Immortalized Human Mesothelial Cells-SV40
Cat.No.: CSC-I2097Z
Species: homo sapiens
Morphology: Polygonal
Culture Properties: Adherent
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
free from contaminations (bacteria incl. mycoplasma, fungi, HIV, HAV, HBV, HCV, Parvo-B19) and cross-contaminations
Note: Never can cells be kept at -20°C.
The Immortalized Human Mesothelial Cells-SV40 cell line derives from human peritoneal mesothelial tissue and gains immortality following SV40 large T antigen (SV40T) gene transduction. Mesothelial cells are a single layer of cells covering the inner walls of body cavities such as the abdominal cavity, thoracic cavity, and pericardial cavity. Their main functions include secreting lubricating fluid, participating in immune responses, regulating inflammation, and maintaining tissue homeostasis.
Research uses this cell line to explore how pleural epithelial cells transform malignantly through genetic modifications and environmental exposure tests. For example, SV40-immortalized human pleural epithelial cells develop into tumor cells that show malignant characteristics after they acquire oncogenes such as Ha-ras or PDGF A-chain using transfection. This characteristic makes SV40-immortalized cells an important tool for studying the mechanisms of malignant transformation in pleural epithelial cells. In addition, exposure to asbestos heightens the transformation potential of SV40-immortalized cells due to the joint carcinogenic effects of both asbestos and SV40.
Effect of Glucose-Based PD Fluid and TGF-β1 on Mesothelial Cell miR-200c Expression
Peritoneal fibrosis and loss of transport function are common complications in long-term peritoneal dialysis (PD) patients, driven by epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in mesothelial cells. Dysregulation of microRNA (miR) expression is implicated in EMT and fibrosis.
Chu et al. investigated the role of miR-200c in EMT and fibrogenesis in mesothelial cells, using a murine PD model and cultured cells (immortalized human mesothelial cells), to understand its potential as a therapeutic target for peritoneal fibrosis. MiR-200c is expressed in mesothelial cells. Exposure to 1.36% glucose-based PD fluid Dianeal® resulted in a 21.8 ± 4.5% decrease in miR-200c levels compared to cells in serum-free medium (SFM) (Fig. 1A). TGF-β1 which promotes peritoneal fibrosis diminished miR-200c expression in a dose-responsive manner resulting in a 40.7% reduction at 10 ng/mL compared to SFM. MiR-200c repression resulted in lower E-cadherin and decorin expression while raising levels of mesenchymal markers ZEB2, Notch1, Jagged2, SNAIL, FSP-1, α-smooth muscle actin, fibronectin, and collagen I as shown in Figure 1. TGF-β1 did not affect vimentin expression. Mesenchymal markers and EMT transcription factors appeared within 24 hours of TGF-β1 treatment yet mesothelial cell phenotype changes emerged only after 48 hours (Fig. 1J). The application of decorin before TGF-β1 stimulation reduced TGF-β1's ability to suppress miR-200c expression (Fig. 1B).
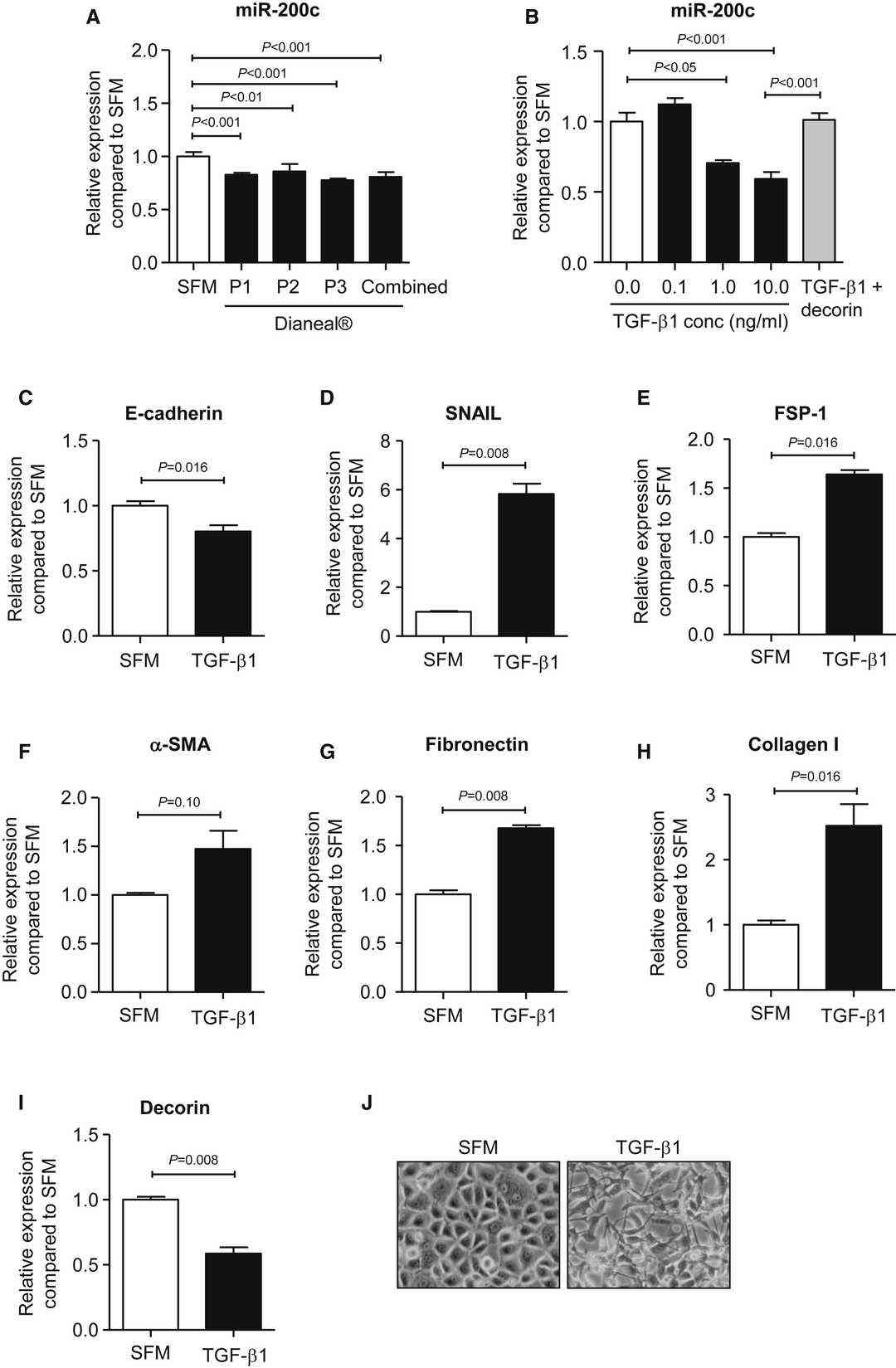 Fig. 1. Effect of Dianeal® or TGF-β1 on Gene Expression of miR-200c and Mediators of EMT and Fibrosis in Mesothelial Cells (Chu J Y S, Chau M K M, et al., 2019).
Fig. 1. Effect of Dianeal® or TGF-β1 on Gene Expression of miR-200c and Mediators of EMT and Fibrosis in Mesothelial Cells (Chu J Y S, Chau M K M, et al., 2019).
Fcf Exposure Decreases Proliferation of Cells of Mesothelial Origin
Malignant mesothelioma (MM) is an aggressive cancer with limited treatment options and poor prognosis. Septin 7, a cytoskeleton protein, is implicated in MM progression. Blum et al. tested the effects of forchlorfenuron (FCF), a plant hormone that inhibits septin function, on MM cell lines and other tumor cell lines derived from various organs.
Human MSTO-211H cells derived from a biphasic MM, growing in vitro and exposed to FCF at concentrations ranging from 6.25 µM to 200 µM; cell proliferation was monitored using the Incucyte live-cell imaging system (Fig. 2). Results showed FCF exposure decreases proliferation of cells of mesothelial origin. For comparison of effects in MM cells vs. non-transformed mesothelial cells we included the two immortalized non-tumorigenic cell lines Met-5A and LP9/TERT-1. IC50 values were higher in immortalized human mesothelial cells (Met-5A) and LP9/TERT-1 cells (76 and 62 µM, respectively) than in MM cell lines, indicative of a lower sensitivity of non-transformed mesothelial cells to the growth-inhibiting/cytotoxic effects of FCF. On average, epithelioid MM-derived cells (H28, ZL55, JL-1, H226) showed a slightly higher sensitivity to FCF than most MM cells derived from biphasic MM (MSTO-211H, SPC111, SPC212) or the sarcomatoid MM-derived ZL34 cells. This is in line with the observation that patients diagnosed with a sarcomatoid MM are in general more resistant to the first-line chemotherapy consisting of cisplatin and pemetrexed treatment.
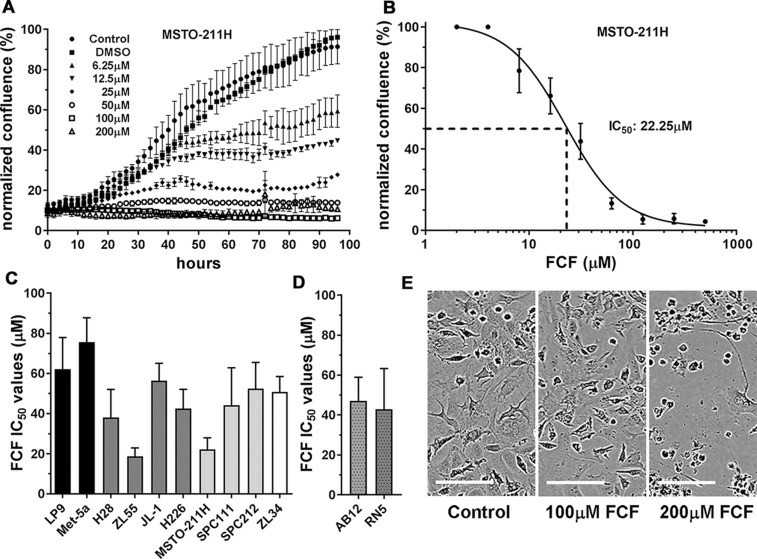 Fig. 2. Proliferation-inhibiting effect of FCF in cells of mesothelial origin (Blum W, Henzi T, et al., 2019).
Fig. 2. Proliferation-inhibiting effect of FCF in cells of mesothelial origin (Blum W, Henzi T, et al., 2019).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells