Immortalized (Conditionally) Mouse Colonic Epithelial Cells (YAMC)
Cat.No.: CSC-I9183L
Species: Mus musculus
Source: Colon
Culture Properties: Adherent
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Note: Never can cells be kept at -20 °C.
CIK-HT003 HT® Lenti-SV40T Immortalization Kit
2) Biochemical assays (i.e. method of Nagatsuet aland method of Dahlquist) were used to measure brush border-associated enzymes alkaline phosphatase, dipeptidyl peptidase IV and sucrase.
Immortalized (Conditionally) Mouse Colonic Epithelial Cells (YAMC)
The YAMC cell line was established from the H-2Kb-tsA58 transgenic mice which expresses the temperature-sensitive SV40 large T antigen gene (tsA58). Under the permissive temperature (33 °C), this gene is expressed and thus allows continuous proliferation of the cells. However, under the non-permissive temperature (39.5 °C), the expression of this gene is suppressed, causing cell division arrest and eventually leading to apoptosis. These cells still possess basic properties of intestinal epithelial cells such as enzyme secretion and cell adhesion. For example, they secrete low levels of brush border peptidases and disaccharidases, and their expression can be modulated by sodium butyrate or dimethyl oleate. Furthermore, these cells express E-cadherin, a key protein that allows the adhesion of epithelial cells to each other.
YAMC cells are an excellent tool to study colon cancer and intestinal inflammation. When the Ras or β-catenin genes are activated, the YAMC cells can be transformed to be invasive and metastatic. Since YAMC cells are sensitive to a number of inflammatory factors and oxidative stress products, they have been used for drug screening and toxicity tests. Also, they are utilized to study the function of a variety of signaling pathways including MAPK, NF-κB, ErbB, and miRNA.
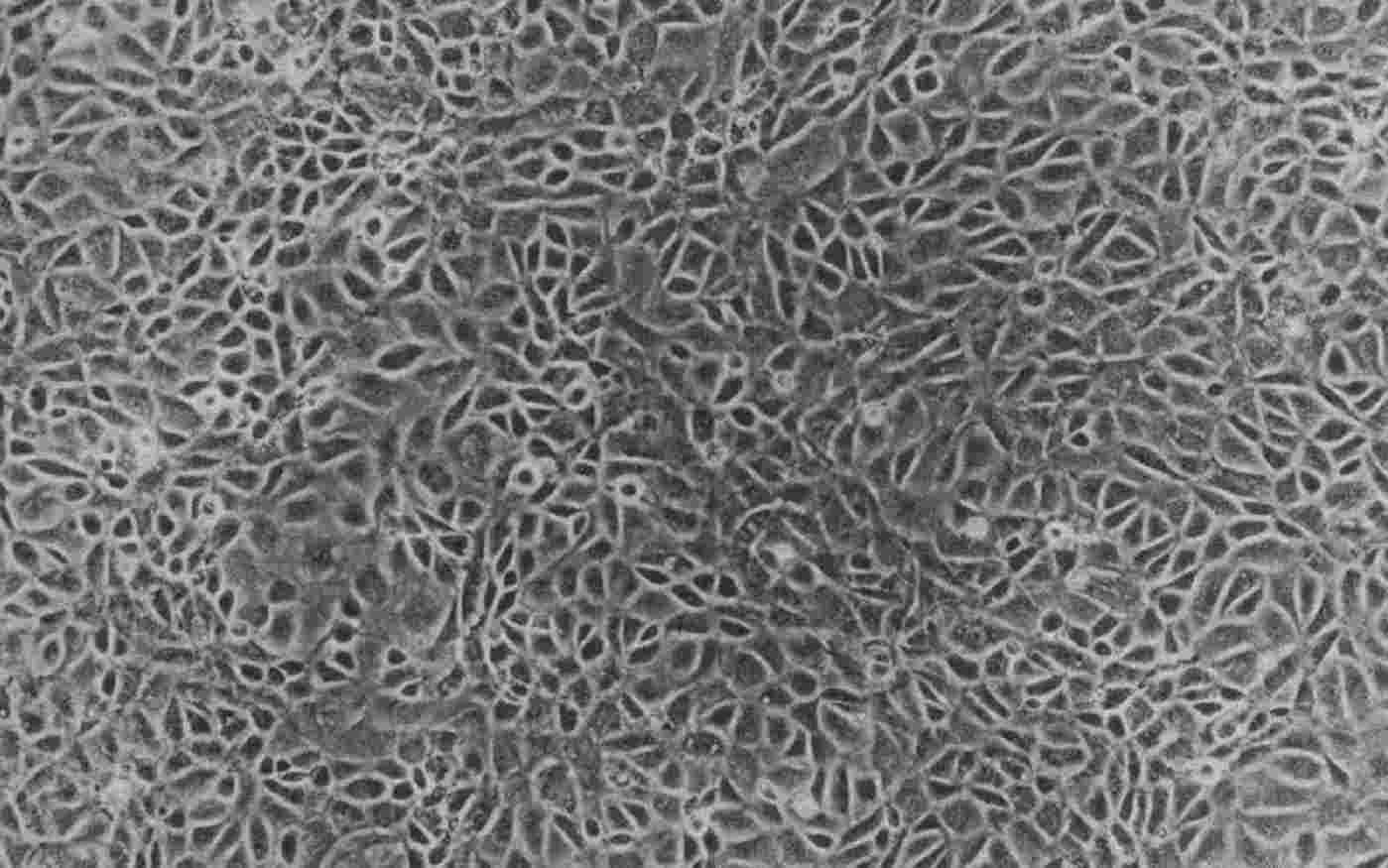 Fig. 1. Monolayer culture of YAMC cells at passage 5 (Whitead RH, Eeden PV, et al., 1993).
Fig. 1. Monolayer culture of YAMC cells at passage 5 (Whitead RH, Eeden PV, et al., 1993).
IGF2BP2 Recognizes and Binds to m6A Site of NCOA3 and Promotes mRNA Stability of NCOA3
Ulcerative colitis (UC), an idiopathic and chronic inflammatory disease, primarily targets the mucosal lining of the colon. This research endeavors to reveal the mechanism of insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2) and nuclear receptor coactivator-3 (NCOA3) in UC-induced intestinal mucosal barrier dysfunction.
To assess the impact of IGF2BP2 on intestinal mucosal barrier integrity under DSS-induced colitis, they generated a murine model of UC by administering DSS to trigger colitis manifestations. Results showed that IGF2BP2 overexpression improved mucosal barrier dysfunction in these mice. In LPS-induced Caco-2 cells, NCOA3 expression was low, suggesting it might be a downstream target of IGF2BP2. RIP assays in YAMC cells showed NCOA3 mRNA was significantly enriched on IGF2BP2 compared to IgG controls, confirming their interaction (Fig. 1A). MeRIP assays indicated that increased IGF2BP2 in YAMC cells heightened the m6A modification of NCOA3 mRNA (Fig. 1D). mRNA stability tests revealed that IGF2BP2 upregulation enhanced NCOA3 mRNA levels and extended its half-life (Fig. 1E). DSS treatment reduced NCOA3 expression in mouse colons, but IGF2BP2 elevation restored it (Fig. 1F and G). Overall, IGF2BP2 binds to the m6A site of NCOA3, enhancing its mRNA stability via m6A modification.
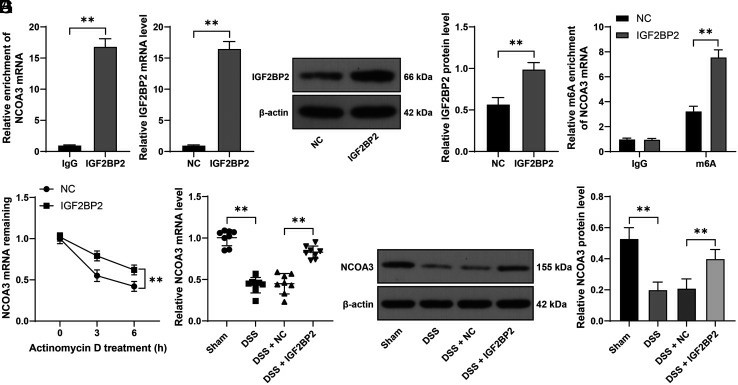 Fig. 1. IGF2BP2 recognizes and binds to m6A site of NCOA3 and promotes mRNA stability of NCOA3 (Li R, Gu B, et al., 2025).
Fig. 1. IGF2BP2 recognizes and binds to m6A site of NCOA3 and promotes mRNA stability of NCOA3 (Li R, Gu B, et al., 2025).
Pantothenate Protects the Intestinal Epithelial Barrier and Prevents Colitis in Adult Mice
HMOs (human milk oligosaccharides), particularly 2'-fucosyllactose (2'-FL), promote the growth of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus, which have been associated with several health benefits associated with breast milk. Schalich et al. determined how 2'-FL protects from intestinal inflammation in adulthood by altering the gut microbiota.
Through exploratory metabolomics, they identified pantothenate as a protective metabolite that fortifies the intestinal barrier against oxidative stress. They next studied how pantothenate could exert direct effects on intestinal epithelial cells to protect the intestinal barrier by using in vitro assays. They evaluated the effect of pantothenate on the oxidative stress-induced disruption of the epithelial barrier. H2O2 reduced the paracellular permeability in Caco2 cells measured by transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) in a time-dependent manner, which was significantly reduced by pantothenate treatment (Fig. 2A). Furthermore, H2O2-induced redistribution of ZO-1 from apical tight junctional complexes to the cytoplasmic compartment of YAMC cells was prevented by pantothenate (Fig. 2B). In order to determine how pantothenate reduces oxidative stress in YAMC cells they measured the activity of glutathione peroxidase (GPX), the enzyme with antioxidant properties that eliminates free radicals to reduce oxidative stress. Pantothenate at 0.1 mM increased GPX activity in YAMC cells compared to control cells (P = 0.0171, Fig. 2C).
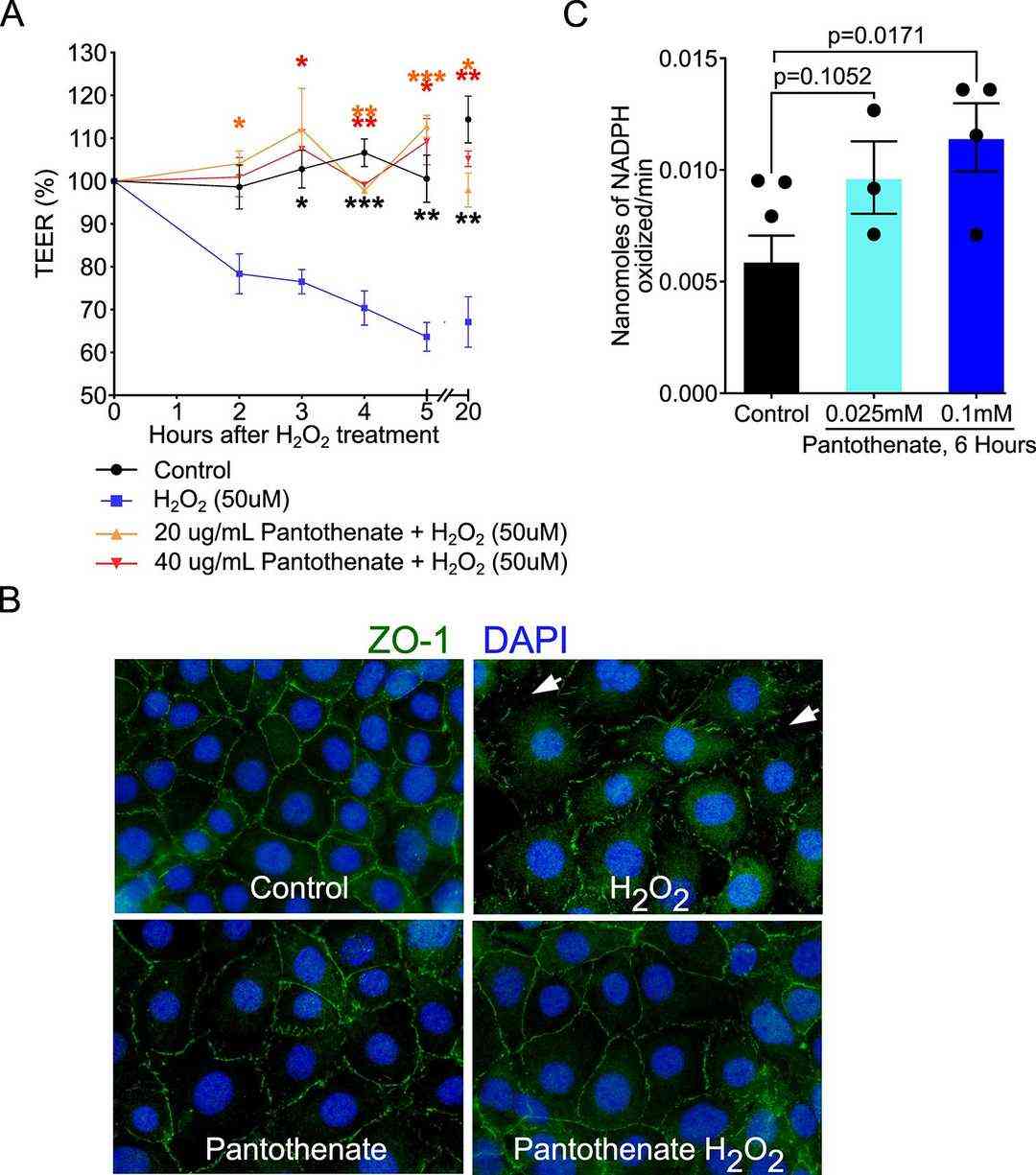 Fig. 2. Pantothenate preserves the intestinal epithelial barrier and inhibits oxidative stress in intestinal epithelial cells (Schalich KM, Buendia MA, et al., 2024).
Fig. 2. Pantothenate preserves the intestinal epithelial barrier and inhibits oxidative stress in intestinal epithelial cells (Schalich KM, Buendia MA, et al., 2024).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells