Lung Tumor Cells
- Background
- Applications
- Scientific Data
- FAQ
Lung cancer remains one of the most prevalent and deadly forms of cancer worldwide. Lung tumor cells originate from the epithelial cells lining the airways. These cells undergo genetic mutations that lead to uncontrolled growth, resulting in tumors. There are two main types of lung cancer: small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) and non-SCLC (NSCLC), each with distinct biological features and clinical behaviors. NSCLC is further categorized into adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
Lung tumor cells are characterized by a range of morphological features that distinguish them from their healthy counterparts. They often exhibit larger cell sizes, irregular shapes, and prominent, irregularly shaped nuclei, which are hallmarks of their rapid and uncontrolled proliferation. Additionally, lung tumor cells can display a high degree of cellular heterogeneity, with varying levels of differentiation and distinct subpopulations within the same tumor.
Genetic and Molecular Alterations in Lung Tumor Cells
- Gene mutations. Mutations in genes such as TP53, KRAS, and EGFR are commonly found in lung tumor cells. These mutations lead to the activation of oncogenes and the inactivation of tumor suppressor genes, promoting tumor growth and survival.
- Epigenetic changes. Epigenetic modifications, including DNA methylation and histone modification, play a significant role in lung cancer development. These changes can silence tumor suppressor genes and promote tumor growth.
- Chromosomal aberrations. Lung tumor cells often exhibit chromosomal rearrangements and numerical abnormalities. For instance, the translocation of the ALK gene is associated with a subset of lung adenocarcinomas, representing a target for specific inhibitors.
- Protein expression changes. Altered protein expression in lung tumor cells can affect various cellular processes, including cell cycle regulation, apoptosis, and angiogenesis.
In Vitro Modeling of Lung Cancer
Lung tumor cell lines are widely used to create in vitro models that mimic the tumor microenvironment. These models allow researchers to study the interaction between cancer cells and surrounding stromal cells, which is vital for understanding tumor growth, invasion, and metastasis. The ability to replicate the complexity of lung cancer in a dish makes it possible to test the effectiveness of potential therapies under controlled conditions.
High-Throughput Screening
The use of lung tumor cells in high-throughput screening (HTS) assays has accelerated the identification of novel therapeutic compounds. By exposing large libraries of compounds to lung tumor cells, researchers can quickly determine which substances have the potential to inhibit tumor cell growth or induce cell death. This approach is particularly valuable for discovering new drug candidates that can be further developed for clinical use.
Drug Resistance and Sensitivity
Lung tumor cells are used to investigate the mechanisms of drug resistance and to identify biomarkers that can predict patient response to specific treatments. This research can lead to more effective combination therapies and personalized treatment plans.
Gene Therapy and RNA Interference
Lung tumor cells are essential for developing gene therapy approaches, where genes are introduced, edited, or silenced to treat or prevent disease. RNA interference (RNAi) techniques, which use small RNA molecules to silence genes, are tested on lung tumor cells to identify potential therapeutic targets and develop novel treatments.
Glut1KO Neutrophils Negatively Impact Tumor Growth
Because the pro- and anti-tumor properties of neutrophils require a better understanding, the consequences of Glut1KO tumor-associated neutrophils (TAN) on tumor progression (Fig. 1A) were explored. Tumors with Glut1KO TANs had reduced cell proliferation as measured by phospho-Histone H3 (pHH3) and a reduced phospho-ERK1/2 (pERK) staining, a marker of tumor progression (Fig. 1B-C). Moreover, tumor growth rates monitored by longitudinal micro-computed tomography (μCT) were significantly diminished in mice with Glut1KO TANs (Fig. 1D). Next, to determine if TANs affect lung tumor cells in vitro, their behavior was measured using a KP-derived cell line (SV2) cultured alone, with control TANs or with Glut1KO TANs. A stronger negative impact on tumor cell growth was observed in Glut1KO TANs, as revealed by a reduced spreading of co-cultured SV2 cells (Fig. 1E). This suggests that Glut1KO TANs have a reduced tumor-supportive capacity or are endowed with anti-tumor properties.
To test if the reduced tumor-supportive function of Glut1KO TANs can be extended to other models, B16-F1 melanoma cells were injected via the tail vein of control or Glut1KO syngeneic recipient mice and the number of lung lesions was counted three weeks later. In this experimental metastasis model, there were fewer lesions in Glut1KO conditions (Fig. 1F). Furthermore, tumor cell proliferation was reduced in these tumors compared to control tumors, as indicated by a reduced proportion of pHH3-positive cells (Fig. 1G). Thus, TAN-mediated tumor support relies on Glut1 in different cancer types.
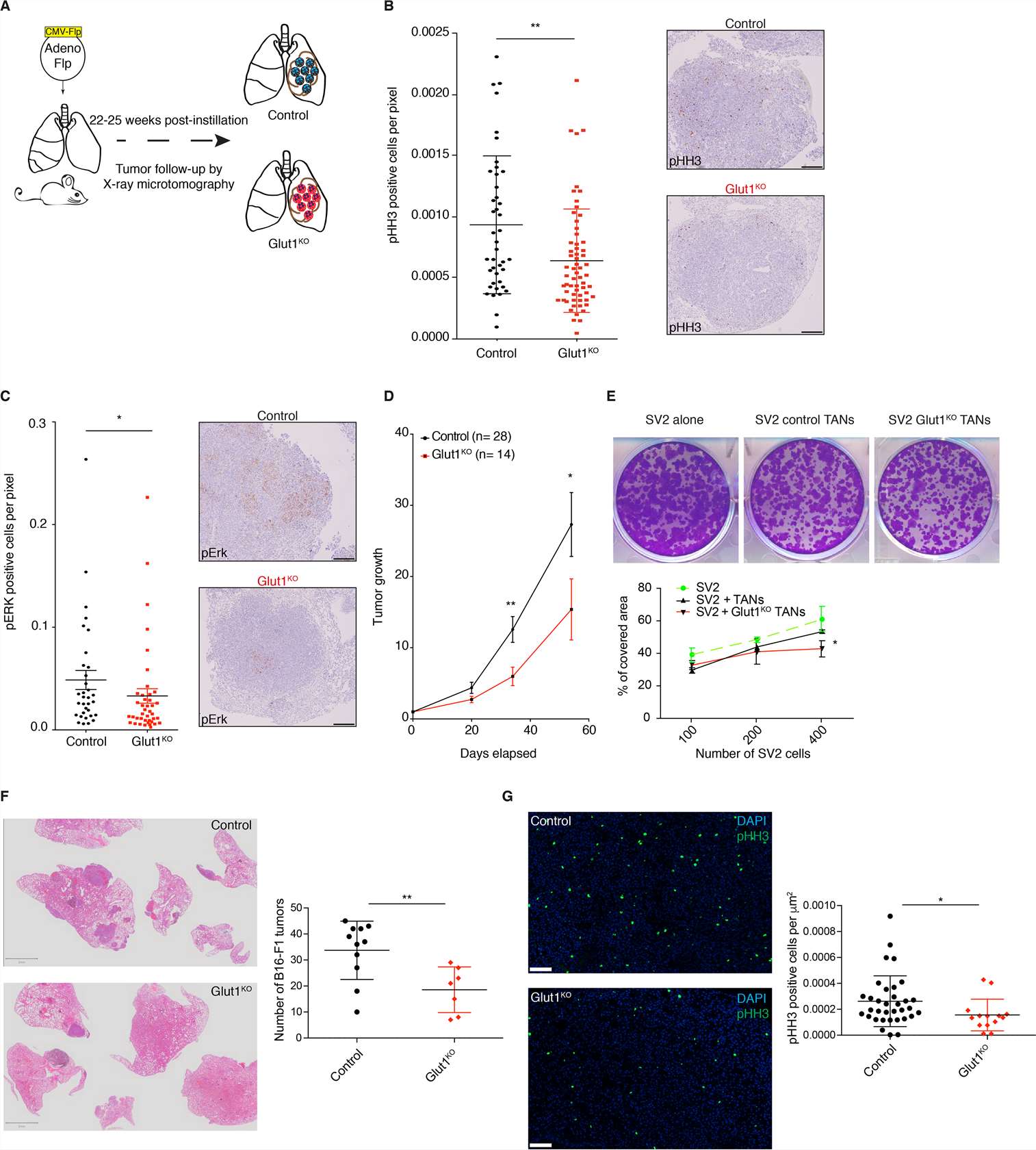 Fig.
1 Glut1 deletion in neutrophils reduces tumor growth. (Ancey PB, et al, 2021)
Fig.
1 Glut1 deletion in neutrophils reduces tumor growth. (Ancey PB, et al, 2021)
Secretion of EpCAM+ Lung Tumor Cell-Derived Exosomes is p53-dependent
To test the hypothesis that lung tumor cell-derived exosomes re-direct macrophage polarization, exosomes were isolated from conditioned media obtained from adenocarcinoma human alveolar basal epithelial cells (A549) and p53 null human lung cancer cells (H358) including the non-tumor epithelial cell line (HEK293) as a negative control. NanoSight analysis of isolated exosomes confirmed the particle size under a range of 50–200 nm (Fig. 2A) consistent with previous observations. The H358 exosomes were significantly smaller than those isolated from A549 (Fig. 2B). NanoSight analysis also showed a significantly lower concentration of H358 exosomes compared to A549 and HEK293 exosomes isolated from an equal volume of conditioned media (Fig. 2C), suggesting that as reported previously, p53 may regulate exosomes secretion from lung tumor cells. Further ImageStream analysis revealed the expression of epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) and exosome-specific surface markers, including CD9, CD63, tumor susceptibility gene 101 (TSG-101), and CD81 (Fig. 2D, E) confirming the tumor cell-derived vesicles as exosomes.
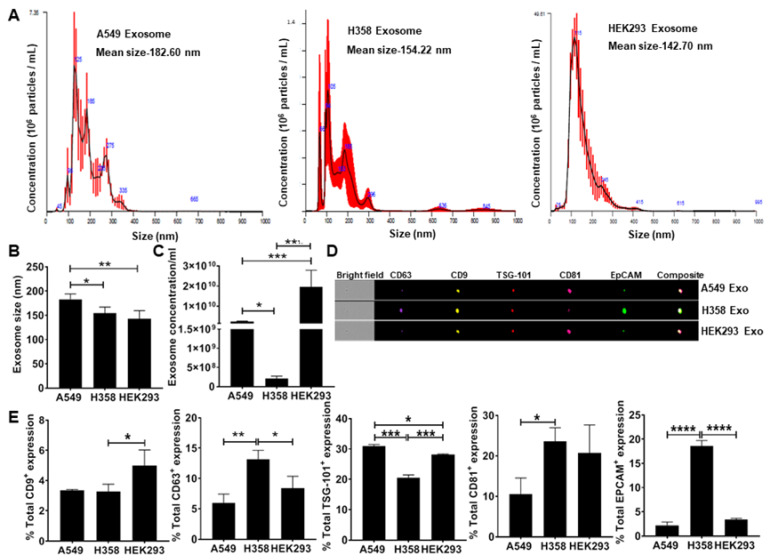 Fig.
2 Quantitation and characterization of tumor-cell derived exosomes. NanoSight and ImageStream analyses of
A549-derived exosomes determined size, concentration, and characterization. Human lung cancer cells A549, H358,
and non-tumor cells HEK293 were cultured in exosome-depleted media for 24 h. (Pritchard A, et al.,
2020)
Fig.
2 Quantitation and characterization of tumor-cell derived exosomes. NanoSight and ImageStream analyses of
A549-derived exosomes determined size, concentration, and characterization. Human lung cancer cells A549, H358,
and non-tumor cells HEK293 were cultured in exosome-depleted media for 24 h. (Pritchard A, et al.,
2020)
Lung tumor cells are abnormal cells that have undergone uncontrolled growth and division within the lungs. These cells can form solid masses or tumors that can be cancerous (malignant) or non-cancerous (benign).
The two main types of lung tumor cells are NSCLC and SCLC cells. NSCLC is the most common type, including adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma. SCLC is a less common but more aggressive type of lung cancer.
They divide and grow uncontrollably, forming a mass or tumor, which may have genetic mutations that allow them to avoid normal cellular growth control mechanisms.
Filters Clear all filters
Species
- African clawed frog (1)
- American mink (1)
- Asian tiger mosquito (1)
- Atlantic salmon (1)
- Bluegill (2)
- Bluestriped grunt (1)
- Bovine (7)
- Brazilian free-tailed bat (1)
- Brown bullhead (2)
- Cabbage looper (1)
- Cabbage moth (6)
- Cat (4)
- Central mudminnow (1)
- Chicken (3)
- Chinese hamster (5)
- Chinook salmon (2)
- Chum salmon (1)
- Coho salmon (1)
- Common carp (2)
- Cotton-top tamarin (1)
- Dog (2)
- Fall armyworm (3)
- Fathead minnow (2)
- Fruit fly (1)
- Gilthead sea bream (2)
- Golden hamster (7)
- Goldfish (6)
- Gray dwarf hamster (1)
- Green monkey (2)
- Gypsy moth (1)
- Horse (1)
- Human (998)
- Japanese eel (1)
- Japanese rice fish (7)
- Koi carp (1)
- Mouse (315)
- Mouse x Gray dwarf hamster (1)
- Mouse x Rat (20)
- Northern pike (1)
- Pig (3)
- Rabbit (2)
- Rainbow trout (3)
- Rat (115)
- Rhesus macaque (1)
- Salt marsh moth (1)
- Sheep (2)
- Snakehead murrel (2)
- Sockeye salmon (1)
- Vervet monkey (2)
- Zebrafish (2)
Source
- Abdomen (1)
- Abdomen Metastasis (2)
- Adipose (2)
- Adrenal Gland (8)
- Adrenal Gland Metastasis (2)
- Aorta (4)
- Artery (1)
- Ascites (28)
- Ascites Metastasis (37)
- Bile Duct (3)
- Bladder (25)
- Bladder Metastasis (1)
- Blastocyst (1)
- Blastula (1)
- Blood (127)
- Bone (27)
- Bone Marrow (57)
- Bone Marrow Metastasis (18)
- Bone Metastasis (6)
- Brain (55)
- Brain Metastasis (8)
- Breast (30)
- Bronchus (1)
- Caudal Peduncle (1)
- Caudal Trunk (2)
- Cecum (3)
- Cerebrospinal Fluid (1)
- Cerebrospinal Fluid Metastasis (1)
- Cervix (32)
- Colon (90)
- Connective Tissue (7)
- Cornea (3)
- Cutaneous Metastasis (1)
- Dermis (2)
- Duodenum (1)
- Embryo (29)
- Endometrium (17)
- Esophagus (44)
- Eye (12)
- Eye Socket (5)
- Fetus (3)
- Fin (9)
- Foreskin (4)
- Gallbladder (1)
- Gingiva (2)
- Globe (2)
- Glomerulus (2)
- Groin (1)
- Head Kidney (2)
- Heart (4)
- Hemolymph (1)
- Hypodermis Metastasis (5)
- Ileum (1)
- Intestine (94)
- Jejunum (1)
- kidney (1)
- Kidney (27)
- Liver (35)
- Liver Metastasis (17)
- Lung (58)
- Lung Metastasis (8)
- Lymph Node (7)
- Lymph Node Metastasis (59)
- Muscle (7)
- Muscle Metastasis (2)
- Nose (2)
- Omentum Metastasis (2)
- Oral Cavity (10)
- Ovary (21)
- Ovary Metastasis (2)
- Pancreas (19)
- Pelvic Wall Metastasis (1)
- Pelvis (1)
- Perianal Space Metastasis (1)
- Pericardial Effusion (1)
- Pericardial Effusion Metastasis (2)
- Perineus (1)
- Peripheral Blood (126)
- Peripheral Nervous System (21)
- Peritoneal Effusion (2)
- Peritoneum (1)
- Peritoneum Metastasis (1)
- Pharynx (3)
- Pituitary Gland (7)
- Pleural Effusion (54)
- Pleural Effusion Metastasis (46)
- Prostate (7)
- Rectum (15)
- Renal Pelvis (1)
- Retroperitoneal Space (2)
- Salivary Gland (2)
- Skeletal Muscle (5)
- Skin (32)
- Skin Metastasis (3)
- Small Intestine (4)
- Small Intestine Metastasis (1)
- Smooth Muscle (2)
- Soft Tissue (1)
- Soft Tissue Metastasis (1)
- Spinal Cord (2)
- Stomach (4)
- Testis (15)
- Thoracic Cavity Metastasis (6)
- Thymus (5)
- Thyroid Gland (16)
- Thyroid Gland Metastasis (1)
- Tongue (5)
- Trachea (1)
- Umbilical Cord (1)
- Umbilical Cord Blood (1)
- Urachus (1)
- Ureter (1)
- Uterus (54)
- Uvea (2)
- Vagina (2)
- Vulva (1)
Disease
- Acute Biphenotypic Leukemia (1)
- Acute Erythroid Leukemia (4)
- Acute Megakaryoblastic Leukemia (4)
- Acute Monocytic Leukemia (9)
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (25)
- Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia (2)
- Adrenal Gland Neuroblastoma (11)
- Adult B Acute Lymphoblastic leukemia (1)
- Adult B Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (6)
- Adult T Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (6)
- Adult T Lymphoblastic Lymphoma (2)
- Adult T-Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma (1)
- Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma (4)
- Alveolar Ridge Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Amelanotic Melanoma (3)
- Ampulla of Vater Adenocarcinoma (1)
- Ampulla of Vater Adenosquamous Carcinoma (3)
- Anaplastic Astrocytoma (3)
- Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (7)
- Askin Tumor (1)
- Astrocytoma (5)
- B Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (2)
- B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (5)
- Bare Lymphocyte Syndrome Type 2 (1)
- Barrett Adenocarcinoma (2)
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (1)
- Bladder Carcinoma (14)
- Bladder Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Bovine Leukemia (2)
- Breast Adenocarcinoma (4)
- Breast Carcinoma (9)
- Breast Ductal Carcinoma (2)
- Burkitt Lymphoma (17)
- Canavan Disease (1)
- Canine Histiocytic Sarcoma (1)
- Cecum Adenocarcinoma (3)
- Central Nervous System Lymphoma (2)
- Cervical Adenocarcinoma (2)
- Cervical Adenosquamous Carcinoma (2)
- Cervical Small Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma (2)
- Chicken Bursal Lymphoma (2)
- Childhood B Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (13)
- Childhood T Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (16)
- Childhood T Lymphoblastic Lymphoma (1)
- Cholangiocarcinoma (2)
- Chronic Eosinophilic Leukemia (1)
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (2)
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (23)
- Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma (2)
- Colon Adenocarcinoma (55)
- Colon Carcinoma (34)
- Colorectal Adenocarcinoma (1)
- Colorectal Carcinoma (1)
- Congenital Pure Red Cell Aplasia (1)
- Cutaneous Melanoma (10)
- Dedifferentiated Chondrosarcoma (1)
- Desmoplastic Melanoma (1)
- Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (28)
- Down Syndrome (2)
- EBV-Related Burkitt Lymphoma (12)
- Embryonal Carcinoma (3)
- Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma (3)
- Endometrial Adenocarcinoma (13)
- Endometrial Adenosquamous Carcinoma (2)
- Endometrial Carcinoma (2)
- Endometrioid Stromal Sarcoma (1)
- Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma (1)
- Epithelioid Sarcoma (3)
- Esophageal Adenocarcinoma (6)
- Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (41)
- Essential Thrombocythemia (1)
- Ewing Sarcoma (2)
- Extraskeletal Myxoid Chondrosarcoma (1)
- Fanconi Anemia (1)
- Fibrosarcoma (1)
- Follicular Lymphoma (2)
- Gallbladder Carcinoma (2)
- Gallbladder Undifferentiated Carcinoma (2)
- Gastric Adenocarcinoma (6)
- Gastric Adenosquamous Carcinoma (1)
- Gastric Carcinoma (5)
- Gastric Choriocarcinoma (1)
- Gastric Fundus Carcinoma (1)
- Gastric Signet Ring Cell Adenocarcinoma (1)
- Gastric Small Cell Carcinoma (2)
- Gastric Tubular Adenocarcinoma (5)
- Gastroesophageal Junction Adenocarcinoma (1)
- Gestational Choriocarcinoma (1)
- Gingival Squamous Cell Carcinoma (2)
- Glioblastoma (18)
- Gliosarcoma (1)
- Goldfish Erythrophoroma (4)
- Hairy Cell Leukemia (1)
- Hamster Kidney Tumor (1)
- Hamster Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (1)
- Hamster Uterine Leiomyosarcoma (1)
- Hepatoblastoma (2)
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma (6)
- Hepatosplenic T-Cell Lymphoma (2)
- Hereditary Thyroid Gland Medullary Carcinoma (1)
- High Grade B-Cell Lymphoma (1)
- High Grade Ovarian Serous Adenocarcinoma (8)
- Hodgkin Lymphoma (9)
- Hypopharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (2)
- Infectious Mononucleosis (1)
- Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma (6)
- Invasive Breast Carcinoma of No Special Type (12)
- Invasive Breast Lobular Carcinoma (1)
- Kidney Neoplasm (1)
- Kidney Rhabdoid Tumor (1)
- Krukenberg Tumor (1)
- Liposarcoma (1)
- Lung Adenocarcinoma (17)
- Lung Giant Cell Carcinoma (8)
- Lung Large Cell Carcinoma (9)
- Lung Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma (1)
- Lung Non-Small Cell Carcinoma (2)
- Lung Small Cell Carcinoma (25)
- Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma (9)
- Lymphoblastic Lymphoma (1)
- Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor (1)
- Mantle Cell Lymphoma (5)
- Mature Gastric Teratoma (1)
- Maxillary Sinus Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Medaka Hepatoma (2)
- Medulloblastoma (3)
- Melanoma (24)
- Meningioma (2)
- Minimally Invasive Lung Adenocarcinoma (1)
- Monophasic Synovial Sarcoma (1)
- Mouse Bladder Transitional Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Mouse Chondrosarcoma (1)
- Mouse Colon Adenocarcinoma (3)
- Mouse Ependymoma (2)
- Mouse Erythroid Leukemia (13)
- Mouse Fibrosarcoma (5)
- Mouse Glioblastoma (1)
- Mouse Hemangioendothelioma (1)
- Mouse Hepatocellular Carcinoma (1)
- Mouse Insulinoma (3)
- Mouse Intestinal Tract Neuroendocrine Adenoma (1)
- Mouse Islet Cell Adenoma (1)
- Mouse Kidney Carcinoma (1)
- Mouse Leukemia (10)
- Mouse Leydig Cell Tumor (1)
- Mouse Lymphoma (8)
- Mouse Mammary Gland Malignant Neoplasm (23)
- Mouse Melanoma (9)
- Mouse Multiple Myeloma (5)
- Mouse Myeloid Leukemia (3)
- Mouse Neoplasm (1)
- Mouse Neuroblastoma (21)
- Mouse Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Mouse Osteosarcoma (3)
- Mouse Pituitary Gland Neoplasm (1)
- Mouse Plasmacytoma (1)
- Mouse Precursor T Cell Lymphoblastic Lymphoma/Leukemia (2)
- Mouse Pulmonary Adenoma (1)
- Mouse Pulmonary Malignant Tumor (3)
- Mouse Pulmonary Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Mouse Rectum Carcinoma (2)
- Mouse Reticulum Cell Sarcoma (2)
- Mouse Sarcoma (1)
- Mouse Teratocarcinoma (8)
- Mouse Thymic Lymphoma (3)
- Mycosis Fungoides (1)
- Myelodysplastic Syndrome (1)
- Myxofibrosarcoma (1)
- Natural Killer Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma (2)
- Neuroblastoma (26)
- Oral Cavity Squamous Cell Carcinoma (15)
- Osteoid Osteoma (1)
- Osteosarcoma (15)
- Ovarian Carcinoma (1)
- Ovarian Clear Cell Adenocarcinoma (1)
- Ovarian Endometrioid Adenocarcinoma (4)
- Ovarian Granulosa Cell Tumor (1)
- Ovarian Mucinous Adenocarcinoma (2)
- Ovarian Serous Adenocarcinoma (2)
- Ovarian Serous Cystadenocarcinoma (2)
- Ovarian Small Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma (13)
- Pancreatic Carcinoma (5)
- Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (12)
- Papillomavirus-Independent Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Papillomavirus-Related Cervical Adenocarcinoma (7)
- Papillomavirus-Related Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma (4)
- Papillomavirus-Related Endocervical Adenocarcinoma (16)
- Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (3)
- Pharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Plasma Cell Myeloma (15)
- Pleural Epithelioid Mesothelioma (5)
- Pleural Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma (2)
- Poorly Differentiated Thyroid Gland Carcinoma (1)
- Primary Cutaneous T-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (1)
- Primary Effusion Lymphoma (7)
- Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor (1)
- Prostate carcinoma (1)
- Prostate Carcinoma (9)
- Rat C-Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Rat Cholangiocarcinoma (1)
- Rat Colon Adenocarcinoma (5)
- Rat Digestive System Neoplasm (1)
- Rat Fibrosarcoma (1)
- Rat Hepatocellular Carcinoma (20)
- Rat Histiocytic Sarcoma (1)
- Rat Insulinoma (2)
- Rat Leukemia (1)
- Rat Leydig Cell Adenoma (1)
- Rat Lung Carcinoma (1)
- Rat Malignant Glioma (4)
- Rat Malignant Meningioma (1)
- Rat Malignant Oligodendroglioma (2)
- Rat Malignant Thymoma (3)
- Rat Mammary Gland Adenocarcinoma (10)
- Rat Neuroblastoma (3)
- Rat Osteosarcoma (2)
- Rat Pituitary Gland Neoplasm (6)
- Rat Prostate Adenocarcinoma (3)
- Rat Rhabdomyosarcoma (1)
- Rat Sarcoma (2)
- Rat Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Rat Urinary Bladder Transitional Cell Carcinoma (2)
- Rat Urinary System Neoplasm (6)
- Rectal Adenocarcinoma (13)
- Rectosigmoid Adenocarcinoma (1)
- Recurrent Bladder Carcinoma (1)
- Renal Cell Carcinoma (7)
- Renal Pelvis Urothelial Carcinoma (1)
- Retinoblastoma (11)
- Sacral Chordoma (1)
- Sacrococcygeal Teratoma (1)
- Salivary Gland Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
- Sezary Syndrome (1)
- Shwachman-Diamond Syndrome (1)
- Skin Squamous Cell Carcinoma (2)
- Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma (1)
- Testicular Embryonal Carcinoma (8)
- Testicular Teratoma (2)
- Testicular Yolk Sac Tumor (1)
- Thyroid Gland Anaplastic Carcinoma (10)
- Thyroid Gland Follicular Carcinoma (4)
- Thyroid Gland Papillary Carcinoma (3)
- Thyroid Gland Sarcoma (1)
- Thyroid Gland Squamous Cell Carcinoma (2)
- Tongue Adenosquamous Carcinoma (1)
- Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma (6)
- Type I Endometrial Adenocarcinoma (1)
- Ureter Urothelial Carcinoma (1)
- Uterine Carcinosarcoma (2)
- Uterine Corpus Leiomyosarcoma (1)
- Uterine Corpus Sarcoma (2)
- Uveal Melanoma (2)
- Vaginal Melanoma (2)
- Vulvar Melanoma (1)
- Vulvar Squamous Cell Carcinoma (1)
Description: Species: human female 57 years old; Tissue: lung; Tumor: adenocarcinoma; Derived from: pleural fluid
Description: Species: human, Caucasian male 62 years old; Tissue: lung; Tumor: carcinoma, large cell; Derived ...
Description: Species: human male; Tissue: lung; Tumor: carcinoma, small cell; Derived from: metastatic lymph node
Description: Species: human male; Tissue: lung; Tumor: carcinoma, small cell; Derived from: pleural effusion
Description: established from the lung tissue of a male patient with minimally invasive lung adenocarcinoma
Description: Established from the pleural fluid of a 57-year-old woman with adenocarcinoma of the lung in 1986
Description: Established from the supraclavicular tumor cells-containing lymph node of a 71-year-old man with ...
Description: Established from the pleural effusion metastasis of a patient with small cell lung carcinoma in ...
Description: Established from a surgical lung specimen of a 57-year-old Caucasian man who underwent surgery for ...
Description: Established from the pleural effusion of a 61-year-old Caucasian man with large cell lung carcinoma ...
Description: Established from a male patient with a non-small cell lung carcinoma in 1981
Description: Established in 1979 from the bone marrow aspirated from a 55-year-old white man with small cell ...
Description: Established in 1985 from the lymph node from a 42-year-old white man with metastatic small cell ...
Description: Established from the pleural effusion of a 49-year-old white woman in 1986 prior to treatment for ...
Description: Derived from the lung of a 56-year-old black man with small cell lung carcinoma prior to treatment ...
Description: Derived from the pleural effusion of a 50-year-old white male with extensive small cell lung ...
Description: The Gefitinib-resistant cell line HCC-827/GR has been developed by repeatedly exposing the parent ...
Description: established from the lung tissue of a male patient with lung squamous cell carcinoma