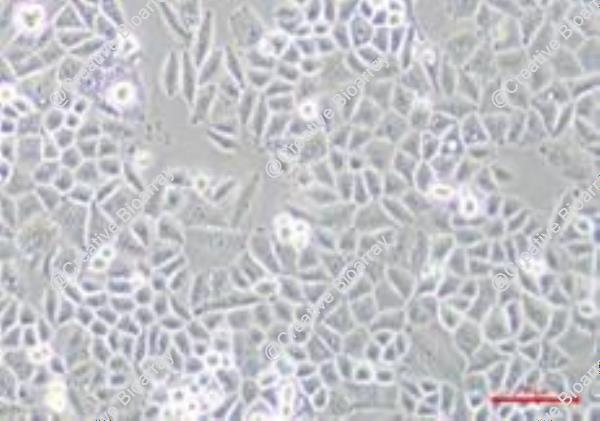
Immortalized Human Ovarian Epithelial Cells-SV40
Cat.No.: CSC-I9009L
Species: homo sapiens
Source: Ovaries
Morphology: Polygonal (at low density), Cuboidal (at high density)
Culture Properties: Adherent
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
- Documents
Note: Never can cells be kept at -20 °C.
CIK-HT003 HT® Lenti-SV40T Immortalization Kit
The origin of epithelial ovarian cancer has long been a matter of debate, with proposed sources including ovarian surface epithelial (OSE) cells, secondary Müllerian tract structures, or fallopian tube epithelium. Despite being the second most common type of gynecological cancer and the leading cause of death in the United States, in vitro cell models that mimic normal ovarian epithelial cells and their malignant counterparts are lacking.
Primary ovarian cells can only be maintained in vitro for a few passages before becoming senescence or undergoing spontaneous transformation. Cells immortalized with tumor antigens can be grown as cell lines, but an obvious concern is that their properties may be altered by tumor antigen-induced cell transformation. A deeper understanding of the role of ovarian stroma in ovarian biology and carcinogenesis requires the availability of ovarian cell lines that can continuously grow in vitro but are not transformed. To address this gap, we established immortalized human OSE (IHOSE) cell lines that have stable growth without malignant properties. The epithelial characteristics were confirmed by cytokeratin 7 and cytokeratin 18 marker expression. Confirmation of these characteristics and stability of IHOSE cell line could provide a useful resource for comparative or gene expression studies on ovarian cancer, helping to identify novel therapeutic and/or diagnostic targets.
Identification and Characterization of Multipotential Stem Cells in Immortalized Normal Ovarian Surface Epithelial Cells
The IOSE80 cell line represents immortalized cells of the ovarian epithelium. These cells were obtained from normal human ovarian epithelial cells that had been transfected with SV-40T. It not only maintains some morphological characteristics and molecular markers of normal ovarian epithelium but also has strong proliferation ability in vitro. It is commonly used to study the origin of epithelial ovarian cancer or as a control for epithelial ovarian cancer cell research. However, its characteristics have not yet been fully identified. This study aims to determine whether IOSE80 have the characteristics of stem cell proliferation and multilineage differentiation and their application in regenerative medicine.
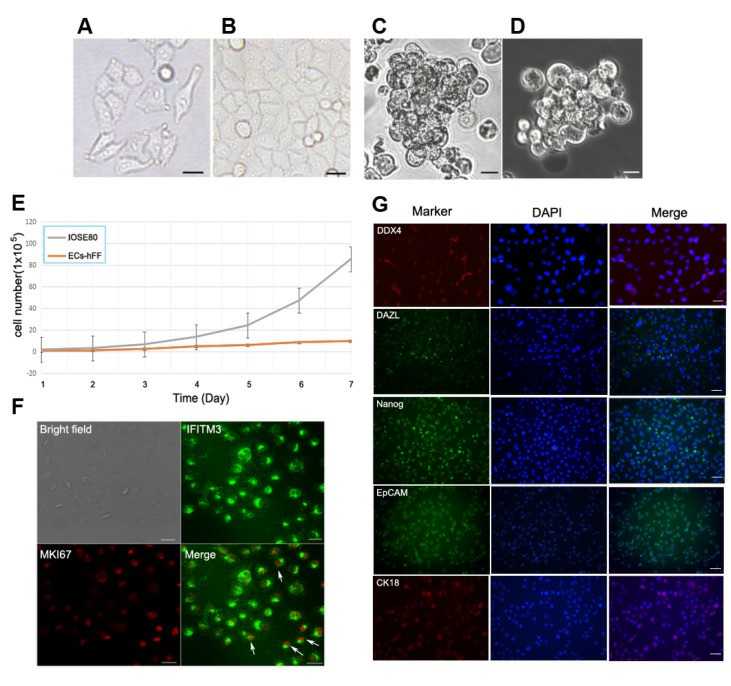 Fig. 1. Characteristics of the IOSE80 cell line (Hou, Lin, et al. 2024).
Fig. 1. Characteristics of the IOSE80 cell line (Hou, Lin, et al. 2024).
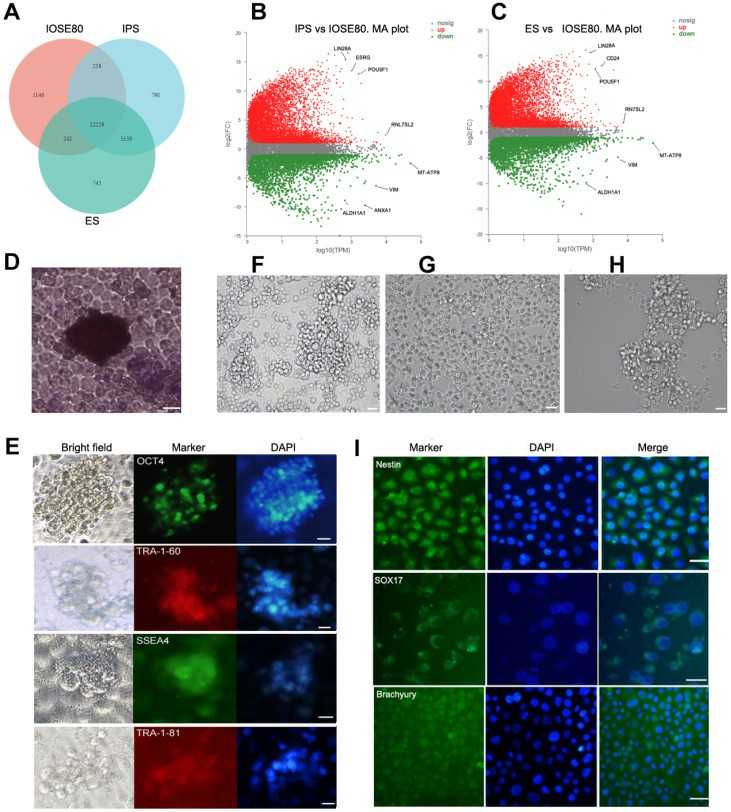 Fig. 2. Comparison of transcriptomic differences between IOSE80 cells and pluripotent stem cells (Hou, Lin, et al. 2024).
Fig. 2. Comparison of transcriptomic differences between IOSE80 cells and pluripotent stem cells (Hou, Lin, et al. 2024).
SMS2 But Not SMS1 is Upregulated in Ovarian Cancer Cells and SMS2 Overexpression Promotes Growth and Migration in Immortalized Normal Ovary Epithelial Cells
Sphingomyelin synthase 1 (SMS1) and 2 (SMS2) are two enzymes required for sphingomyelin de novo synthesis, and their roles in tumor transformation and development have been recently recognized. In this work, we systematically evaluated the expression patterns of SMS1 and 2 in ovarian cancer patient samples and cell lines. Furthermore, we analyzed the functions of SMS2 and its underlying mechanisms.
We found that 6 of 7 ovarian cancer cell lines demonstrated higher SMS2 protein levels than IHOEC (human normal ovary epithelial cell immortalized with SV40 lentiviral transfection) (Fig. 3A). The upregulation of SMS2 but not SMS1 in ovarian cancer cells was not only on the protein level but also seen on the mRNA level (Fig. 3B). We next transfected IHOEC with mammalian expression construct containing SMS2 and confirmed SMS2 overexpression (Fig. 3C). We further found that SMS2 overexpression significantly increased proliferation and migration in IHOEC (Fig. 3D, 3E). Of note, proliferation and migration were increased by ~1.5-fold and ~5-fold respectively, suggesting that SMS2 might play a predominant role in migration rather than proliferation.
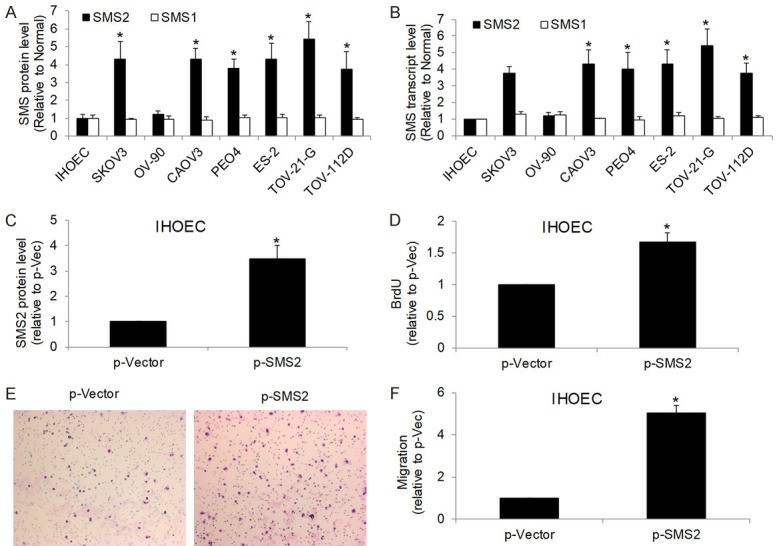 Fig. 3. SMS2 overexpression promotes growth and migration in immortalized human ovarian epithelial cells (IHOEC).
Fig. 3. SMS2 overexpression promotes growth and migration in immortalized human ovarian epithelial cells (IHOEC).
Primary cells reach a state of replicative senescence after a certain amount of proliferation, and a certain number of divisions, thus limiting the proliferation of senescent or damaged cells. GeneCopoeia provides cell immortalization reagents that induce immortalization using recombinant lentiviral-carrying genes, such as simian virus 40 (SV40) large T-antigen and human telomerase reverse transcriptase protein (hTERT), can significantly extend the lifespan of primary cells.
Immortalized Human Ovarian Epithelial Cells-SV40 are ovarian epithelial cells that have been transformed using the SV40 large T antigen, allowing them to proliferate while retaining key characteristics of normal ovarian epithelial cells. These models are essential for studying ovarian biology and related diseases.
These cells are widely applicable and can be used in various research fields, including:
Ovarian cancer research and drug response studies.
Investigating ovarian physiology and hormone regulation.
Studies on cell signaling pathways in ovarian cells.
Research on epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in cancer.
Toxicology assessments regarding ovarian toxicity.
Ask a Question
Average Rating: 5.0 | 1 Scientist has reviewed this product
Final choice
With many considerations, we finally chose Creative Bioarray's cellular products.
09 Oct 2022
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Write your own review
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells