KYSE-140
Cat.No.: CSC-C0404
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Esophagus
Morphology: adherent cells growing as monolayer with the tendency to pile up
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: cytokeratin +, cytokeratin-7 -, cytokeratin-8 +, cytokeratin-17 +, cytokeratin-18 +, cy
The KYSE-140 cell line originates from the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tissue of a 54-year-old male patient. The tumor developed in the mid-thoracic esophagus and reached a1 infiltration depth which indicates muscle layer invasion without full penetration. Researchers isolated the cell line from the patient's tumor because it displayed standard epithelial features. Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma represents a widespread cancer type which develops due to both genetic and environmental influences including HPV infection and habits like smoking and drinking.
Researchers utilize KYSE-140 cells to test the effectiveness of different anticancer treatments including both chemotherapeutic agents (such as 5-FU and Paclitaxel) and targeted therapeutic approaches (such as GOLPH3 inhibitors). Photodynamic therapy demonstrates exceptional effectiveness in KYSE-140 cells which suggests its potential for cancer treatment applications. KYSE-140 cells help researchers understand gene functions in esophageal squamous carcinoma because miR-155-5p levels are higher in them than in other esophageal cancer cell lines. The microRNA interacts with MAP3K10 and its reduced expression causes a halt in both cell proliferation and migration. KYSE-140 cells show high clonogenicity which points to a cancer stem cell subpopulation and therefore become vital for cancer stem cell research and therapeutic strategy development.
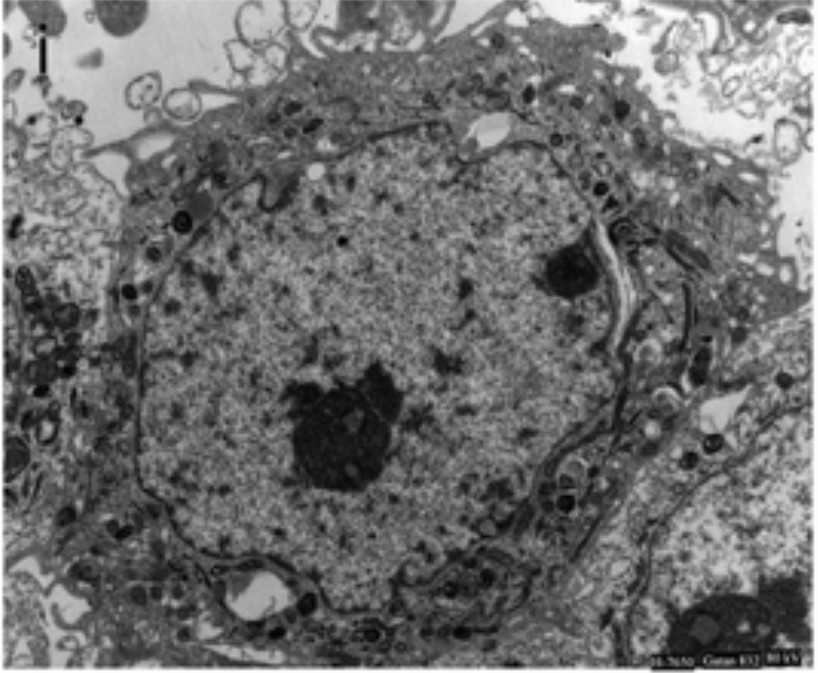 Fig. 1. Transmission electron microscopy of the KYSE140 cells (Xu Y, Lin Z, et al., 2014).
Fig. 1. Transmission electron microscopy of the KYSE140 cells (Xu Y, Lin Z, et al., 2014).
Isoliquiritigenin (ILQ) Inhibited EGFR Activation in ESCC Cells
ESCC is a deadly cancer, rampant in China, linked to high alcohol and tobacco use. EGFR overexpression is noticed in ESCC, associated with tumor aggression. The chalconoid isoliquiritigenin (ILQ) from licorice, known for antioxidative and anticancer effects, is evaluated against ESCC. Ye's team assessed ILQ's antitumor activity through in vitro and in vivo experiments, focusing on its impact on EGFR and downstream signaling pathways (Akt and ERK1/2). The effect of ILQ on EGFR activation was analyzed, showing dose-dependent reduction in EGFR phosphorylation, indicating suppression of EGFR activity (Fig. 1a). This led to decreased phosphorylation of downstream molecules ERK and AKT. After starvation, the phosphorylation of EGFR in ESCC cells (KYSE140, KYSE520, and TE1) was very low, and EGF substantially stimulated the activation of EGFR, but EGF-induced phosphorylation of EGFR was substantially suppressed by ILQ in a dose- and time-dependent manner (Fig. 1b and c). EGFR knockdown using shRNA showed decreased colony formation after ILQ treatment, but cells with reduced EGFR were less sensitive to ILQ, highlighting EGFR pathway inhibition's role in ILQ's antitumor effects (Fig. 1e and f).
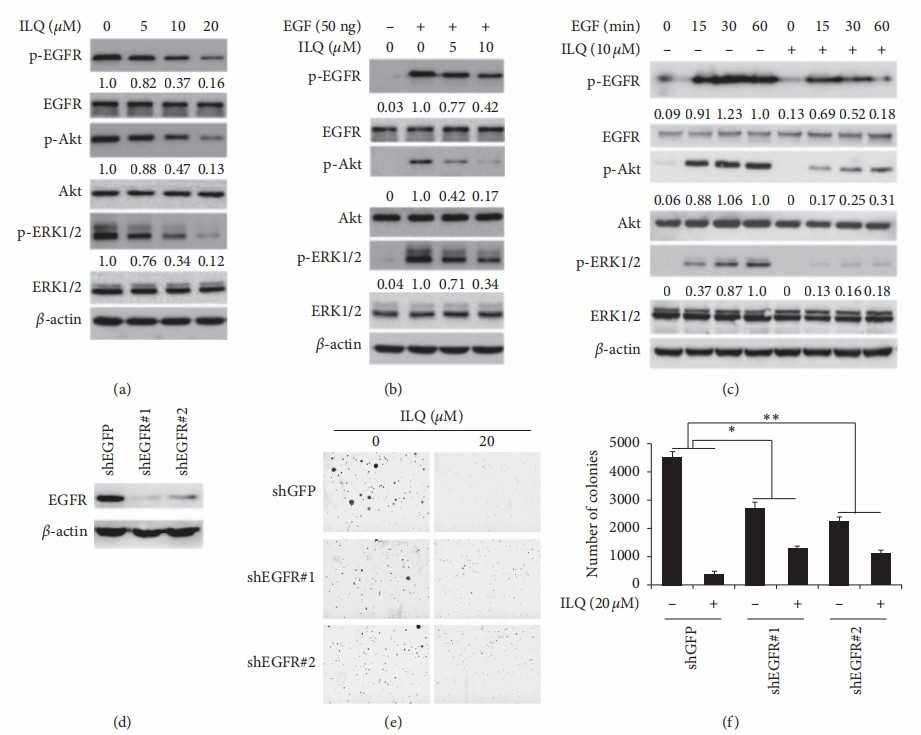 Fig. 1. Isoliquiritigenin (ILQ) suppressed EGFR activation in ESCC cells (Ye L, Zhang J, et al., 2020).
Fig. 1. Isoliquiritigenin (ILQ) suppressed EGFR activation in ESCC cells (Ye L, Zhang J, et al., 2020).
KIF23 knockdown inhibited the proliferation of ESCA cells
Esophageal carcinoma (ESCA) is a highly aggressive cancer with low survival rates, largely due to uncontrolled cell proliferation and metastasis, which are often linked to epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Xu et al. identified differentially expressed DEGs in ESCA from GEO datasets, focusing on KIF23. Expression analysis and functional assays, including cell proliferation tests, are conducted. The expression levels of KIF23 in four ESCA cell lines were measured using qRT-PCR to confirm its upregulation in ESCA. The analysis revealed that Eca-109, KYSE-140, EC9706 and TE-1 cell lines exhibited increased KIF23 mRNA and protein levels when compared to normal cells, with Eca-109 and KYSE-140 showing particularly high levels of expression (Fig. 2A–C). The research team selected these two specific cell lines for additional investigation. Scientists achieved KIF23 knockdown by using si-KIF23 which led to a substantial decrease in protein levels in ESCA cells (Fig. 2D and E). The reduction of ESCA cell proliferation occurred following KIF23 silencing according to results from CCK-8 and EdU assays (Fig. 2F–I). KIF23 inhibition leads to a reduction in ESCA cell growth as shown in Fig. 2F–I.
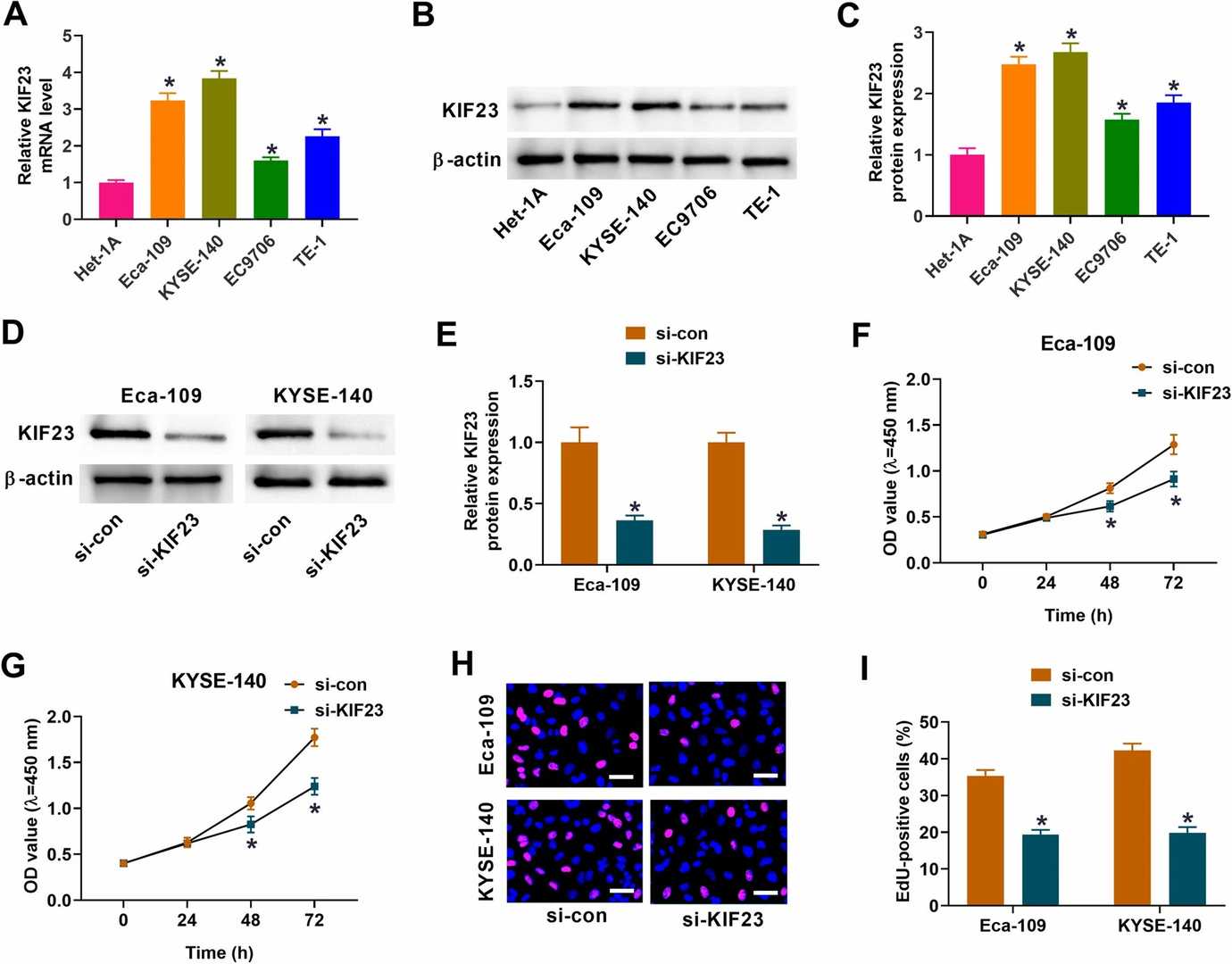 Fig. 2. Impact of KIF23 knockdown on the proliferation of ESC cells (Xu Q, Li X, et al., 2023).
Fig. 2. Impact of KIF23 knockdown on the proliferation of ESC cells (Xu Q, Li X, et al., 2023).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells





