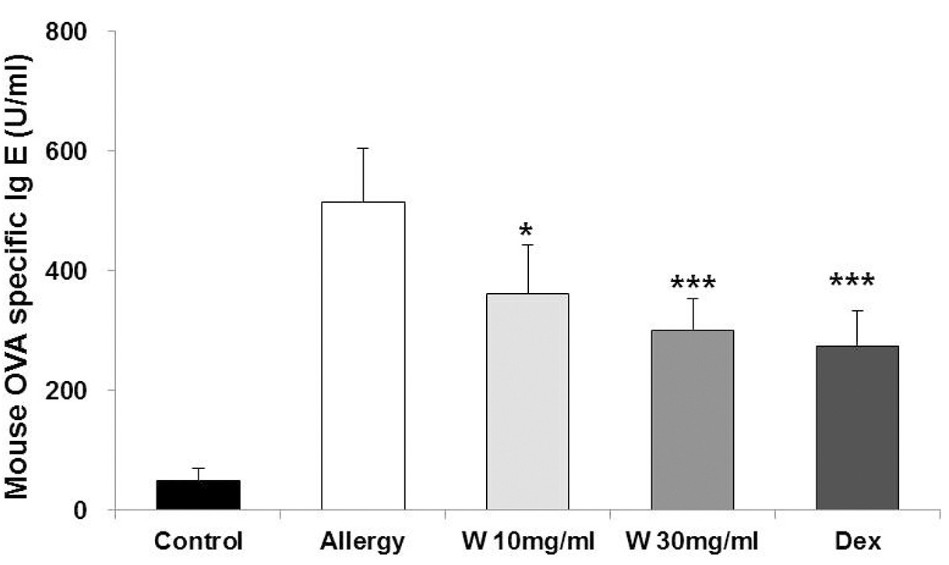 Fig. 3 Effect of wogonin on OVA-specific IgE levels in serum of the allergic rhinitis (AR) mouse model. (Kim et al. 2018)
Fig. 3 Effect of wogonin on OVA-specific IgE levels in serum of the allergic rhinitis (AR) mouse model. (Kim et al. 2018)
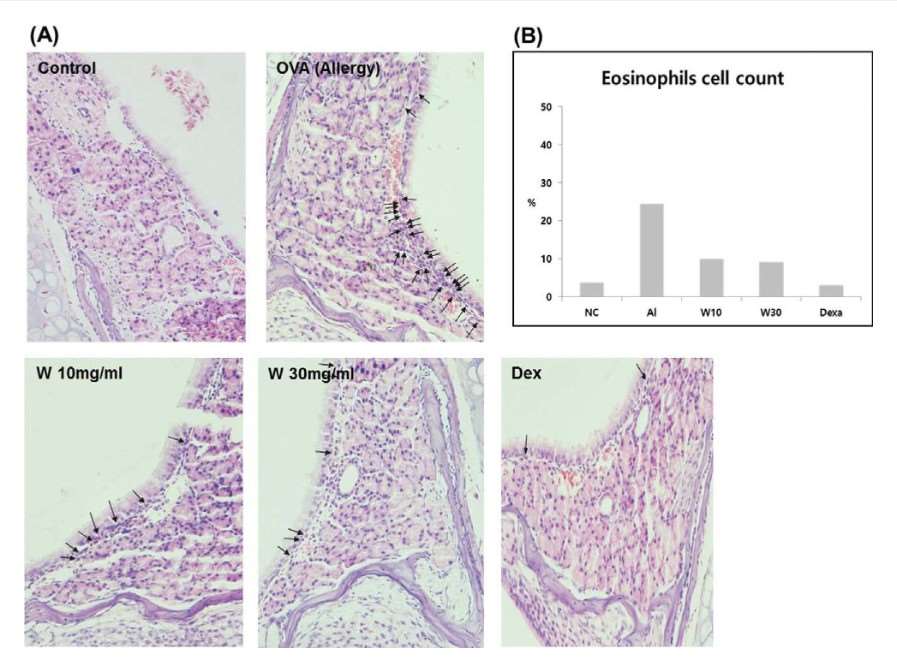 Fig. 4 Effects of wogonin on the filtration of eosinophils (arrows) into nasal mucosa of mice with allergic rhinitis (AR). (Kim et al. 2018)
Fig. 4 Effects of wogonin on the filtration of eosinophils (arrows) into nasal mucosa of mice with allergic rhinitis (AR). (Kim et al. 2018)
Quotation and Ordering
Creative Bioarray stands as a visionary research institute and premier service provider in the realm of preclinical research. We are devoted to crafting top-tier disease models that propel preclinical research initiatives forward. Our mission is to expedite your drug development journey. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us at any time or submit an inquiry to us directly.
References
- Kim, K.A., et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of wogonin on allergic responses in ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis in the mouse. Allergy & Rhinology, 2018, 9: 2152656718764145.
- Bousquet, J., et al. Allergic rhinitis. Nature Reviews Disease Primers, 2020, 6(1): 95.
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Oral Mucositis Model
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
- Graft-versus-host Disease (GvHD) Models
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Schizophrenia Model
- Depression Models
- Pain Models
-
Metabolic Disease Models
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Animal Model of Hyperuricemia
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model
- High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Methionine and Choline Deficient (MCD) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Gubra-Amylin NASH (GAN) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Model
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer (DFU) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthotopic Kidney Transplantation Model
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Model
- Peritoneal Fibrosis Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
- Otology Disease Models