32D
Cat.No.: CSC-C1101
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
Source: Bone Marrow
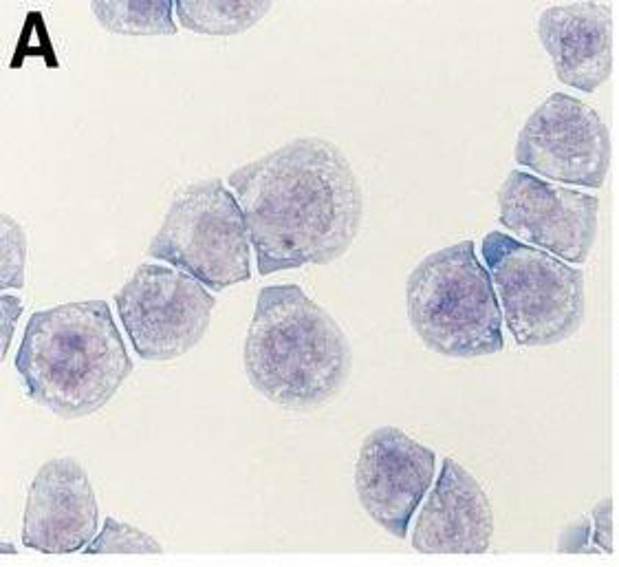
Morphology: mostly round cells growing singly or in small clusters in suspension, some cells are loosely adherent
Culture Properties: suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: CD11b +, F4/80 (+)
Viruses: ELISA: reverse transcriptase negative; PCR: SMRV -
32D is a murine myeloid progenitor cell line first established from Friend virus-transformed bone‑marrow cells of C3H/HeJ mice. It is an IL‑3‑dependent suspension line which grows rapidly in RPMI‑1640 medium containing 10 % heat‑inactivated fetal bovine serum and recombinant mouse IL‑3 (≈10 U ml⁻¹) at 37 °C under 5 % CO₂. The 32D cell is 8-12 µm in diameter and displays an undifferentiated myeloid precursor morphology. The cells are either single suspended cells or grow as clusters of semi‑adherent cells. 32D has a doubling time of approximately 15 h in optimal IL‑3 conditions, but will arrest in the absence of IL‑3. The line can be modified with oncogenic kinases, such as FLT3‑ITD or MPL/TPOR to become IL‑3‑independent, making 32D a good generic line to test oncogene function.
The requirement for IL‑3 makes 32D an extensively used line to dissect IL‑3 signaling pathways, such as JAK/STAT, PI3K/AKT and MAPK. The line has been used extensively as an AML model system for the evaluation of FLT3‑ITD-driven leukemogenesis and tyrosine‑kinase inhibitor sensitivity. 32D can also be directed to undergo granulocytic or monocytic differentiation upon treatment with G‑CSF or other growth factors.
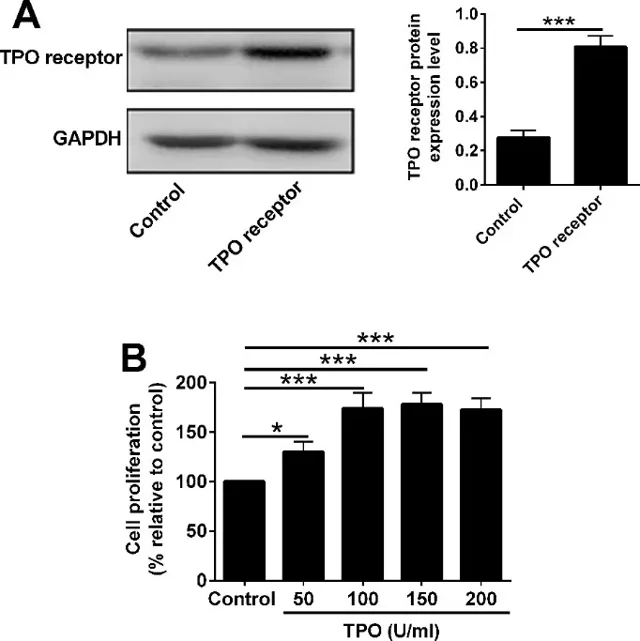
rhTPO Promoted Proliferative Potential of 32D Cells with TPO Receptor Overexpression via Regulating STAT3/STAT5 Expression
Aplastic anemia (AA) serum suppresses proliferation and increases apoptosis of myeloid progenitor 32D cells. Qian's team asked whether recombinant human thrombopoietin (rhTPO) can rescue these defects and clarify the underlying mechanism.
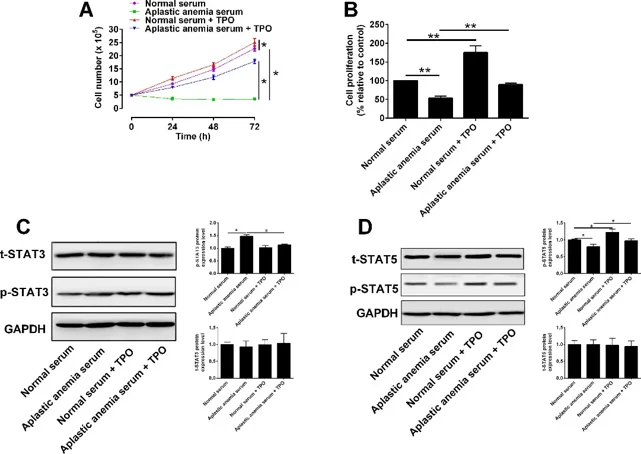
32D cells were infected with lentivirus to overexpress the TPO receptor; Western blot confirmed robust up-regulation (Fig. 1A). CCK-8 assays showed that rhTPO promoted proliferation in a concentration-dependent manner, with maximal effect at 100 U/ml, which was chosen for subsequent experiments. To compare the influence of normal versus aplastic anaemia (AA) serum, four groups were established: (1) normal serum, (2) AA serum, (3) normal serum + 100 U/ml rhTPO, and (4) AA serum + 100 U/ml rhTPO. Trypan-blue exclusion revealed that AA serum almost abolished proliferation at 24, 48 and 72 h, whereas rhTPO increased cell numbers but failed to restore them to the normal-serum level (Fig. 2A). CCK-8 gave the same picture: AA serum strongly inhibited proliferation, and rhTPO only partially reversed this inhibition without reaching normal-serum values (Fig. 2B). They previously observed that AA serum raises p-STAT3 and lowers p-STAT5 during 32D apoptosis. Here, Western blot showed that rhTPO decreased the elevated p-STAT3 and restored the reduced p-STAT5 in AA serum-treated cells (Fig. 2C, D). Thus, rhTPO's ability to rescue proliferation correlates closely with its modulation of STAT3/5 phosphorylation.
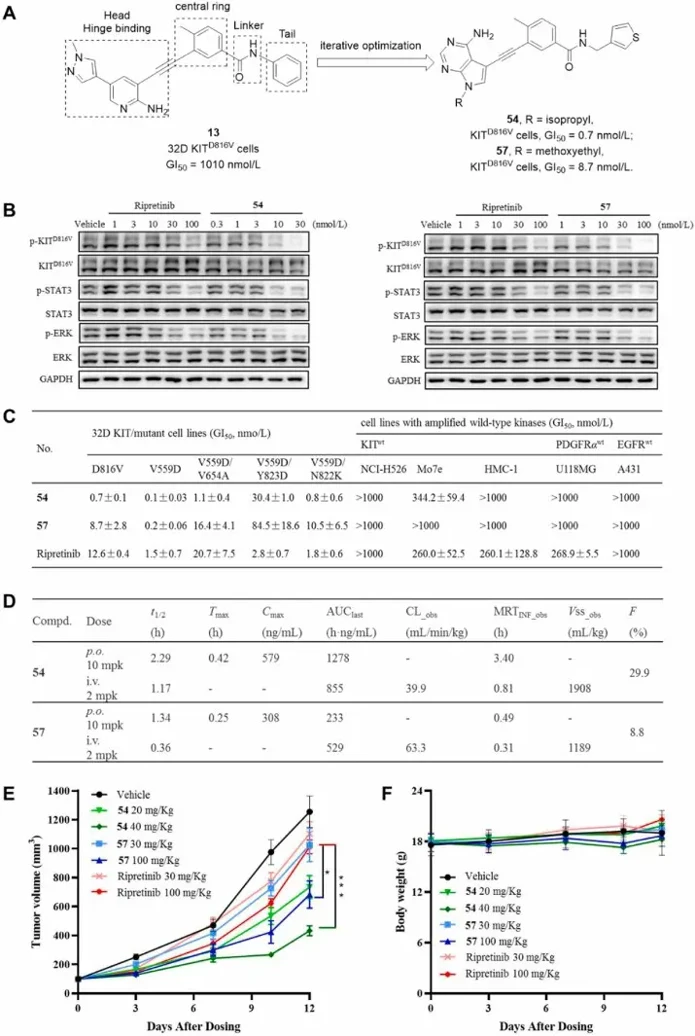
Discovery of Novel Heteroaryl Alkynes for Highly Potent KITD816V Cells Inhibition to Treat Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors
80% GIST carry KIT exon 9/11 mutations; imatinib and later TKIs treat them, but secondary ATP-pocket or A-loop mutations-especially D816V-drive pan-resistance. Existing multikinase inhibitors show modest D816V potency and off-target toxicity, leaving a clinical void. Xie's team aims to develop a highly potent, selective agent that robustly suppresses KITD816V-driven GIST with minimal wild-type KIT interference.
They previously identified type II o-aminopyridyl alkyne CSF-1R inhibitors (e.g., 13, Fig. 3A). Switch-control theory predicts they can flip KIT D816V back to its inactive state. Because KIT's A-loop is phosphate-independent and type II inhibition is hard to reproduce biochemically, they screened directly on KITD816V-transformed 32D cells. Compound 13 showed modest activity (GI₅₀ = 1010 nM). Iterative optimization of linker, tail, central ring and hinge binder then delivered heteroaryl alkynes 54 and 57 with greatly improved potency (Fig. 3A). In 32D-KITD816V cells (Fig. 3B), 54 and 57 outperformed ripretinib by abolishing KIT, STAT3 and ERK phosphorylation. Across a panel of clinically relevant KIT mutants (Fig. 3C), both compounds maintained sub-nanomolar to picomolar GI₅₀ values; 54 was 16-19-fold more potent than ripretinib against V559D, V559D/V654A and V559D/N822K. In KIT-wt-amplified lines (NCI-H526, Mo7e, HMC-1) 54/57 showed markedly reduced activity, yielding wide therapeutic windows, and exhibited ≥1428-fold selectivity over EGFRwt or PDGFRαwt-driven cells. Ripretinib, by contrast, retained strong inhibition of KITwt (GI₅₀ ≈ 260 nM) and PDGFRαwt cells, displaying narrower margins. Thus 54/57 promise potent mutant-KIT suppression with diminished on-target wild-type toxicity.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells