Hyperlipoidemia Model
Hyperlipoidemia is a condition caused by abnormal lipid metabolism or transport, such as Total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), high - density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c) and low - density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c). And it is one of the main risk factors for cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, cancer, and diabetes. In recent years, the morbidity and mortality of hyperlipidemia has increased significantly, and it has become a major threat to human health.
Creative Bioarray specializes in providing customized pharmacodynamic research services to help customers assess the efficacy of drug candidates and study the associated pathological mechanisms through hyperlipoidemia model.
Models available
- Hgih-fat diet induced rat/mouse model
Species available
- Mouse
- Rat
- Rabbit
Our capabilities
- We screen novel preclinical drugs targeting hyperlipoidemia.
- We detect inflammatory cytokines and enzymes by elisa.
- We perform histopathological examination by H&E staining.
Assays available
- PK/PD collection
- Histopathological evaluation
- Biochemical analysis
With extensive experience in the field of hyperlipoidemia, we are confident to help you to overcome any upcoming challenges. Our experts are fully capable of customizing our protocols and assays to meet your specific needs. With our help, we wish to facilitate your research with high efficiency.
Study examples
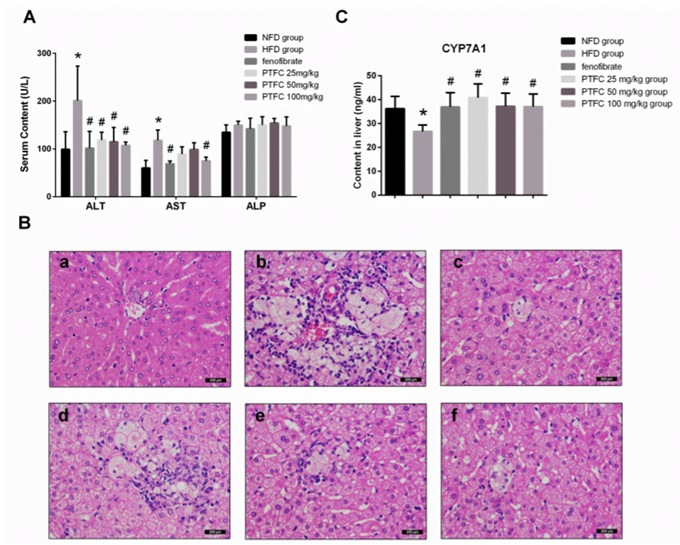 Figure. 1. Effect of PTFC on liver function and hepatocytes pathological damage caused by hyperlipemia. (A) hamsters were treated with NFD, HFD, HFD combined with 100 mg/kg fenofibrate, HFD combined with 25mg/kg, 50mg/kg, 100mg/kg PTFC, and serum ALT, AST and ALP of each group were tested in the end of 6th week before hamsters were sacrificed. (B) Effects of PTFC on the morphology of hepatocytes in hyperlipidemic golden hamsters. (C) Levels of CYP7A1 in liver tissue homogenate of each group were examined by elisa.
Figure. 1. Effect of PTFC on liver function and hepatocytes pathological damage caused by hyperlipemia. (A) hamsters were treated with NFD, HFD, HFD combined with 100 mg/kg fenofibrate, HFD combined with 25mg/kg, 50mg/kg, 100mg/kg PTFC, and serum ALT, AST and ALP of each group were tested in the end of 6th week before hamsters were sacrificed. (B) Effects of PTFC on the morphology of hepatocytes in hyperlipidemic golden hamsters. (C) Levels of CYP7A1 in liver tissue homogenate of each group were examined by elisa.
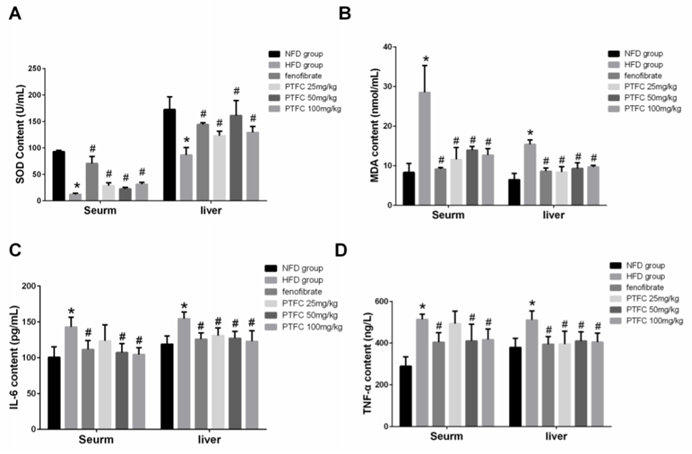 Figure. 2. Amelioration of PTFC on antioxidation activity and inflammation induced by Hyperlipidemia in both liver and serum.
Figure. 2. Amelioration of PTFC on antioxidation activity and inflammation induced by Hyperlipidemia in both liver and serum.
Quotation and ordering
If you have any special needs or questions regarding our services, please feel free to contact us. We look forward to cooperating with you in the future.
Reference
Meng-Jie Zhao, et al. Hypolipidemic effect of XH601 on hamsters of Hyperlipidemia and its potential mechanism[J]. Lipids in Health & Disease, 16(1).
For research use only. Not for any other purpose.
Disease Models
- Oncology Models
-
Inflammation & Autoimmune Disease Models
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Models
- Glomerulonephritis Models
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Models
- Ocular Inflammation Models
- Sjögren's Syndrome Model
- LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury Model
- Peritonitis Models
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis Model
- Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Models
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Animal Models
- Oral Mucositis Model
- Asthma Model
- Sepsis Model
- Psoriasis Model
- Atopic Dermatitis (AD) Model
- Scleroderma Model
- Gouty Arthritis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Air Pouch Synovitis Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Experimental Autoimmune Myasthenia Gravis (EAMG) Model
- Graft-versus-host Disease (GvHD) Models
-
Cardiovascular Disease Models
- Surgical Models
- Animal Models of Hypertension
- Venous Thrombosis Model
- Atherosclerosis model
- Cardiac Arrhythmia Model
- Hyperlipoidemia Model
- Doxorubicin-induced Heart Failure Model
- Isoproterenol-induced Heart Failure Model
- Arterial Thrombosis Model
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Models
- Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
-
Neurological Disease Models
- Alzheimer's Disease Modeling and Assays
- Seizure Models
- Parkinson's Disease Models
- Ischemic Stroke Models
- Acute Spinal Cord Injury (ASCI) Model
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Model
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Model
- Tourette Syndrome (TS) Model
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) Model
- Huntington's Disease (HD) Model
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) Models
- Schizophrenia Model
- Depression Models
- Pain Models
-
Metabolic Disease Models
- Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Model
- Animal Model of Hyperuricemia
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Model
- High-Fat Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Methionine and Choline Deficient (MCD) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Gubra-Amylin NASH (GAN) Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- Streptozotocin (STZ) Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Model
- High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Model
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer (DFU) Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Liver Disease Models
- Rare Disease Models
- Respiratory Disease Models
- Digestive Disease Models
-
Urology Disease Models
- Cisplatin-induced Nephrotoxicity Model
- Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury (RIRI) Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) Models
- Passive Heymann Nephritis (PHN) Model
- Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Model
- Kidney Stone Model
- Doxorubicin-Induced Nephropathy Model
- Orthotopic Kidney Transplantation Model
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Model
- Peritoneal Fibrosis Model
- Cardio-Renal-Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome Model
- Orthopedic Disease Models
- Ocular Disease Models
- Skin Disease Models
- Infectious Disease Models
- Otology Disease Models