CYP and UGT Reaction Phenotyping Assay
- Service Details
- Features
- FAQ
- Explore Other Options
Reaction phenotyping (identifying which drug-metabolizing enzymes contribute to a candidate's clearance) has always been an early foundational step in preclinical ADME and DDI risk assessment. The primary goals are to determine the fraction metabolized (fm) by individual enzymes, characterize enzyme kinetics, and flag enzymes that could mediate clinically relevant drug–drug interactions. These data feed quantitative DDI predictions and guide the need and design of clinical DDI studies.
In recent years, the scope of reactions typically explored during reaction phenotyping has been extended beyond classical CYP450 isoforms to also focus on phase II conjugation enzymes (particularly UGTs) as well as non-CYP pathways (CES, AOX, FMOs, SULTs, NATs, etc). The recognition of UGT- and non-CYP–mediated metabolism has increased due to their potential impact on drug exposure and interaction risk for specific chemotypes.
Why reaction phenotyping is necessary?
- The FDA and ICH M12 final guidance now clearly support in vitro enzyme phenotyping for drug–drug interaction assessments and to determine when follow-up clinical studies are needed.
- Identification of enzymes contributing to ≥ 25% of metabolic clearance (fm ≥ 25%) is a common threshold used as a trigger for more detailed DDI evaluation or clinical interaction studies.
- Regulators expect robust, well-documented in vitro approaches (recombinant enzymes, human liver microsomes/hepatocytes, inhibitor cocktails, and orthogonal methods) to support mechanistic conclusions.
Creative Bioarray's Reaction Phenotyping Assay
Brief Workflow
Step 1: Metabolite Generation
Add the test compound to human hepatocytes, liver microsomes (HLMs) or recombinant CYP/UGT enzymes for in vitro incubation
Step 2: Reaction Optimization
Optimize the incubation reaction conditions (pH, temperature, cofactor concentration, etc.).
Step 3: Sample Analysis
The incubated samples are then extracted and analyzed by high-resolution LC-MS/MS, providing sensitive detection, structural elucidation and quantification of the primary and secondary metabolites.

Step 4: Enzyme Identification
A range of selective chemical inhibitors are used to probe the contribution of specific enzymes to the metabolism of the parent drug.
Step 5: Data Interpretation & Reporting
The results are analyzed to determine which enzymes are responsible for the formation of each major metabolite, followed by a comprehensive report detailing the findings.
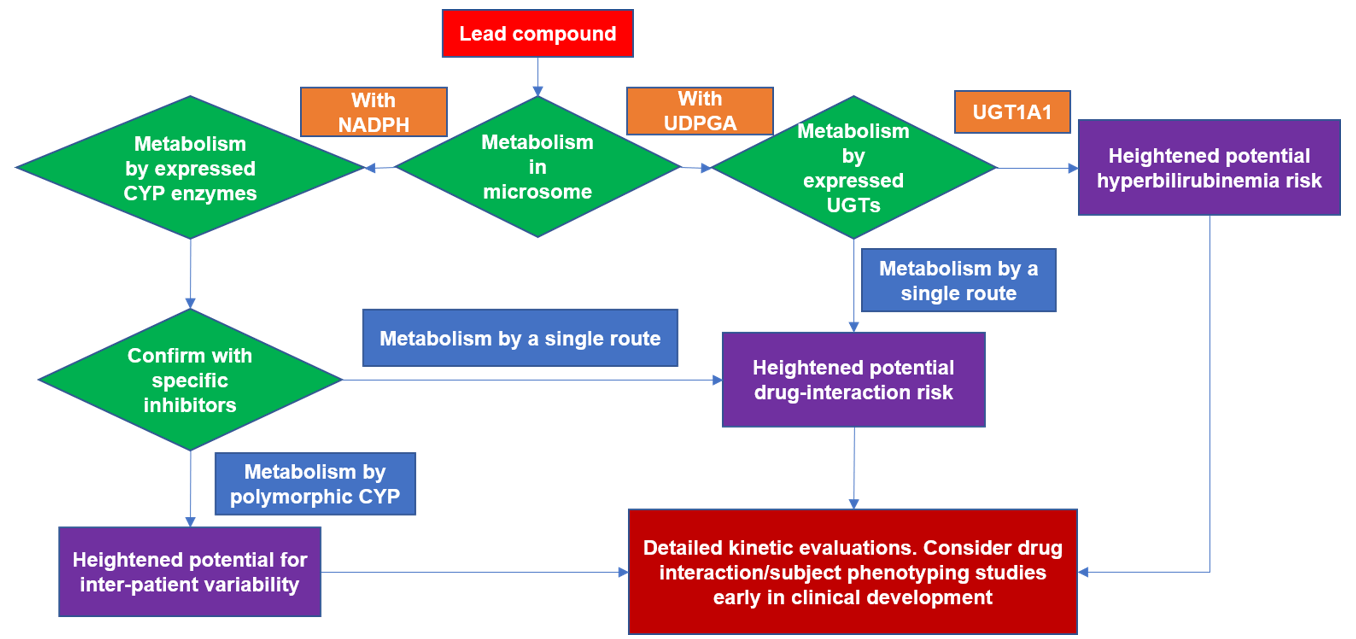 Figure 1. Flowchart for typical reaction phenotyping evaluation of a lead drug candidate.
Figure 1. Flowchart for typical reaction phenotyping evaluation of a lead drug candidate.
Our Capabilities:
- Cytochrome P450 (CYP) Enzymes: CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP3A4/5
- UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) Enzymes: UGT1A1, UGT1A3, UGT1A4, UGT1A6, UGT1A9, UGT2B7, UGT2B15
- Other Non-CYP Enzymes: Such as Flavin-containing Monooxygenases (FMO), Aldehyde Oxidase (AO), Xanthine Oxidase (XO), Monoamine Oxidase (MAO), Carboxylesterase (CES)
Protocol
| Parameters | Details |
| Test Concentration | 5μm (or other concentrations) |
| Incubation Temperature | 37°C |
| Time Points | 0, 5, 15, 30, 45, 60, 120 minutes |
| Number of Replicates | n ≥ 3 per time point |
| Analysis Method | LC-MS/MS |
| Cofactor | NADPH regenerating system for CYP, UDPGA for UGT |
| Positive controls | Probe substrates for each enzyme (e.g., midazolam for CYP3A4) |
| Data delivered | Raw data files, processed chromatograms, kinetic parameters (Km, Vmax), fm estimates, interpretation report |
Reaction phenotyping is part of our broad drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics (DMPK) services. Other DMPK services include Cytochrome P450 Induction Assay, Cytochrome P450 Inhibition Assay, UGT Induction, and UGT Inhibition. These services provide a complete picture of your compound's interaction with the major metabolic pathways, crucial for a robust DDI risk assessment.
Key Features

Comprehensive enzyme coverage
full CYP + broad UGT panel and optional non-CYP pathways for compounds with atypical metabolism.

Experienced DMPK team
senior scientists with long track records in reaction phenotyping, metabolite identification, and regulatory interactions.

Flexible reporting
clear interpretative reports targeted for discovery, preclinical packages, or regulatory submissions.
FAQ
What is the difference between reaction phenotyping and inhibition assays?
Reaction phenotyping reveals the specific enzyme(s) responsible for a compound's metabolic processes whereas inhibition assays measure the extent to which a compound inhibits particular enzymes. Both are essential for a complete drug-drug interaction (DDI) risk assessment.
What the benefits of CYP and UGT reaction phenotyping for early drug development?
Reaction phenotyping is an important component of the early drug discovery process. Identifying the enzymes responsible for metabolizing candidate compounds allows rapid screening of those compounds with more desirable metabolic properties. This assay will help to determine the pathway(s) by which a drug will be cleared from the body, and to what degree a metabolic drug-drug interaction may occur. With this valuable information early in the preclinical development process, you can make well informed decisions and avoid late-stage development failures due to unexpected metabolic liabilities, saving time and money.
When should we test UGTs?
Test UGTs when initial stability/metabolite profiling or physicochemical properties (polar functionality) suggest glucuronidation, or when HLM/hepatocyte incubations show significant conjugates. This is becoming more and more important as the amounts of molecules with high phase II clearance increases.
What kind of sample do I need to submit?
We require a sufficient quantity of your test compound in a stable, soluble form. Our team will provide detailed instructions on sample preparation and submission to ensure optimal assay performance.
Reference
- Chen Y, Fretland AJ, et al. Utility of intersystem extrapolation factors in early reaction phenotyping and the quantitative extrapolation of human liver microsomal intrinsic clearance using recombinant cytochromes P450. Drug Metab Dispos. 2011 Mar; 39 (3):373-82.
Explore Other Options