Acetic Acid-Induced Gastric Ulcer Model
Creative Bioarray stands as one of the most trusted CROs, specializing in preclinical drug development. For gastric ulcer research and the development of anti-gastric ulcer drugs, we offer an acetic acid-induced gastric ulcer model. Furthermore, we provide an extensive range of services, including model selection, model establishment, experimental design, data collection, and analysis, to ensure you can obtain the most reliable results.
Chronic gastric ulcer (CGU) is a prevalent digestive ailment, arising from the self-digestion of the gastrointestinal mucosa by gastric juices, extending beyond the muscularis mucosa. Clinical data reveals that CGU affects approximately 5% to 10% of the general population, with a rising trend each year. Fortunately, CGU is a treatable gastric condition, and its clinical management strategies are becoming increasingly diverse. Commonly prescribed medications for CGU include omeprazole, lansoprazole, metronidazole, ranitidine, sucralfate, and colloidal bismuth, among others. While these drugs offer rapid relief, they are associated with a significant recurrence rate following cessation of treatment. To address this challenge and explore safer therapeutic options, Creative Bioarray provides our clients with the acetic acid-induced gastric ulcer model, enabling them to evaluate the efficacy of their test compounds.
Our Acetic Acid-Induced Gastric Ulcer Model
- Animal Available
Rat - Modeling Method
After anesthetizing the animals with sodium pentobarbital, an upper midline laparotomy is performed. Subsequently, either acetic acid or normal saline is injected into the submucosa in proximity to the antrum. To safeguard against any risk of infection, antibiotics are liberally applied to the peritoneal cavity. Finally, the abdominal muscles and skin are meticulously sutured. - Group Setting
- Control group
- Model group
- Three dose groups of test compounds
(Adjustable on demand according to your requirements)
- Endpoints
- Observation of stomach
- Blood/tissue collection
- H&E staining: stomach
- qPCR or Western blot
- Other customized endpoints: available upon request
Example Data
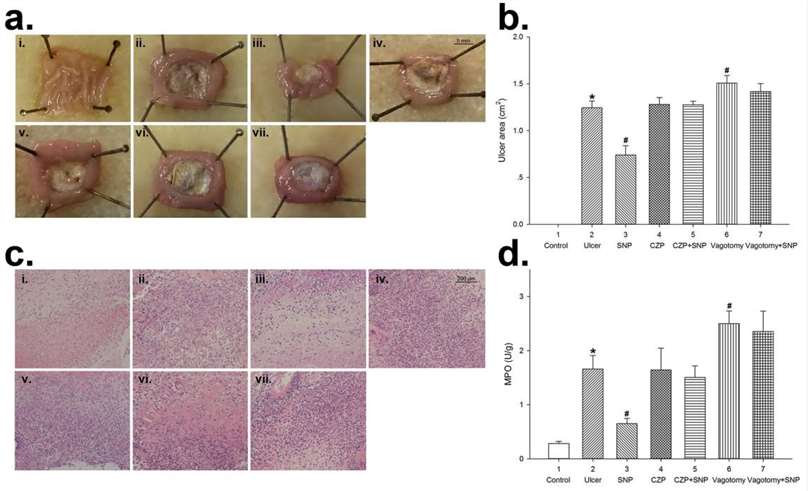 Fig. 1 Sodium nitroprusside (SNP) alleviated acetic acid-induced gastric ulcer in rats. (a) Photographs showing the gross appearance of the gastric mucosa in rats treated with acetic acid in the wall of stomach compared with normal tissue of NS control group. Different sizes of ulcer are seen in the six acid-treated groups except the NS control. (i) NS control group; (ii) ulcer control group; (iii) SNP group; (iv) CZP group; (v) CZP + SNP group; (vi) vagotomy group; (vii) vagotomy + SNP group. (b) Summary values showing the gastric ulcer area (UA) in the seven groups. (c) Histopathological examination of the gastric mucosa in the five groups. (d) Summary values showing the local MPO levels in the rat stomach in each group.
Fig. 1 Sodium nitroprusside (SNP) alleviated acetic acid-induced gastric ulcer in rats. (a) Photographs showing the gross appearance of the gastric mucosa in rats treated with acetic acid in the wall of stomach compared with normal tissue of NS control group. Different sizes of ulcer are seen in the six acid-treated groups except the NS control. (i) NS control group; (ii) ulcer control group; (iii) SNP group; (iv) CZP group; (v) CZP + SNP group; (vi) vagotomy group; (vii) vagotomy + SNP group. (b) Summary values showing the gastric ulcer area (UA) in the seven groups. (c) Histopathological examination of the gastric mucosa in the five groups. (d) Summary values showing the local MPO levels in the rat stomach in each group.
In addition, we also offer other gastric ulcer animal models that you may be interested in:
Quotation and Ordering
At Creative Bioarray, we are dedicated to selecting gastric ulcer models and appropriate endpoints tailored to your specific project needs. If you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us at any time or submit an inquiry directly. We are here to assist you in every step of your preclinical drug development journey.
Reference
- Han, T., et al. Nitric oxide donor protects against acetic acid-induced gastric ulcer in rats via S-nitrosylation of TRPV1 on vagus nerve. Sci Rep, 2017, 18;7(1):2063.