Cardiovascular Disease Models
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death and morbidity in many countries, which affect the heart and blood vessels, leading to a variety of consequences including ischemia, stroke, angina pectoris, and cardiomyopathy. Although investment in cardiovascular drug development is increasing, the number of drugs approved is declining. This is due to the cardiotoxicity of many drugs that target cardiovascular diseases and the highest incidence and severity of adverse drug reactions in late clinical development.
At Creative Bioarray, we have successfully developed various cardiovascular models to help developing drugs for cardiovascular diseases. The application of animal models helps increase our understanding of cardiovascular diseases and provides new approaches to improve the diagnosis and treatment of the diseases. In addition, these models can also be used for screening of adverse drug reactions. Besides, in vitro and in silicon models have recently been proposed to assist in assessing cardiotoxicity.
We provide a variety of models and key technologies of CVD to help with the development of your new compounds. We can also help design the best scheme accordingly using the following models.
Our portfolio of cardiovascular disease models covers:
- Surgical models
- Animal models of hypertension
- Venous thrombosis model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac arrhythmia model
- Hyperlipoidemia model
- Drug-induced heart failure model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
We typically combine various endpoints to obtain the high quality and repeatable data needed for the project. All experimental models were tested in a dose-dependent manner using an approved positive control. We also have the flexibility and expertise to develop custom in vivo models to meet your specific needs.
Our capabilities for analyses include but not limited to
- Cardiac dysfunction
- Cardiac hypertrophy
- Endothelial dysfunction
- Blood pressure monitoring
- Vascular stiffening
Data & Figures
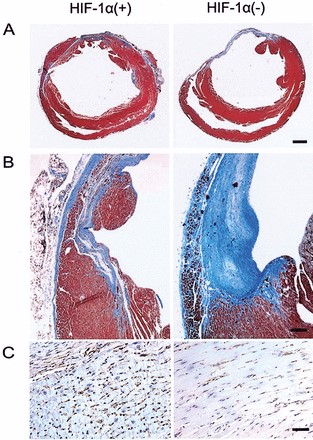 Figure 1. Histology of infarcted hearts. Four weeks after infarction, hearts were excised, sectioned at the level of the papillary muscles, and stained with Masson’s trichrome.
Figure 1. Histology of infarcted hearts. Four weeks after infarction, hearts were excised, sectioned at the level of the papillary muscles, and stained with Masson’s trichrome.
Quotation and ordering
We have extensive experience in developing disease models based on scientific publications. To discuss any of these models further or to discuss the possibility of developing alternative models, please do not hesitate to contact us.
Reference
- Kido, M. et al. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1-Alpha Reduces Infarction and Attenuates Progression of Cardiac Dysfunction After Myocardial Infarction in the Mouse. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 46, 2116–2124 (2005).
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Oral Mucositis Model
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
- Graft-versus-host Disease (GvHD) Models
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Schizophrenia Model
- Depression Models
- Pain Models
-
Metabolic Disease Models
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Animal Model of Hyperuricemia
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model
- High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Methionine and Choline Deficient (MCD) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Gubra-Amylin NASH (GAN) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Model
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer (DFU) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthotopic Kidney Transplantation Model
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Model
- Peritoneal Fibrosis Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
- Otology Disease Models